|
Acanthobothrium Bullardi
''Acanthobothrium bullardi'' is a species of parasitic onchobothriid tapeworm first found in the whiptail stingray, ''Dasyatis brevis'', in the Gulf of California The Gulf of California ( es, Golfo de California), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Bermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja C .... This species of parasitic tapeworm was originally discovered alongside four other varieties of tapeworms in the Gulf of California during a survey of the area that was done in the years 1993 as well as 1996. References Further reading *Reyda, Florian B., and Janine N. Caira. "Five new species of ''Acanthobothrium'' (Cestoda: Tetraphyllidea) from ''Himantura uarnacoides'' (Myliobatiformes: Dasyatidae) in Malaysian Borneo." Comparative Parasitology 73.1 (2006): 49–71. *Maleki, Loghman, Masoumeh Malek, and Harry W. Palm. "Two new species of ''Acanthobothrium'' (Tetraph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapeworm
Eucestoda, commonly referred to as tapeworms, is the larger of the two subclasses of flatworms in the class Cestoda (the other subclass is Cestodaria). Larvae have six posterior hooks on the scolex (head), in contrast to the ten-hooked Cestodaria. All tapeworms are endoparasites of vertebrates, living in the digestive tract or related ducts. Examples are the pork tapeworm (''Taenia solium'') with a human definitive host, and pigs as the secondary host, and '' Moniezia expansa'', the definitive hosts of which are ruminants. Body structure Adult Eucestoda have a white-opaque dorso-ventrally flattened appearance, and are elongated, ranging in length from a few millimeters to 25 meters. Almost all members, except members of the orders Caryophyllidea and Spathebothriidea, are polyzoic with repeated sets of reproductive organs down the body length, and almost all members, except members of the order Dioecocestidae, are protandral hermaphrodites. Most except caryophyllideans c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whiptail Stingray
The whiptail stingrays are a family, the Dasyatidae, of rays in the order Myliobatiformes. They are found worldwide in tropical to temperate marine waters, and a number of species have also penetrated into fresh water in Africa, Asia, and Australia. Members of this family have flattened pectoral fin discs that range from oval to diamond-like in shape. Their common name comes from their whip-like tails, which are much longer than the disc and lack dorsal and caudal fins. All whiptail stingrays, except the porcupine ray (''Urogymnus asperrimus''), have one or more venomous stings near the base of the tail, which is used in defense. They range in size from or more across in the case of the smalleye stingray and giant freshwater stingray. Genera The taxonomy of Dasyatidae was revised by Peter Last, Gavin Naylor, and Mabel Manjaji-Matsumoto in 2016, based on morphological and molecular phylogenetic data. The placement of ''Megatrygon'' within the family is provisional pending furt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dasyatis Brevis
The diamond stingray (''Dasyatis dipterura'') is a species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae. It is found in the coastal waters of the eastern Pacific Ocean from southern California to northern Chile, and around the Galápagos and Hawaiian Islands. This bottom-dweller generally inhabits sandy or muddy flats near rocky reefs and kelp forests, to a depth of , though off Hawaii it may range considerably deeper. As its common name suggests, this species has an angular, diamond-shaped pectoral fin disc that is plain brown or gray above, with rows of tubercles along the midline and on the "shoulders". The long, whip-like tail has both dorsal and ventral fin folds, which distinguish this ray from the closely similar longtail stingray (''D. longa''). It typically grows to across. When searching for food, diamond stingrays may form groups of up to hundreds of individuals. It is most active at night and preys mainly on burrowing invertebrates and small bony fishes, which are ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
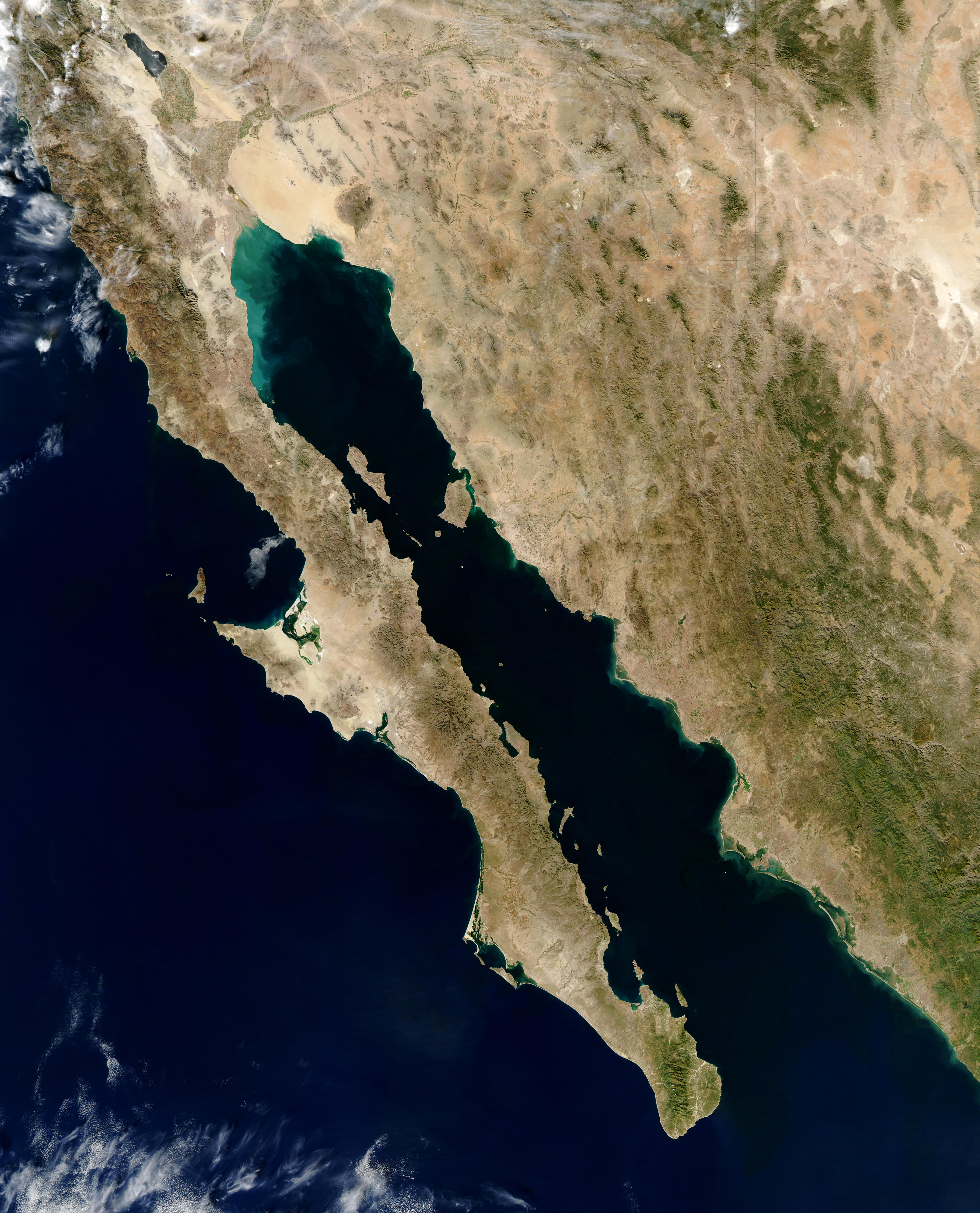
Gulf Of California
The Gulf of California ( es, Golfo de California), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Bermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja California Peninsula from the Mexican mainland. It is bordered by the states of Baja California, Baja California Sur, Sonora, and Sinaloa with a coastline of approximately . Rivers that flow into the Gulf of California include the Colorado, Fuerte, Mayo, Sinaloa, Sonora, and the Yaqui. The surface of the gulf is about . Maximum depths exceed because of the complex geology, linked to plate tectonics. The gulf is thought to be one of the most diverse seas on Earth and is home to more than 5,000 species of micro-invertebrates. Parts of the Gulf of California are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Geography History The marine expeditions of Fortún Ximénez, Hernán Cortés, Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo, Francisco de Ulloa, Hernando de Alarc� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cestoda
Cestoda is a class of parasitic worms in the flatworm phylum (Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, known as tapeworms. Their bodies consist of many similar units known as proglottids—essentially packages of eggs which are regularly shed into the environment to infect other organisms. Species of the other subclass, Cestodaria, are mainly fish infecting parasites. All cestodes are parasitic; many have complex life histories, including a stage in a definitive (main) host in which the adults grow and reproduce, often for years, and one or two intermediate stages in which the larvae develop in other hosts. Typically the adults live in the digestive tracts of vertebrates, while the larvae often live in the bodies of other animals, either vertebrates or invertebrates. For example, ''Diphyllobothrium'' has at least two intermediate hosts, a crustacean and then one or more freshwater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |