|
Acoustic Tweezers
Acoustic tweezers (also known as acoustical tweezers) are a set of tools that use sound waves to manipulate the position and movement of very small objects. Strictly speaking, only a single-beam based configuration can be called acoustical tweezers. However, the broad concept of acoustical tweezers involves two configurations of beams: single beam and standing waves. The technology works by controlling the position of acoustic pressure nodesGorkov, L. P.; Soviet Physics- Doklady, 1962, 6(9), 773-775. that draw objects to specific locations of a standing acoustic field. The target object must be considerably smaller than the wavelength of sound used, and the technology is typically used to manipulate microscopic particles. Acoustic waves have been proven safe for biological objects, making them ideal for biomedical applications. Recently, applications for acoustic tweezers have been found in manipulating sub-millimetre objects, such as flow cytometry, cell separation, cell trapping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Waves
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid. In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the brain. Only acoustic waves that have frequencies lying between about 20 Hz and 20 kHz, the audio frequency range, elicit an auditory percept in humans. In air at atmospheric pressure, these represent sound waves with wavelengths of to . Sound waves above 20 kHz are known as ultrasound and are not audible to humans. Sound waves below 20 Hz are known as infrasound. Different animal species have varying hearing ranges, allowing some to even hear ultrasounds. Definition Sound is defined as "(a) Oscillation in pressure, stress, particle displacement, particle velocity, etc., propagated in a medium with internal forces (e.g., elastic or viscous), or the superposition of such propagated oscillation. (b) Auditory sensation evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stokes Problem
In fluid dynamics, Stokes problem also known as Stokes second problem or sometimes referred to as Stokes boundary layer or Oscillating boundary layer is a problem of determining the flow created by an oscillating solid surface, named after Sir George Stokes. This is considered one of the simplest unsteady problems that has an exact solution for the Navier–Stokes equations. In turbulent flow, this is still named a Stokes boundary layer, but now one has to rely on experiments, numerical simulations or approximate methods in order to obtain useful information on the flow. Flow description Consider an infinitely long plate which is oscillating with a velocity U \cos \omega t in the x direction, which is located at y=0 in an infinite domain of fluid, where \omega is the frequency of the oscillations. The incompressible Navier–Stokes equations reduce to :\frac = \nu \frac where \nu is the kinematic viscosity. The pressure gradient does not enter into the problem. The initial, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holographic Direct Sound Printing
Holographic direct sound printing (HDSP) is a method of 3D printing which use acoustic holograms, developed by researchers at Concordia University. Researchers claim that the printing process can be carried out 20 times faster and that it presents the advantages that an object can be created at once and several objects can be created at the same time. According to researchers, it can be used to print inside opaque surfaces, for example inside the human body, thus opening new opportunities in medicine. It is based on Direct Sound Printing method, introduced in 2022. A similar method, to print 3D objects using ultrasound holograms, based on acoustic trapping, was proposed by researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research and Heidelberg University, in February 2023. See also * Acoustic tweezers Acoustic tweezers (also known as acoustical tweezers) are a set of tools that use sound waves to manipulate the position and movement of very small objects. Strictly speaking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustic Levitation
Acoustic levitation is a method for suspending matter in air against gravity using acoustic radiation pressure from high intensity sound waves. It works on the same principles as acoustic tweezers by harnessing acoustic radiation forces. However acoustic tweezers are generally small scale devices which operate in a fluid medium and are less affected by gravity, whereas acoustic levitation is primarily concerned with overcoming gravity. Technically dynamic acoustic levitation is a form of acoustophoresis, though this term is more commonly associated with small scale acoustic tweezers. Typically sound waves at Ultrasound, ultrasonic frequencies are used thus creating no sound audible to humans. This is primarily due to the high intensity of sound required to counteract gravity. However, there have been cases of audible frequencies being used. There are various techniques for generating the sound, but the most common is the use of Piezoelectric speaker, piezoelectric transducers which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bessel Beam
Bessel may refer to: Mathematics and science * Bessel beam * Bessel ellipsoid * Bessel function in mathematics * Bessel's inequality in mathematics * Bessel's correction In statistics, Bessel's correction is the use of ''n'' − 1 instead of ''n'' in the formula for the sample variance and sample standard deviation, where ''n'' is the number of observations in a sample. This method corrects the bias in ... in statistics * Bessel filter, a linear filter often used in audio crossover systems * Bessel transform, also known as Fourier-Bessel transform or Hankel transform * Bessel window, in signal processing * Besselian date, see Epoch (astronomy)#Besselian years Places * Bessel Fjord, NE Greenland * Bessel Fjord, NW Greenland * Bessel (crater), a small lunar crater People Surname * Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel (1784–1846), German mathematician, astronomer, and systematizer of the Bessel functions * Johann Franz Bessel (1672–1749), German Benedictine abbot an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal can flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a common direction as in a solid. There are many types of LC Phase (matter), phases, which can be distinguished by their Optics, optical properties (such as Texture (crystalline), textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. An LC material may not always be in an LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapour). Liquid crystals can be divided into three main types: thermotropic, lyotropic, and #Metallotropic liquid crystals, metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fig
The fig is the edible fruit of ''Ficus carica'', a species of tree or shrub in the flowering plant family Moraceae, native to the Mediterranean region, together with western and southern Asia. It has been cultivated since ancient times and is now widely grown throughout the world.''The Fig: its History, Culture, and Curing'', Gustavus A. Eisen, Washington, Govt. print. off., 1901 ''Ficus carica'' is the type species of the genus ''Ficus'', which comprises over 800 tropical and subtropical plant species. A fig plant is a deciduous tree or large shrub, growing up to tall, with smooth white bark. Its large leaves have three to five deep lobes. Its fruit (referred to as syconium) is tear-shaped, long, initially green but may ripen toward purple or brown, and has sweet soft reddish flesh containing numerous crunchy seeds. The milky sap of the green parts is an irritant to human skin. In the Northern hemisphere, fresh figs are in season from late August to early October. They tole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Blood Cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen () to the body tissue (biology), tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. Erythrocytes take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillary, capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin (Hb), an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiological Cell (biology), cell function such as erythrocyte deformabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
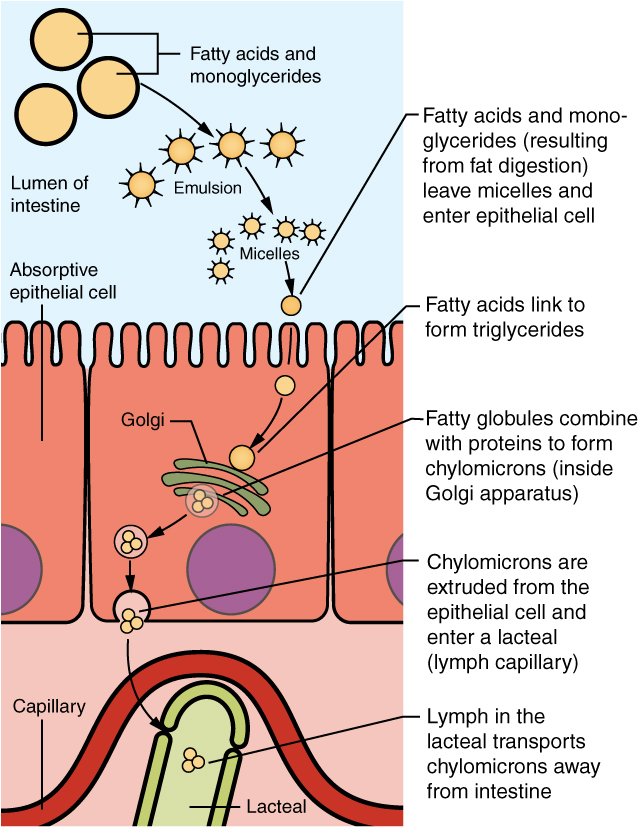
Lipid Metabolism
Lipid metabolism is the synthesis and degradation of lipids in cells, involving the breakdown and storage of fats for energy and the synthesis of structural and functional lipids, such as those involved in the construction of cell membranes. In animals, these fats are obtained from food and are synthesized by the liver. Lipogenesis is the process of synthesizing these fats. The majority of lipids found in the human body from ingesting food are triglycerides and cholesterol. Other types of lipids found in the body are fatty acids and membrane lipids. Lipid metabolism is often considered the digestion and absorption process of dietary fat; however, there are two sources of fats that organisms can use to obtain energy: from consumed dietary fats and from stored fat. Vertebrates (including humans) use both sources of fat to produce energy for organs such as the heart to function. Since lipids are hydrophobic molecules, they need to be solubilized before their metabolism can begin. Lipid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figure 2
Figure may refer to: General *A shape, drawing, depiction, or geometric configuration *Figure (wood), wood appearance *Figure (music), distinguished from musical motif *Noise figure, in telecommunication *Dance figure, an elementary dance pattern *A person's figure, human physical appearance *Figure–ground (perception), the distinction between a visually perceived object and its surroundings Arts *Figurine, a miniature statuette representation of a creature *Action figure, a posable jointed solid plastic character figurine *Figure painting, realistic representation, especially of the human form *Figure drawing *Model figure, a scale model of a creature Writing *figure, in writing, a type of floating block (text, table, or graphic separate from the main text) *Figure of speech, also called a rhetorical figure *Christ figure, a type of character * in typesetting, text figures and lining figures Accounting *Figure, a synonym for number *Significant figures in a decimal number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustic Radiation Force
Acoustic radiation force (ARF) is a physical phenomenon resulting from the interaction of an acoustic wave with an obstacle placed along its path. Generally, the force exerted on the obstacle is evaluated by integrating the acoustic radiation pressure (due to the presence of the sonic wave) over its time-varying surface. The magnitude of the force exerted by an acoustic plane wave at any given location can be calculated as: : , F^, = \frac where :*, F^, is a force per unit volume, here expressed in kg/(s2cm2); :*\alpha is the absorption coefficient in Np/cm (nepers per cm); :*I is the temporal average intensity of the acoustic wave at the given location in W/cm2; and :*c is the speed of sound in the medium in cm/s. The effect of frequency on acoustic radiation force is taken into account via intensity (higher pressures are more difficult to attain at higher frequencies) and absorption (higher frequencies have a higher absorption rate). As a reference, water has an acoustic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numerical Method
In numerical analysis, a numerical method is a mathematical tool designed to solve numerical problems. The implementation of a numerical method with an appropriate convergence check in a programming language is called a numerical algorithm. Mathematical definition Let F(x,y)=0 be a well-posed problem, i.e. F:X \times Y \rightarrow \mathbb is a real or complex functional relationship, defined on the Cartesian product of an input data set X and an output data set Y, such that exists a locally lipschitz function g:X \rightarrow Y called resolvent, which has the property that for every root (x,y) of F, y=g(x). We define numerical method for the approximation of F(x,y)=0, the sequence In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is cal ... of problems : \left \_ = \left \_, with F_n:X_n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |