|
Active Suspension
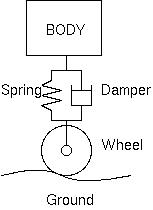
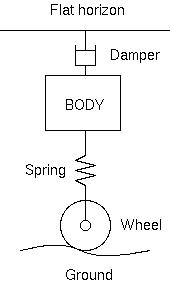
An active suspension is a type of Suspension (vehicle), automotive suspension that uses an onboard control system to control the vertical movement of the vehicle's wheels and axles relative to the chassis or vehicle frame, rather than the conventional passive suspension that relies solely on large spring (device), springs to maintain static support and dampen the vertical wheel movements caused by the road surface. Active suspensions are divided into two classes: true active suspensions, and adaptive or semi-active suspensions. While adaptive suspensions only vary shock absorber firmness to match changing road or dynamic conditions, active suspensions use some type of actuator to raise and lower the chassis independently at each wheel. These technologies allow car manufacturers to achieve a greater degree of ride quality and car handling by keeping the chassis parallel to the road when turning corners, preventing unwanted contacts between the vehicle frame and the ground (especiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suspension (vehicle)
Suspension is the system of tires, tire air, spring (device), springs, shock absorbers and Linkage (mechanical), linkages that connects a vehicle to its wheels and allows relative motion between the two. Suspension systems must support both road holding/Automobile handling, handling and ride quality, which are at odds with each other. The tuning of suspensions involves finding the right compromise. The suspension is crucial for maintaining consistent contact between the road wheel and the road surface, as all forces exerted on the vehicle by the road or ground are transmitted through the tires' contact patches. The suspension also protects the vehicle itself and any cargo or luggage from damage and wear. The design of front and rear suspension of a car may be different. History An early form of suspension on ox-drawn carts had the platform swing on iron chains attached to the wheeled frame of the carriage. This system remained the basis for most suspension systems unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braking
A brake is a mechanical device that inhibits motion by absorbing energy from a moving system. It is used for slowing or stopping a moving vehicle, wheel, axle, or to prevent its motion, most often accomplished by means of friction. Background Most brakes commonly use friction between two surfaces pressed together to convert the kinetic energy of the moving object into heat, though other methods of energy conversion may be employed. For example, regenerative braking converts much of the energy to electrical energy, which may be stored for later use. Other methods convert kinetic energy into potential energy in such stored forms as pressurized air or pressurized oil. Eddy current brakes use magnetic fields to convert kinetic energy into electric current in the brake disc, fin, or rail, which is converted into heat. Still other braking methods even transform kinetic energy into different forms, for example by transferring the energy to a rotating flywheel. Brakes are generally ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-levelling Suspension
Self-levelling refers to an automobile suspension system that maintains a constant ride height of the vehicle above the road, regardless of load. Purpose Many vehicle systems on a conventional vehicle are negatively affected by the change in attitude coming from changes in load - specifically a heavy load in the rear seat or luggage compartment. This change in attitude affects aerodynamic properties, headlight aim, braking, bumpers, shock absorption from the suspension and the vehicle's performance in a collision. Most of the braking power is on the front wheels of a vehicle, which means you will have more effective braking when more weight is over the front wheels. When the rear end has a heavy load, the braking is not as effective. The weight is concentrated on the rear end of the vehicle, and the rear brakes need to do all of the work. When braking quickly in this situation, the front brakes will be easier to lock up because of the lack of weight transfer to the front of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring (device)
A spring is a device consisting of an Elasticity (physics), elastic but largely rigid material (typically metal) bent or molded into a form (especially a coil) that can return into shape after being compressed or extended. Springs can Energy storage, store energy when compressed. In everyday use, the term most often refers to coil springs, but there are many different spring designs. Modern springs are typically manufactured from spring steel. An example of a non-metallic spring is the Bow (weapon), bow, made traditionally of flexible Taxus baccata, yew wood, which when Bow draw, drawn stores energy to propel an arrow. When a conventional spring, without stiffness variability features, is compressed or stretched from its resting position, it exerts an opposing force approximately proportional to its change in length (this approximation breaks down for larger deflections). The ''rate'' or ''spring constant'' of a spring is the change in the force it exerts, divided by the cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
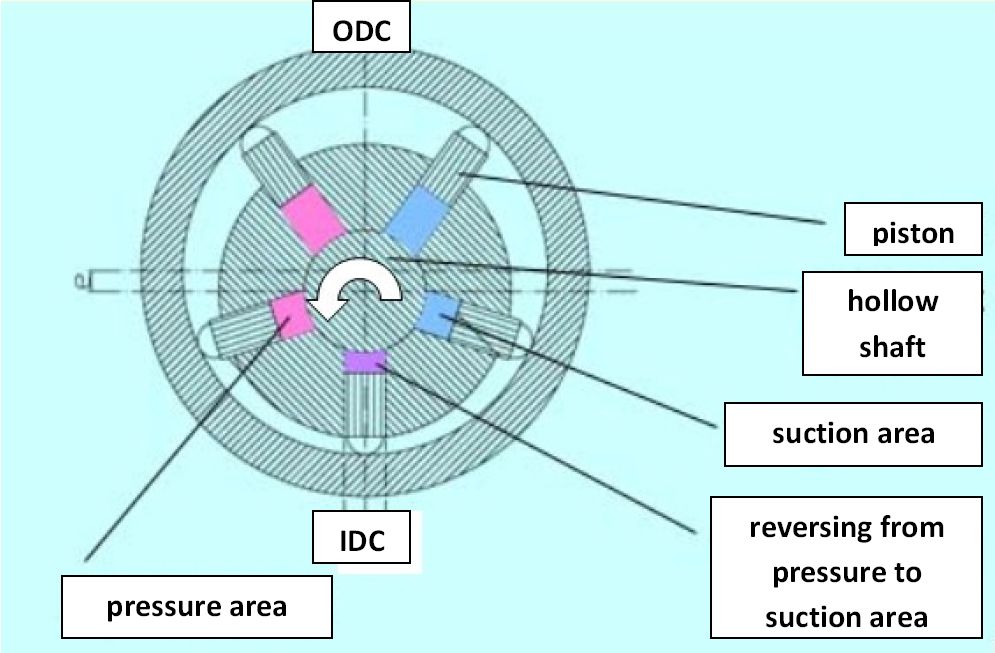
Radial Piston Pump
A radial piston pump is a form of hydraulic pump. The working pistons extend in a radial direction symmetrically around the drive shaft, in contrast to the axial piston pump. Construction The stroke of each piston is caused by an eccentric drive shaft or an external eccentric tappet (e.g., stroke ring). When filling the workspace of the pumping pistons from "inside" (e.g., over a hollow shaft) it is called an ''inside impinged'' (but outside braced) radial piston pump ''(picture 1)''. If the workspace is filled from "outside" it's called an ''outside impinged'' radial piston pump (but inside braced) ''(picture 2)''. Function The general mode of operation will be explained at the movement of one pumping piston by means of picture 1: The outer ring for bracing of the pumping pistons is in eccentric position to the hollow shaft in the center. This eccentricity determines the stroke of the pumping piston. The piston starts in the inner dead center (IDC) with suction process. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citroën
Citroën ()The double-dot diacritic over the 'e' is a diaeresis () indicating the two vowels are sounded separately, and not as a diphthong. is a French automobile brand. The "Automobiles Citroën" manufacturing company was founded on 4 June 1919 by André Citroën. Citroën has been owned by Stellantis since 2021 and previously was part of the PSA Group after Peugeot acquired 89.95% share in 1976. Citroën's head office is located in the Stellantis Poissy Plant in Saint-Ouen-sur-Seine since 2021 (previously in Rueil-Malmaison) and its offices studies and research in Vélizy-Villacoublay, Poissy (CEMR), Carrières-sous-Poissy and Sochaux-Montbéliard. In 1934, the firm established its reputation for innovative technology with the Citroën Traction Avant, Traction Avant. This was the world's first car to be mass-produced with front-wheel drive and four-wheel independent suspension, as well as unibody construction, omitting a separate chassis, and instead using the body of the car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Magès
Paul Ernest Mary Magès (1908–1999) is known for his invention of the first self-leveling automobile suspension, known as hydro-pneumatic suspension. This system replaced conventional steel springs with an adaptive system of hydraulic struts, resulting in a motoring experience that felt like no other automobile of the era. This suspension achieved its initial design brief: fast travel on poor road surfaces. This advantage is still noted today, especially in applications where ride quality is important, like ambulance design. His formal schooling was modest. He earned his National diploma (''Brevet d'Etudes du Premier Cycle''), a preparatory course for the Académie des Arts et Métiers in Marseille. At age 17, he sent his résumé to Citroën, one of the major automobile manufacturers in France, where he was hired to maintain equipment. In 1936 he became a technical draftsman, and in January 1942, CEO Pierre-Jules Boulanger assigned him to the development department to solve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydropneumatic Suspension
Hydropneumatic suspension is a type of motor vehicle suspension system, invented by Paul Magès, produced by Citroën, and fitted to Citroën cars, as well as being used under licence by other car manufacturers. Similar systems are also widely used on modern tanks and other large military vehicles. The suspension was referred to as ' in early literature, pointing to oil and air as its main components. The purpose of this system is to provide a sensitive, dynamic and high-capacity suspension that offers superior ride quality on a variety of surfaces. A hydropneumatic system combines the advantages of hydraulic systems and pneumatic systems so that gas absorbs excessive force and liquid in hydraulics directly transfers force. The suspension system usually features both self-leveling and driver-variable ride height, to provide extra clearance in rough terrain. This type of suspension for automobiles was inspired by the pneumatic suspension used for aircraft landing gear, which wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
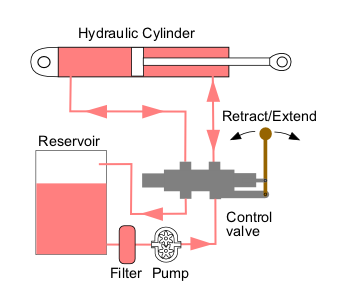
Hydraulic Machinery
Hydraulic machines use liquid fluid power to perform work. Heavy construction vehicles are a common example. In this type of machine, hydraulic fluid is pumped to various hydraulic motors and hydraulic cylinders throughout the machine and becomes pressurized according to the resistance present. The fluid is controlled directly or automatically by control valves and distributed through hoses, tubes, or pipes. Hydraulic systems, like pneumatic systems, are based on Pascal's law which states that any pressure applied to a fluid inside a closed system will transmit that pressure equally everywhere and in all directions. A hydraulic system uses an incompressible liquid as its fluid, rather than a compressible gas. The popularity of hydraulic machinery is due to the large amount of power that can be transferred through small tubes and flexible hoses, the high power density and a wide array of actuators that can make use of this power, and the huge multiplication of forces t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damping
In physical systems, damping is the loss of energy of an oscillating system by dissipation. Damping is an influence within or upon an oscillatory system that has the effect of reducing or preventing its oscillation. Examples of damping include viscous damping in a fluid (see viscous drag), surface friction, radiation, resistance in electronic oscillators, and absorption and scattering of light in optical oscillators. Damping not based on energy loss can be important in other oscillating systems such as those that occur in biological systems and bikes (ex. Suspension (mechanics)). Damping is not to be confused with friction, which is a type of dissipative force acting on a system. Friction can cause or be a factor of damping. Many systems exhibit oscillatory behavior when they are disturbed from their position of static equilibrium. A mass suspended from a spring, for example, might, if pulled and released, bounce up and down. On each bounce, the system tends to return to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acceleration Sensor
An accelerometer is a device that measures the proper acceleration of an object. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of the object relative to an observer who is in free fall (that is, relative to an inertial frame of reference). Proper acceleration is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration with respect to a given coordinate system, which may or may not be accelerating. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth's gravity straight upwards of about ''g'' ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, an accelerometer that is in free fall will measure zero acceleration. Accelerometers have many uses in industry, consumer products, and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabilize flight. Micromachined micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) acceler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Suspension
An active suspension is a type of Suspension (vehicle), automotive suspension that uses an onboard control system to control the vertical movement of the vehicle's wheels and axles relative to the chassis or vehicle frame, rather than the conventional passive suspension that relies solely on large spring (device), springs to maintain static support and dampen the vertical wheel movements caused by the road surface. Active suspensions are divided into two classes: true active suspensions, and adaptive or semi-active suspensions. While adaptive suspensions only vary shock absorber firmness to match changing road or dynamic conditions, active suspensions use some type of actuator to raise and lower the chassis independently at each wheel. These technologies allow car manufacturers to achieve a greater degree of ride quality and car handling by keeping the chassis parallel to the road when turning corners, preventing unwanted contacts between the vehicle frame and the ground (especiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |