|
Abraham The Great Of Kashkar
Abraham the Great of Kashkar was the father of the Assyrian monastic revival in the 6th century. He is a doctor and saint of the Church of the East. He was born in Kashkar in Persia around 492. He left there to preach the Gospel at Al-Hirah, leaving there to study monastic life at Scetes. Monasticism was very popular in early Syrian and Mesopotamian Christianity. Some held the view that only a life of celibacy could lead to salvation. Initially, all monks and nuns were hermits, but in about 350 Mar Awgin founded the first cenobitic Cenobitic (or coenobitic) monasticism is a monastery, monastic tradition that stresses community life. Often in the West the community belongs to a religious order, and the life of the cenobitic monk is regulated by a Monastic rule, religious ru ... monastery of Mesopotamia on Mount Izla above the city Nisibis, patterned upon the Egyptian model. Soon there were many monasteries. But at the synod of Beth Lapat the Church of the East decide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epiphany (holiday)
Epiphany ( ), also known as "Theophany" in Eastern Christian tradition, is a Christian feast day commemorating the visit of the Magi, the baptism of Jesus, and the wedding at Cana. In Western Christianity, the feast commemorates principally (but not solely) the visit of the Magi to the Christ Child, and thus Jesus Christ's physical manifestation to the Gentiles. It is sometimes called Three Kings' Day, and in some traditions celebrated as Little Christmas. Moreover, the feast of the Epiphany, in some denominations, also initiates the liturgical season of Epiphanytide. Eastern Christians, on the other hand, commemorate the baptism of Jesus in the River Jordan, seen as his manifestation to the world as the Son of God, and celebrate it as the Feast of the Epiphany or of the Theophany. The traditional site of the ministry of John the Baptist is in Al-Maghtas in Jordan, with the baptism of Jesus once marked in Byzantine times by a cross in the middle of the Jordan River, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
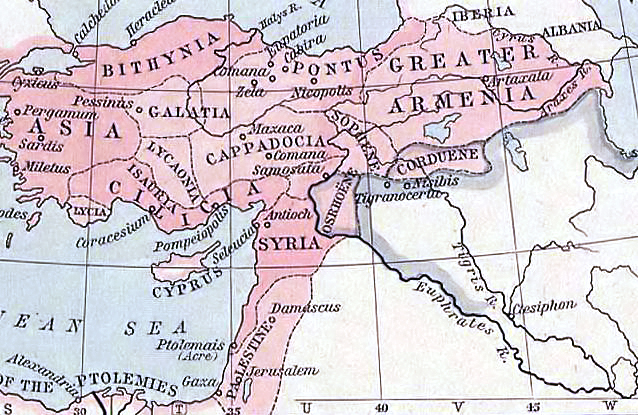
Nisibis
Nusaybin () is a municipality and Districts of Turkey, district of Mardin Province, Turkey. Its area is 1,079 km2, and its population is 115,586 (2022). The city is populated by Kurds of different tribal affiliation. Nusaybin is separated from the larger Kurds, Kurdish-majority city of Qamishli by the Syria–Turkey border. The city is at the foot of the Mount Izla escarpment at the southern edge of the Tur Abdin hills, standing on the banks of the Jaghjagh River (), the ancient Mygdonius (). The city existed in the Assyrian Empire and is recorded in Akkadian language, Akkadian inscriptions as ''Naṣibīna''. Having been part of the Achaemenid Empire, in the Hellenistic period the settlement was re-founded as a ''polis'' named "Antioch on the Mygdonius" by the Seleucid dynasty after the conquests of Alexander the Great. A part of first the Roman Republic and then the Roman Empire, the city (; ) was mainly Syriac language, Syriac-speaking, and control of it was contested be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Christian Monks
''Egyptian'' describes something of, from, or related to Egypt. Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to: Nations and ethnic groups * Egyptians, a national group in North Africa ** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of recorded history ** Egyptian cuisine, the local culinary traditions of Egypt * Egypt, the modern country in northeastern Africa ** Egyptian Arabic, the language spoken in contemporary Egypt ** A citizen of Egypt; see Demographics of Egypt * Ancient Egypt, a civilization from c. 3200 BC to 343 BC ** Ancient Egyptians, ethnic people of ancient Egypt ** Ancient Egyptian architecture, the architectural structure style ** Ancient Egyptian cuisine, the cuisine of ancient Egypt ** Egyptian language, the oldest known language of Egypt and a branch of the Afroasiatic language family * Copts, the ethnic Egyptian Christian minority ** Coptic language or Coptic Egyptian, the latest stage of the Egyptian language, spoken in Egypt until the 17th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyrian Church Of The East Saints
Assyrian may refer to: * Assyrian people, an indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia. * Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire. ** Early Assyrian Period ** Old Assyrian Period ** Middle Assyrian Empire ** Neo-Assyrian Empire ** Post-imperial Assyria * Assyrian language (other) * Assyrian Church (other) * SS ''Assyrian'', several cargo ships * ''The Assyrian'' (novel), a novel by Nicholas Guild * The Assyrian (horse), winner of the 1883 Melbourne Cup See also * Assyria (other) * Syriac (other) * Assyrian homeland, a geographic and cultural region in Northern Mesopotamia traditionally inhabited by Assyrian people * Syriac language, a dialect of Middle Aramaic that is the minority language of Syrian Christians * Upper Mesopotamia * Church of the East (other) Church of the East, also called ''Nestorian Church'', an Eastern Christian denomination formerly spread across Asia, separated since the schism of 1552. Church of the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monks Of The Church Of The East
A monk (; from , ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a man who is a member of a religious order and lives in a monastery. A monk usually lives his life in prayer and contemplation. The concept is ancient and can be seen in many religions and in philosophy across numerous cultures. The Greek word for "monk" may be applied to men or women. In English, however, "monk" is applied mainly to men, while ''nun'' is typically used for female monastics. Although the term ''monachos'' is of Christian origin, in the English language ''monk'' tends to be used loosely also for both male and female ascetics from other religious or philosophical backgrounds. However, being generic, it is not interchangeable with terms that denote particular kinds of monk, such as cenobite, hermit, anchorite, or hesychast. Traditions of Christian monasticism exist in major Christian denominations, with religious orders being present in Catholicism, Lutheranism, Oriental Orthodoxy, Eastern Orthodoxy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century Iranian People
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. Owing in part to the collapse of the Roman Empire along with its literature and civilization, the sixth century is generally considered to be the least known about in the Dark Ages. In its second golden age, the Sassanid Empire reached th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
586 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 586 ( DLXXXVI) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 586 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Spring – Emperor Maurice rejects a peace proposal of the Persians, in exchange for renewed payments in gold. * Battle of Solachon: A Byzantine army under command of Philippicus defeats the Sassanid Persians, near Dara. * The Avars besiege Thessalonica (Central Macedonia), the second city of the Byzantine Empire.History of the Byzantine Empire from DCCXVI to MLVII, George Finlay, p. 316 * The Vlachs are first mentioned in a Byzantine chronicle (approximate date). Europe * April 21 – King Liuvigild dies at Toledo after an 18-year reign, and is succeeded by his second son Reccared I. * Slavs advance to the gates of Thessaloniki and the Peloponnese. * Avars dest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
490s Births
49 may refer to: * 49 (number) * "Forty Nine", a song by Karma to Burn from the album '' V'', 2011 * one of the years 49 BC, AD 49, 1949, 2049 * 49 Pales 49 Pales () is a large, dark main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by German-French astronomer Hermann Goldschmidt on 19 September 1857 from his balcony in Paris. The asteroid is named after Pales, the goddess of shepherds in Roman mytholog ..., a main-belt asteroid * Tatra 49, a three-wheeled motor vehicle {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick George Holweck
Frederick George Holweck (born Friedrich Georg Holweck; December 29, 1856 – February 15, 1927) was a German-Americans, German-American Catholic Church, Catholic parish priest and scholar, hagiographer and church historian. Monsignor Holweck contributed some articles to the ''Catholic Encyclopedia''. As rector of St. Francis de Sales Oratory (St. Louis), St. Francis de Sales Church at St. Louis, Missouri, he was tasked with rebuilding the church after the original was destroyed by the St. Louis Tornado, Great St. Louis Tornado of 1896. The second edifice, incorporating many of the characteristics of German ecclesiastical architecture is familiarly known as "the Cathedral of South St. Louis." He also served as vicar-general of the Archdiocese of St. Louis. Life Frederick George Holweck was born in Wiesloch, Grand Duchy of Baden, Baden, on December 29, 1856, the son of Sebastian and Mary E. Holweck. He was educated at the gymnasia in Freiburg and Karlsruhe. Because of the Kulturk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feast Day
The calendar of saints is the traditional Christian method of organizing a liturgical year by associating each day with one or more saints and referring to the day as the feast day or feast of said saint. The word "feast" in this context does not mean "a large meal, typically a celebratory one", but instead "an annual religious celebration, a day dedicated to a particular saint". The system rose from the early Christian custom of commemorating each martyr annually on the date of their death, their birth into heaven, a date therefore referred to in Latin as the martyr's ''dies natalis'' ('day of birth'). In the Eastern Orthodox Church, a calendar of saints is called a ''Menologion''. "Menologion" may also mean a set of icons on which saints are depicted in the order of the dates of their feasts, often made in two panels. History As the number of recognized saints increased during Late Antiquity and the first half of the Middle Ages, eventually every day of the year had at l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babai The Great
Babai the Great ( , c. 551 – 628) was an early Assyrian people, Assyrian church father of the Church of the East. He set several of the foundational pillars of the Church, revived the monastic movement, and formulated its Christology in a systematic way. He served as a monastic visitor and coadjutor with Aba I, Mar Aba as unofficial heads of the Church of the East (formerly falsely referred to as "Nestorian Church") after Gregory (Nestorian patriarch), Catholicos Gregory until 628 Anno Domini, AD, leaving a legacy of strong discipline and deep religious Orthodoxy. He is revered in the modern Assyrian Church of the East and Ancient Church of the East. Biography Babai the Great (not to be confused with Mar Babai I, the first autonomous leader of the Church of the East) was born in the Assyrian town of Beth Ainata in Beth Zabdai, on the west bank of the Tigris, near Nisibis. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dadisho Of Mount Izla
Dadishoʿ (528/9–604) was a monk and author of the Church of the East. He was the second abbot of the great monastery of Mount Izla after its founder, Abraham of Kashkar. He has sometimes been conflated (e.g., by Giuseppe Assemani) with Dadishoʿ Qaṭraya, who lived a century later. The biography of Dadishoʿ written by his successor as abbot, Babai the Great, is lost, but it was used as a source for Ishoʿdnaḥ's ''Book of Chastity'' (8th century) and Thomas of Marga's ''Book of Governors'' (9th century). According to Ishoʿdnaḥ, his family came from Beth Aramaye, but Babai says in another work that they were from Beth Daraye. In his youth, he studied in the school of Nisibis and later that of Arbela. Upon completing his formal education, he went into the mountains of Adiabene to live as an anchorite. In Adiabene, Dadishoʿ was joined by several disciples, including Sahrowai, the future bishop of Arzun. He moved to the diocese of Marga and lived seven years in the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |