|
Abraham Of Arbela
Abraham of Arbela (died 345) (also known as Abramius) was a bishop of Arbela (also Persian) in Assyria. During the imprisonment of Bishop Ioannis of Arbela, he was appointed as his deputy by the local religious community. The church historian Sozomen (died 450) described in the second book of his Christian Church, among other things, the persecutions and tortures that took place in the Persian Empire under Shapur II (died 379). In paragraph 8 of chapter 8 he says: Among the names he had been able to retrieve, the name of Bishop Abraham of Arbela also appeared. He was tortured and later beheaded under Shapur II because he refused to worship the sun in Telman. The saint is venerated on February 5. He has two feast days – February 4 and 5, but January 31 in the Catholic Church.Roman Martyrology The ''Roman Martyrology'' ( la, Martyrologium Romanum) is the official martyrology of the Catholic Church. Its use is obligatory in matters regarding the Roman Rite liturgy, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erbil
Erbil, also called Hawler (, ar, أربيل, Arbīl; syr, ܐܲܪܒܹܝܠ, Arbel), is the capital and most populated city in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. It lies in the Erbil Governorate. It has an estimated population of around 1,600,000. Human settlement at Erbil may be dated back to the fifth millennium BC. At the heart of the city is the ancient Citadel of Erbil and Mudhafaria Minaret. The earliest historical reference to the region dates to the Third Dynasty of Ur of Sumer, when King Shulgi mentioned the city of Urbilum. The city was later conquered by the Assyrians. In the 3rd millennium BC Erbil was an independent power in its area. It was conqureed for a time by the Gutians. Beginning in the late 2nd millennium BC it came under Assyrian control. Subsequent to this, it was part of the geopolitical province of Assyria under several empires in turn, including the Median Empire, the Achaemenid Empire ( Achaemenid Assyria), Macedonian Empire, Seleucid Empire, Arme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
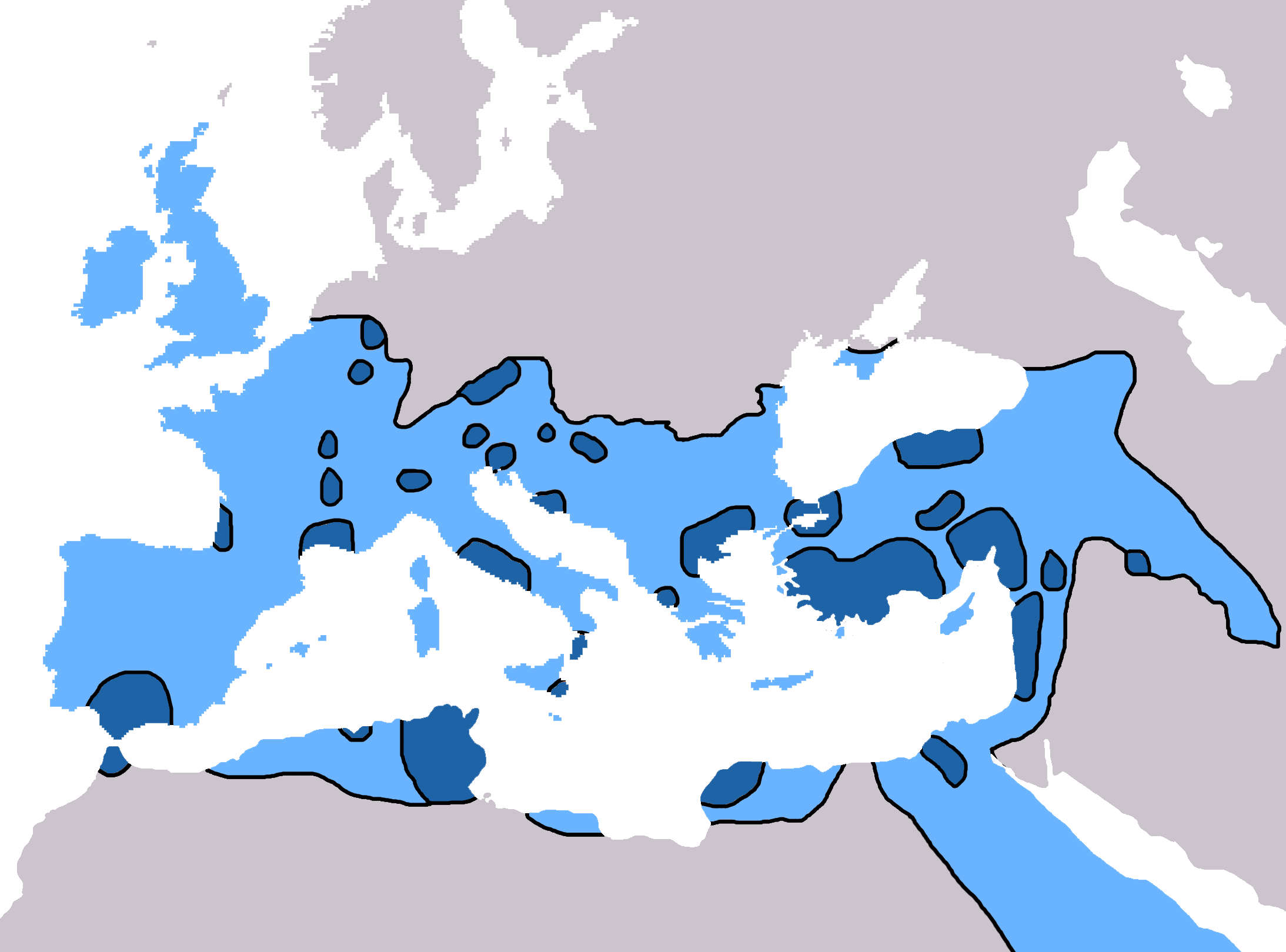
Assyria (Roman Province)
Assyria () was reputedly a Roman province that lasted only two years (116–118 AD). History According to Eutropius and Festus, two historians who wrote under the direction of the Emperor Valens in the second half of the 4th century, at a time when the Roman emperor Trajan was perceived as "a valuable paradigm for contemporary events and figures", Assyria was one of three provinces (with Armenia and Mesopotamia) created by Trajan in AD 116 following a successful military campaign against Parthia that in that year saw him cross the River Tigris from Mesopotamia and take possession, in spite of resistance, of the territory of Adiabene and then march south to the Parthian capital of Seleucia-Ctesiphon and to Babylon. There is numismatic evidence for the Trajanic provinces of Armenia and Mesopotamia, but none for that of Assyria, whose existence is questioned by C.S. Lightfoot and F. Miller. Despite Rome's military victory, Trajan's 116 conquest was plagued with difficulties. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sozomen
Salamanes Hermias Sozomenos ( grc-gre, Σαλαμάνης Ἑρμείας Σωζομενός; la, Sozomenus; c. 400 – c. 450 AD), also known as Sozomen, was a Roman lawyer and historian of the Christian Church. Family and home He was born around 400 in Bethelia, a small town near Gaza, into a wealthy Christian family of Palestine. He told the history of Southern Palestine derived from oral tradition. He appeared to be familiar with the region around Gaza, and mentioned having seen Bishop Zeno of Majuma, at the seaport of Gaza. Grandfather Sozomen wrote that his grandfather lived at Bethelia, near Gaza, and became a Christian together with his household, probably under Constantius II. A neighbor named Alaphrion was miraculously healed by Saint Hilarion who cast out a demon from Alaphrion, and, as eyewitnesses to the miracle, his family converted, along with Alaphrion's. The conversion marked a turning-point in the Christianization of southern Palestine, according to his ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Church
In ecclesiology, the Christian Church is what different Christian denominations conceive of as being the true body of Christians or the original institution established by Jesus. "Christian Church" has also been used in academia as a synonym for Christianity, despite the fact that it is composed of multiple churches or denominations, many of which hold a doctrinal claim of being the " one true church", to the exclusion of the others. For many Protestant Christians, the Christian Church has two components: the church visible, institutions in which "the Word of God purely preached and listened to, and the sacraments administered according to Christ's institution", as well as the church invisible—all "who are truly saved" (with these beings members of the visible church). In this understanding of the invisible church, "Christian Church" (or catholic Church) does not refer to a particular Christian denomination, but includes all individuals who have been saved. The branch the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shapur II
Shapur II ( pal, 𐭱𐭧𐭯𐭥𐭧𐭥𐭩 ; New Persian: , ''Šāpur'', 309 – 379), also known as Shapur the Great, was the tenth Sasanian Empire, Sasanian King of Kings (Shahanshah) of Iran. The List of longest-reigning monarchs, longest-reigning monarch in History of Iran, Iranian history, he reigned for the entirety of his 70-year life, from 309 to 379. He was the son of Hormizd II (r. 302–309). His reign saw the military resurgence of the country, and the expansion of its territory, which marked the start of the first Sasanian golden era. He is thus along with Shapur I, Kavad I and Khosrow I, regarded as one of the most illustrious Sasanian kings. His three direct successors, on the other hand, were less successful. At the age of 16, he launched enormously successful military campaigns against Arab insurrections and tribes who knew him as 'Dhū'l-Aktāf'' ("he who pierces shoulders"). Shapur II pursued a harsh religious policy. Under his reign, the collection of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feast Day
The calendar of saints is the traditional Christian method of organizing a liturgical year by associating each day with one or more saints and referring to the day as the feast day or feast of said saint. The word "feast" in this context does not mean "a large meal, typically a celebratory one", but instead "an annual religious celebration, a day dedicated to a particular saint". The system arose from the early Christian custom of commemorating each martyr annually on the date of their death, or birth into heaven, a date therefore referred to in Latin as the martyr's ''dies natalis'' ('day of birth'). In the Eastern Orthodox Church, a calendar of saints is called a '' Menologion''. "Menologion" may also mean a set of icons on which saints are depicted in the order of the dates of their feasts, often made in two panels. History As the number of recognized saints increased during Late Antiquity and the first half of the Middle Ages, eventually every day of the year h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Martyrology
The ''Roman Martyrology'' ( la, Martyrologium Romanum) is the official martyrology of the Catholic Church. Its use is obligatory in matters regarding the Roman Rite liturgy, but dioceses, countries and religious institutes may add duly approved appendices to it. It provides an extensive but not exhaustive list of the saints recognized by the Church. History In 1582, Pope Gregory XIII decreed a revision of the Julian calendar, creating a new system, now called, after him, the Gregorian calendar. The ''Roman Martyrology'' was first published in 1583. A second edition was published in the same year. The third edition, in 1584, was made obligatory wherever the Roman Rite was in use. The main source was the Martyrology of Usuard, completed by the "Dialogues" of Pope Gregory I and the works of some of the Fathers, and for the Greek saints by the catalogue known as the Menologion of Sirlet. Its origins can be traced back to the Martyrologium Hieronymianum, which was originally base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Missing
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
345 Deaths
The Year 345 ( CCCXLV) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Amantius and Albinus (or, less frequently, year 1098 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 345 for this year has been used ever since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place India * Merchant Knai Thomman and 400 followers visit the Malabar Coast in Kerala (India), and assist the church there. * The Kadamba Dynasty is founded by Mayurasharma. Italy * Constans orders the Basilica di Santa Tecla to be constructed in Lombardy. Births * Evagrius Ponticus, Christian monk and ascetic (d. 399) * Afranius Syagrius, Roman politician and administrator * Quintus Aurelius Symmachus, Roman consul and intellectual (d. 402) * Tyrannius of Aquileia, historian and theologian (approximate date) Deaths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th-century Mesopotamian Bishops
The 4th century (per the Julian calendar and Anno Domini/Common era) was the time period which lasted from 301 ( CCCI) through 400 ( CD). In the West, the early part of the century was shaped by Constantine the Great, who became the first Roman emperor to adopt Christianity. Gaining sole reign of the empire, he is also noted for re-establishing a single imperial capital, choosing the site of ancient Byzantium in 330 (over the current capitals, which had effectively been changed by Diocletian's reforms to Milan in the West, and Nicomedeia in the East) to build the city soon called Nova Roma (New Rome); it was later renamed Constantinople in his honor. The last emperor to control both the eastern and western halves of the empire was Theodosius I. As the century progressed after his death, it became increasingly apparent that the empire had changed in many ways since the time of Augustus. The two emperor system originally established by Diocletian in the previous century fell in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopotamian Saints
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia occupies modern Iraq. In the broader sense, the historical region included present-day Iraq and Kuwait and parts of present-day Iran, Syria and Turkey. The Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrians and Babylonians) originating from different areas in present-day Iraq, dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of written history () to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BC, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire. Later the Arameans dominated major parts of Mesopotamia (). Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution from around 10,000 BC. It has been identifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |