|
Acharya Tulsi (Jain Monk)
Acharya Tulsi (20 October 1914 – 23 June 1997) was a prominent Jain religious leader. He was the founder of the Anuvrata movement and the Jain Vishva Bharti Institute, Ladnun, and the author of over one hundred books. Acharya Mahapragya, Acharya Mahashraman and Sadhvipramukha Kanakprabha were his disciples. Biography Acharya Tulsi was born on 20 October 1914 in Ladnun, in present Nagaur district of Rajasthan, to Vadana and Jhumarmal Khater. Acharya Kalugani, then the leader of the Śvetāmbara Terapanth association, greatly influenced Tulsi. Tulsi was initiated into monkhood at age 11 in 1925. In 1936, Kalugani nominated Tulsi to be his successor in Gangapur at Rang Bhawan-the house of Ranglal Hiran, making him the ninth Acharya of the Terapanth Sangha. During his leadership of the Sangha, he initiated more than 776 monks and nuns. Scholarship In the 1970s, Acharya Tulsi began researching, compiling translations and commentaries on the Jain Agamas. Acharya Tulsi, along w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion whose three main pillars are nonviolence (), asceticism (), and a rejection of all simplistic and one-sided views of truth and reality (). Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four , supreme preachers of ''dharma''. The first in the current time cycle is Rishabhadeva, who tradition holds lived millions of years ago; the 23rd is Parshvanatha, traditionally dated to the 9th century Common Era, BCE; and the 24th is Mahāvīra, Mahavira, who lived . Jainism is considered an eternal ''dharma'' with the guiding every time cycle of the Jain cosmology, cosmology. Central to understanding Jain philosophy is the concept of ''bhedavijñāna'', or the clear distinction in the nature of the soul and non-soul entities. This principle underscores the innate purity and potential for liberation within every Jīva (Jainism), soul, distinct from the physical and menta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethics Of Jainism
The Five Vows of Jainism include the ''mahāvratas'' (major vows) and ''aṇuvratas'' (minor vows). Overview Jain ethical code prescribes two '' dharmas'' or rules of conduct. One for those who wish to become ascetic and another for the ''śrāvaka'' (householders). Five fundamental vows are prescribed for both votaries. These vows are observed by '' śrāvakas'' (householders) partially and are termed as ''anuvratas'' (small vows). Ascetics observe these fives vows more strictly and therefore observe complete abstinence. These five vows are: * ''Ahiṃsā'' (Non-violence) * ''Satya'' (Truth) * '' Asteya'' (Non-stealing) * ''Brahmacharya'' (Chastity) * ''Aparigraha'' (Non-possession) According to the Jain text '' Puruşārthasiddhyupāya'': Apart from five main vows, a householder is expected to observe seven supplementary vows (''śeelas'') and last '' sallekhanā'' vow. ''Mahāvratas'' (major vows) ''Mahavrata'' (lit. major vows) are the five fundamental observed by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
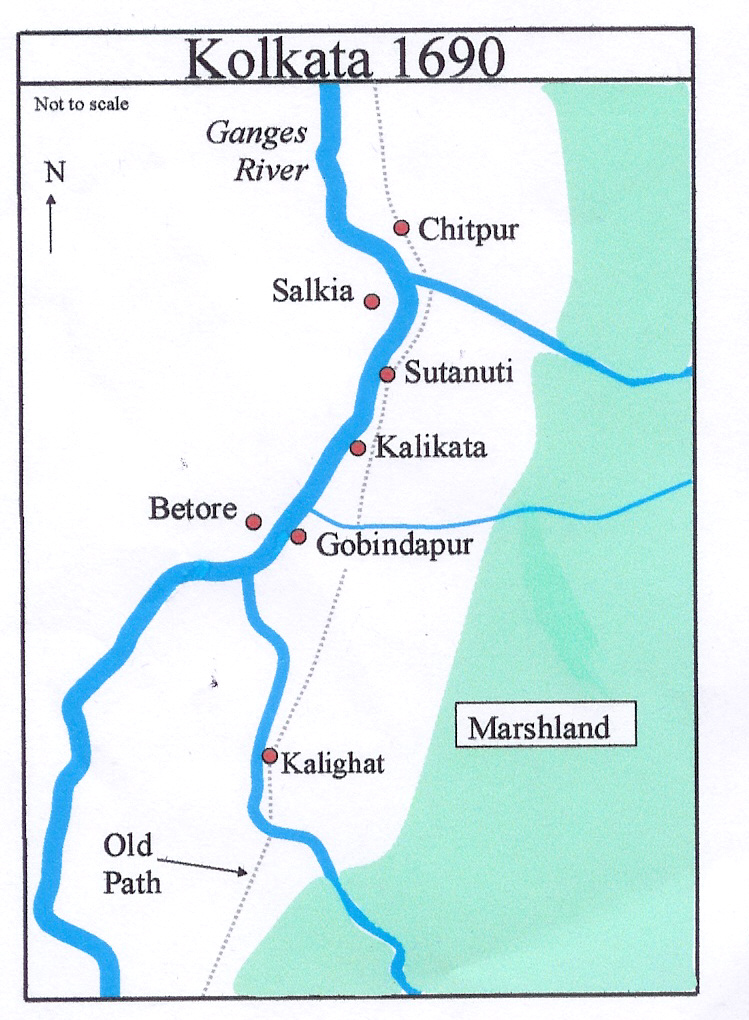
Salkia
Salkia is a neighbourhood in Howrah of Howrah district in the Indian States and territories of India, state of West Bengal. Salkia is under the jurisdiction of Golabari Police Station and Malipanchghara Police Station of Howrah Police Commissionerate, Howrah City Police. It is a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority (KMDA). Location Salkia is located on the west bank of Hooghly River. Pilkhana, West Bengal, Pilkhana is on its south, Liluah and Ghusuri are on its north and Bamangachi is on its west. Market and recreation Haragunge Bazaar is a century-old market, located at heart of North Howrah, on Aurobindo Road, Salkia. Aurobindo Road and Dobson Road are commercial streets in Salkia. Jelia Para Lane is one of the posh residential and commercial area of Salkia. Aurobindo Mall in Salkia (on Aurobindo Road) has a gross leasable area of 1.20 lakh square feet. It was launched in 2017 and has major brands and several restaurants and a three screen m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reserve Bank Of India
Reserve Bank of India, abbreviated as RBI, is the central bank of the Republic of India, and regulatory body responsible for regulation of the Indian banking system and Indian rupee, Indian currency. Owned by the Ministry of Finance (India), Ministry of Finance, Government of India, Government of the Republic of India, it is responsible for the control, issue, and maintenance of the supply of the Indian rupee. It also manages the country's main payment systems and works to promote its economic development. The RBI, along with the Indian Banks' Association, established the National Payments Corporation of India to promote and regulate the payment and settlement systems in India. Bharatiya Reserve Bank Note Mudran, Bharatiya Reserve Bank Note Mudran (BRBNM) is a specialised division of RBI through which it prints and mints Indian currency notes (INR) in two of its currency printing presses located in Mysore (Karnataka; Southern India) and Salboni (West Bengal; Eastern India). Depos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krishan Kant
Krishan Kant (28 February 1927 – 27 July 2002) was an Indian politician who served as the vice president of India from 1997 until his death in 2002. Prior to his vice presidency, Kant was the governor of Andhra Pradesh from 1990 to 1997. He was a member of both houses of the Indian Parliament, representing Chandigarh in the Lok Sabha from 1977 to 1980, and Haryana in the Rajya Sabha from 1966 to 1977. Kant was born to parents who were independence activists in Punjab, British India, and was himself arrested in Lahore during the Quit India movement. After independence, he studied chemical engineering and briefly worked as a scientist with the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi, before turning to politics. Kant was initially associated with the Congress, but later joined the Janata Party and the Janata Dal. He was considered as a candidate for the 2002 presidential election, as was routine for vice presidents. However, the government and the opposition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vice President Of India
The vice president of India (ISO: ) is the deputy to the head of state of the Republic of India, i.e. the president of India. The office of vice president is the second-highest constitutional office after the president and ranks second in the order of precedence and first in the line of succession to the presidency. The vice president is also the ''ex officio'' chairman of the Rajya Sabha. Article 66 of the Constitution of India states the manner of election of the vice president. The vice president is elected indirectly by members of an electoral college consisting of the members of both Houses of Parliament and not the members of state legislative assembly by the system of proportional representation using single transferable votes and the voting is conducted by Election Commission of India via secret ballot. The vice president also acts as the chancellor of the Panjab University and Delhi University. Jagdeep Dhankhar of the Bharatiya Janata Party is the current vic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of India
The president of India (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the head of state of the Republic of India. The president is the nominal head of the executive, the first citizen of the country, and the commander-in-chief, supreme commander of the Indian Armed Forces. Droupadi Murmu is the 15th and current president, having taken office on 25 July 2022. The office of president was created when Constitution of India, India's constitution came into force and it became a republic on Republic Day (India), 26 January 1950. The president is indirect election, indirectly elected by an electoral College (India), electoral college comprising both houses of the Parliament of India and the state Legislative Assembly (India), legislative assemblies of each of States and union territories of India, India's states and territories, who themselves are all directly elected by the citizens. s:Constitution of India/Part V#Article 53 %7BExecutive power of the Union%7D, Article 53 of the Constitution of India stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulsi 1998 Stamp Of India
''Ocimum tenuiflorum'', commonly known as holy basil, ''tulasi'' or ''tulsi'' (), is an aromatic perennial plant in the family Lamiaceae. It is widely cultivated throughout the Southeast Asian tropics. It is native to tropical and subtropical regions of Asia, Australia and the western Pacific. This plant has escaped from cultivation and has naturalized in many tropical regions of the Americas. It is an agricultural and environmental weed. ''Tulasi'' is cultivated for religious and traditional medicine purposes, and also for its essential oil. It is widely used as an herbal tea, commonly used in Ayurveda. It has a place within the Vaishnava tradition of Hinduism, in which devotees perform worship involving the plant or its leaves. Morphology Holy basil is an erect, many-branched subshrub, tall with hairy stems. Leaves are green or purple; they are simple, petioled, with an ovate blade up to long, which usually has a slightly toothed margin; they are strongly scented and ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samana Suttam
''Saman Suttam'' is the religious text created in 1974 by a committee consisting of representatives of each of the major sects of Jainism, Digambaras and Svetambaras, to reconcile the teachings of the sects. After a gap of about nearly two thousand years following composition of Tattvartha Sutra by Acharya Umasvati this was the first text to be recognized by all Jain sects. At Umaswati's time, although multiple orders existed, there was no clear sectarian division. By the 20th century however, Jainism had gradually been divided into several sects. For someone to compile a text at this time, and for it to be approved by all sects, was an exceptional event. Kshullak Jinendra Varni compiled a book, drawing from the original Prakrit (Ardhamagadhi etc.) texts, and as a result of efforts undertaken by Vinoba Bhave. It was critically examined by several monks of different orders including Muni (now Acharya) Vidyanandaji, Muni (later Acharya) Sushil Kumarji, Muni Janakavijaya, Muni N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinoba Bhave
Vinayak Narahar Bhave, also known as Vinoba Bhave (; 11 September 1895 – 15 November 1982), was an Indian advocate of nonviolence and human rights. Often called ''Acharya'' (Teacher in Sanskrit), he is best known for the Bhoodan Movement. He is considered as National Teacher of India and the spiritual successor of Mahatma Gandhi. He was an eminent philosopher. He translated the Bhagavad Gita into the Marathi language by him with the title ''Geetai'' (meaning 'Mother Gīta' in Marathi language, Marathi). Early life and background Vinayak Narahar Bhave was born on 11 September 1895 in a small village called Gagoji (present-day Gagode Budruk) in Raigad district, Kolaba in the Konkan region of what is now Maharashtra. Vinayaka was the eldest son of Narahar Shambhu Rao and Rukmani Devi. The couple had five children; four sons named Vinayaka (affectionately called Vinya), Balakrishna, Shivaji and Dattatreya, and one daughter Shanti. His father was a trained weaver with a modern ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sadhu
''Sadhu'' (, IAST: ' (male), ''sādhvī'' or ''sādhvīne'' (female), also spelled ''saddhu'') is a religious ascetic, mendicant or any holy person in Hinduism and Jainism who has renounced the worldly life. They are sometimes alternatively referred to as'' yogi'', ''sannyasa, sannyasi'' or ''vairagi''. Sādhu means one who practises a 'sadhana' or keenly follows a path of spiritual discipline.″Autobiography of an Yogi″, Yogananda, Paramhamsa, Jaico Publishing House, 127, Mahatma Gandhi Road, Bombay Fort Road, Bombay (Mumbai) – 400 0023 (ed.1997) p.16 Although the vast majority of sādhus are yogi, yogīs, not all yogīs are sādhus. A sādhu's life is solely dedicated to achieving moksha, mokṣa (liberation from the cycle of death and rebirth), the fourth and final Ashrama (stage), aśrama (stage of life), through meditation and contemplation of Brahman. Sādhus often wear simple clothing, such as saffron-coloured clothing in Hinduism and white or nothing in Jainism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abhayagiri Vihāra
Abhayagiri may refer to: * Abhayagiri vihāra a ruined monastic complex of great historical significance in Sri Lanka * Abhayagiri Buddhist Monastery, a Theravadin Buddhist monastery in Redwood Valley, California See also * Abhaya (other) * Giri (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |