|
Addis Alem, Shewa
Addis Alem (, ''New World''; also known as Ejerie) is a town in central Ethiopia. Located in the West Shewa Zone of the Oromia Region, west of Addis Ababa, this town has a latitude and longitude of with an elevation of about 2360 meters above sea level. Based on figures from the Central Statistical Agency in 2005, this town has an estimated total population of 13,423 of whom 6,420 were males and 7,003 were females. The 1994 census reported this town had a total population of 7,516 of whom 3,482 were males and 4,034 were females. It is the largest settlement in Ejerie Aanaa. Ejerie is known for the Basilica Church of St Maryam. Its adjacent museum burned to the ground in 1997; however a new one has since opened. History Ejerie was founded in 1900 by Menelik II as a new capital city; Empress Taytu Betul picked the name. Although at one point he had 20,000 members of the Welega Oromo busy in constructing buildings in the new city, by 1903 he decided to keep the capital a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Kenya to the south, South Sudan to the west, and Sudan to the northwest. Ethiopia covers a land area of . , it has around 128 million inhabitants, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, thirteenth-most populous country in the world, the List of African countries by population, second-most populous in Africa after Nigeria, and the most populous landlocked country on Earth. The national capital and largest city, Addis Ababa, lies several kilometres west of the East African Rift that splits the country into the African Plate, African and Somali Plate, Somali tectonic plates. Early modern human, Anatomically modern humans emerged from modern-day Ethiopia and set out for the Near East and elsewhere in the Middle Paleolithi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aanaa
Districts of Ethiopia, also called woredas (; ''woreda''), are the third level of the administrative divisions of Ethiopia – after '' zones'' and the '' regional states''. These districts are further subdivided into a number of wards called ''kebele'' neighbourhood associations, which are the smallest unit of local government in Ethiopia. Overview Districts are typically collected together into zones, which form a region; districts which are not part of a zone are designated Special Districts and function as autonomous entities. Districts are governed by a council whose members are directly elected to represent each ''kebele'' in the district. There are about 670 rural districts and about 100 urban districts. Terminology varies, with some people considering the urban units to be ''woreda'', while others consider only the rural units to be ''woreda'', referring to the others as urban or city administrations. Although some districts can be traced back to earliest times� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worku Mammo Dessalegn
Worku (Amharic: ወርቁ) is a male name of Ethiopian origin that may refer to: *Asnaketch Worku Asnaketch Worku () (born 1935 – 14 September 2011) was an Ethiopian singer who sang in the Amharic language and a ''krar'' instrumentalist, the instrument which symbolized her fame during the 1960s and 1970's. Asnaketch also had a long disti ... (1935–2011), Ethiopian female singer * Ayelech Worku (born 1979), Ethiopian long-distance runner * Bazu Worku (born 1990), Ethiopian marathon runner * Eyassu Worku (born 1998), American basketball player * Mengistu Worku (1940–2010), Ethiopian footballer and coach * Worku Tesfamichael, Eritrea Minister for Tourism * Worku Bikila (born 1968), Ethiopian runner {{given name, type=both Amharic-language names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abebe Wolde Giorgis
Abebe (Amharic: አበበ) is a male given name and patronymic of Ethiopian origin as well as a surname of Nigerian origin. Notable people with the name include: Given name *Abebe Aregai (1903–1960), Ethiopian Prime Minister from 1957 to 1960 *Abebe Bikila (1932–1973), Ethiopian marathon runner and two-time Olympic champion * Abebe Dinkesa (born 1984), Ethiopian long-distance runner * Abebe Fekadu (born 1970), Ethiopian-Australian Paralympic weightlifter * Abebe Gessese (born 1953), Ethiopian Olympic long jumper * Abebe Mekonnen (boxer) (born 1940), Ethiopian Olympic boxer * Abebe Mekonnen (born 1964), Ethiopian former long-distance runner and 1989 Boston Marathon winner *Abebe Wakgira (born 1921), Ethiopian Olympic long-distance runner * Abebe Zerihun (born 1955), Ethiopian Olympic middle-distance runner *Abiye Abebe (1917–1974), Ethiopian politician and son-in-law of Haile Selassie * Addis Abebe (born 1970), Ethiopian former long-distance runner and 10,000 m Olympic meda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arbegnoch
The Arbegnoch () were Ethiopian anti-fascist World War II resistance fighters in Italian East Africa from 1936 until 1941 who fought against Fascist Italy's occupation of the Ethiopian Empire. The Patriot movement was primarily based in the rural Shewa, Gondar and Gojjam provinces, though it drew support from all over occupied Ethiopia. Several hundred Eritreans also participated. Small cells operated in Addis Ababa and other towns, known as ''Wust Arbagna'' (Insider Patriots). The Black Lions took part in the movement. In 1937/1938, there were an estimated 25,000 active Patriots in Ethiopia. The average band of resistance fighters was estimated in 1938 to have included 400 to 500 members, depending on the agricultural season. The Arbegnoch or Patriots were called Shifta by the Italians. The Patriots had the near-total support of the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church. The majority of participants were Christian highlanders. Ethiopian Muslims were less involved in the Ita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
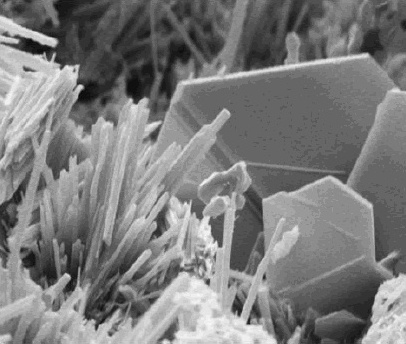
Slaked Lime
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime ( calcium oxide) is mixed with water. Annually, approximately 125 million tons of calcium hydroxide are produced worldwide. Calcium hydroxide has many names including hydrated lime, caustic lime, builders' lime, slaked lime, cal, and pickling lime. Calcium hydroxide is used in many applications, including food preparation, where it has been identified as E number E526. Limewater, also called milk of lime, is the common name for a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide. Solubility Calcium hydroxide is moderately soluble in water, as seen for many dihydroxides. Its solubility increases from 0.66 g/L at 100 °C to 1.89 g/L at 0 °C. Its solubility product ''K''sp of 5.02 at 25 °C, its dissociation in water is large enough that its solutions are basic according to the following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian East Africa
Italian East Africa (, A.O.I.) was a short-lived colonial possession of Fascist Italy from 1936 to 1941 in the Horn of Africa. It was established following the Second Italo-Ethiopian War, which led to the military occupation of the Ethiopian Empire (Abyssinia). It encompassed Italian Somaliland, Italian Eritrea and the acquired Ethiopian territories, all governed by a single administrative unit, the Governo Generale dell'Africa Orientale Italiana. Its establishment contributed to the outbreak of the Second World War by exposing the weaknesses of the League of Nations. Italian East Africa was divided into six governorates. Eritrea and Somalia, Italian possessions since the 1880s, were enlarged with captured Ethiopian territory and became the Eritrea and Somalia Governorates. The remainder of the occupied Ethiopian territories comprised the Harar, Galla-Sidamo, Amhara, and Scioa Governorates. At its largest extent, Italian East Africa occupied territories in British Som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welega Oromo
The Welega (also spelled Wallagga, Wallaga or Wal-arga) is a branch of the Oromo people who live in Oromia Region of Ethiopia, in the former Welega Province; a few live across the border in Sudan. They speak the Oromo language. The Wellega population is approximately 8 million, many of them being Christians. Wallaga is one of the fertile lands of Western Oromia and it is known for its coffee, honey, dairy products, gold, platinum and other natural resources among others. See also *Mecha and Tulama Self-Help Association The Mecha and Tulema Self-Help Association () was an Oromo people, Oromo political and freedom social movement in Ethiopia. The movement was primarily based in Bale, but was active in other regions as well (including Addis Ababa). The organization ... References Oromo groups Ethnic groups in Sudan {{Ethiopia-ethno-group-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taytu Betul
Taytu Betul ( ''Ṭaytu Bəṭul'' ; baptised as Wälättä Mikael; 1851 – 11 February 1918) was Empress of Ethiopia from 1889 to 1913 and the third wife of Emperor Menelik II. An influential figure in the anti-colonial resistance during the late 19th-century Scramble for Africa, she, along with her husband, founded the modern Ethiopian capital Addis Ababa in 1886. Early life According to Raymond Jonas, Taytu Betul (or Taitu) was born in Semien, North Gondar, Ethiopian Empire. Scholarly consensus is that she was born at about 1851. Taytu's father, Ras Betul Haile Maryam, was part of the ruling family of Semien that claimed to be descendants of the Solomonic Dynasty through Emperor Susenyos I. Taytu's uncle was the Amhara warlord Wube Haile Maryam who governed the Semien and Tigray princedom. Education There are no records indicating that Empress Taytu attended school; however, she was taught to read and write in Amharic and Ge'ez. This is a rarity, considering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital City
A capital city, or just capital, is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state (polity), state, province, department (administrative division), department, or other administrative division, subnational division, usually as its Seat of government, seat of the government. A capital is typically a city that physically encompasses the government's offices and meeting places; the status as capital is often designated by its law or constitution. In some jurisdictions, including several countries, different branches of government are in different settlements, sometimes meaning multiple official capitals. In some cases, a distinction is made between the official (constitutional) capital and the seat of government, which is in list of countries with multiple capitals, another place. English language, English-language media often use the name of the capital metonymy, metonymically to refer to the government sitting there. Thus, "London-Washington relations" is widely unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menelik II
Menelik II ( ; horse name Aba Dagnew (Amharic: አባ ዳኘው ''abba daññäw''); 17 August 1844 – 12 December 1913), baptised as Sahle Maryam (ሣህለ ማርያም ''sahlä maryam'') was king of Shewa from 1866 to 1889 and Emperor of Ethiopia from 1889 to his death in 1913. At the height of his internal power and external prestige, the process of Menelik II's conquests, territorial expansion and creation of the modern empire-state was largely completed by 1898.Zewde, Bahru. A history of Ethiopia: 1855–1991. 2nd ed. Eastern African studies. 2001 The Ethiopian Empire was transformed under Menelik: the major signposts of modernisation were put in place, with the assistance of key ministerial advisors. Externally, Menelik led Ethiopian troops against Kingdom of Italy, Italian invaders in the First Italo-Ethiopian War; following a decisive victory at the Battle of Adwa, recognition of Ethiopia's independence by external powers was expressed in terms of diplomatic representa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museum
A museum is an institution dedicated to displaying or Preservation (library and archive), preserving culturally or scientifically significant objects. Many museums have exhibitions of these objects on public display, and some have private collections that are used by researchers and specialists. Museums host a much wider range of objects than a library, and they usually focus on a specific theme, such as the art museums, arts, science museums, science, natural history museums, natural history or Local museum, local history. Public museums that host exhibitions and interactive demonstrations are often tourist attractions, and many draw large numbers of visitors from outside of their host country, with the List of most-visited museums, most visited museums in the world attracting millions of visitors annually. Since the establishment of Ennigaldi-Nanna's museum, the earliest known museum in ancient history, ancient times, museums have been associated with academia and the preserva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |