|
AMD Turion
AMD Turion is the brand name AMD applies to its x86-64 low-power consumption mobile processors codenamed ''K8L''. The Turion 64 and Turion 64 X2/Ultra processors compete with Intel's mobile processors, initially the '' Pentium M'' and the Intel Core and Intel Core 2 processors. Features Turion 64 Earliest Turion 64 processors are plugged into AMD's Socket 754. They are equipped with 512 or 1024 KiB of L2 cache, a 64-bit single channel on-die DDR-400 memory controller, and an 800 MHz HyperTransport bus. Battery saving features, like '' PowerNow!'', are central to the marketing and usefulness of these CPUs. The newer "Richmond" models are designed for AMD's Socket S1 and have a double-channel DDR2 controller. Turion 64 X2 Turion 64 X2 is AMD's 64-bit dual-core mobile CPU, intended to compete with Intel's Core and Core 2 CPUs. The Turion 64 X2 was launched on May 17, 2006, after several delays. These processors use Socket S1 and feature DDR2 memory. They also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
AMD Turion 2005
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California and maintains significant operations in Austin, Texas. AMD is a Information technology, hardware and Fabless manufacturing, fabless company that designs and develops List of AMD processors, central processing units (CPUs), List of AMD graphics processing units, graphics processing units (GPUs), field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), System on a chip, system-on-chip (SoC), and high-performance computing, high-performance computer solutions. AMD serves a wide range of business and consumer markets, including gaming, data centers, artificial intelligence (AI), and embedded systems. AMD's main products include List of AMD microprocessors, microprocessors, motherboard chipsets, embedded processors, and List of AMD graphics processing units, graphics processors for Server (computing), servers, workstations, personal computers, and embedded syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer components such as central processing units (CPUs) and related products for business and consumer markets. It is one of the world's List of largest semiconductor chip manufacturers, largest semiconductor chip manufacturers by revenue, and ranked in the Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 list of the List of largest companies in the United States by revenue, largest United States corporations by revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 Fiscal year, fiscal years, until it was removed from the ranking in 2018. In 2020, it was reinstated and ranked 45th, being the List of Fortune 500 computer software and information companies, 7th-largest technology company in the ranking. It was one of the first companies listed on Nasdaq. Intel supplies List of I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phase-locked Loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is fixed relative to the phase of an input signal. Keeping the input and output phase in lockstep also implies keeping the input and output frequencies the same, thus a phase-locked loop can also track an input frequency. Furthermore, by incorporating a frequency divider, a PLL can generate a stable frequency that is a multiple of the input frequency. These properties are used for clock synchronization, demodulation, frequency synthesis, clock multipliers, and signal recovery from a noisy communication channel. Since 1969, a single integrated circuit can provide a complete PLL building block, and nowadays have output frequencies from a fraction of a hertz up to many gigahertz. Thus, PLLs are widely employed in radio, telecommunications, computers (e.g. to distribute precisely timed clock signals in microprocessors), grid-tie inverters (electronic power converters used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Northbridge (computing)
In computing, a northbridge (also host bridge, or memory controller hub) is a microchip that comprises the core logic chipset architecture on motherboards to handle high-performance tasks, especially for older personal computers. It is connected directly to a CPU via the front-side bus (FSB), and is usually used in conjunction with a slower southbridge to manage communication between the CPU and other parts of the motherboard. Historically, separation of functions between CPU, northbridge, and southbridge chips was necessary due to the difficulty of integrating all components onto a single chip die. However, as CPU speeds increased over time, a bottleneck emerged due to limitations caused by data transmission between the CPU and its support chipset. The trend for integrated northbridges began near the end of the 2000s for example, the Nvidia GeForce 320M GPU in the 2010 MacBook Air was a northbridge/southbridge/GPU combo chip. On older Intel based PCs, the northbridge was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
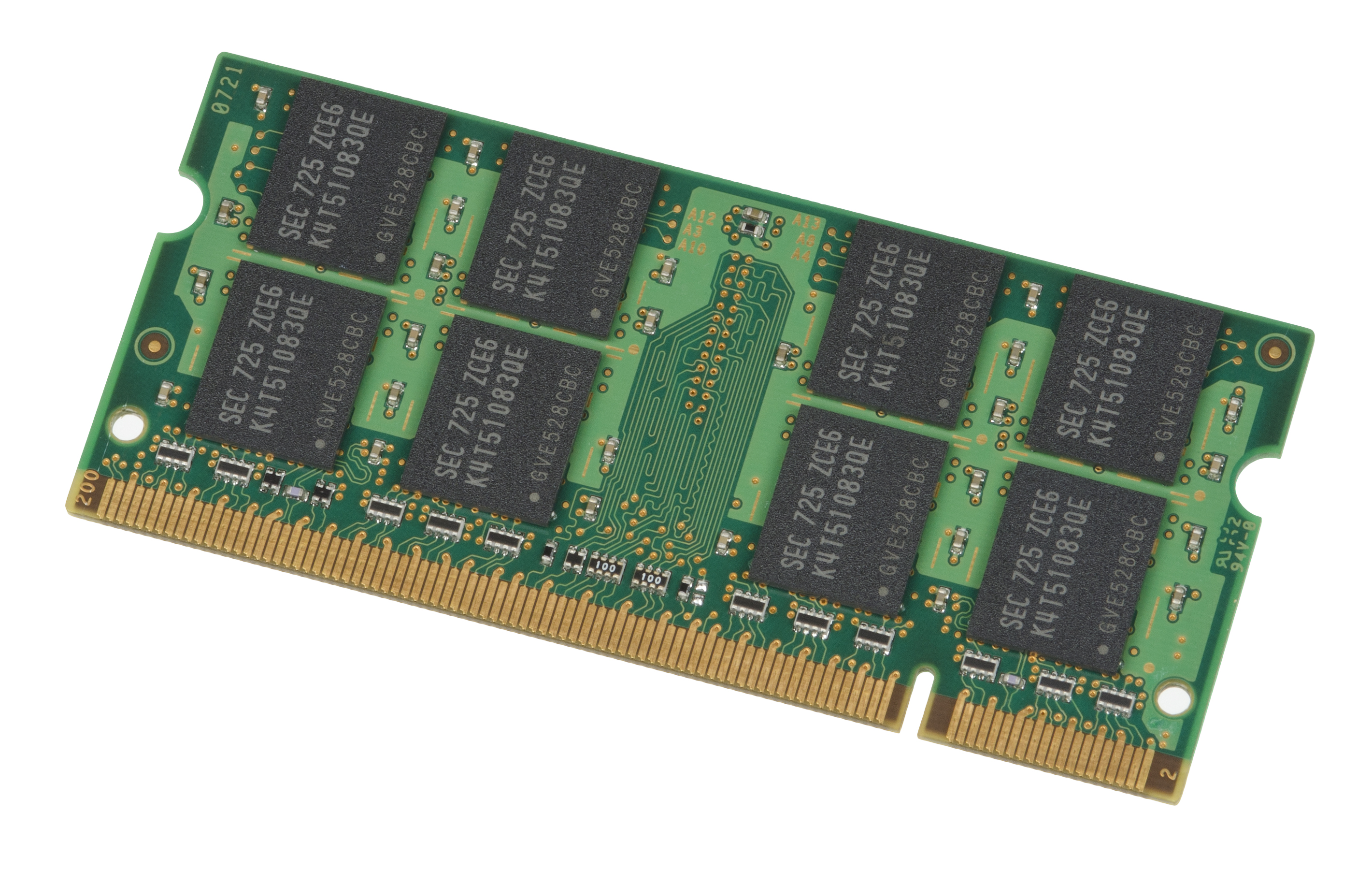
SO-DIMM
A DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) is a popular type of memory module used in computers. It is a printed circuit board with one or both sides (front and back) holding DRAM chips and pins. The vast majority of DIMMs are manufactured in compliance with JEDEC memory standards, although there are proprietary DIMMs. DIMMs come in a variety of speeds and capacities, and are generally one of two lengths: PC, which are , and laptop (SO-DIMM), which are about half the length at . History DIMMs (Dual In-line Memory Module) were a 1990s upgrade for SIMMs (Single In-line Memory Modules) as Intel P5-based Pentium processors began to gain market share. The Pentium had a 64-bit bus width, which would require SIMMs installed in matched pairs in order to populate the data bus. The processor would then access the two SIMMs in parallel. DIMMs were introduced to eliminate this disadvantage. The contacts on SIMMs on both sides are redundant, while DIMMs have separate electrical contacts on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
DDR2-800
Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR2 SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) interface. It is a JEDEC standard (JESD79-2); first published in September 2003. DDR2 succeeded the original DDR SDRAM specification, and was itself succeeded by DDR3 SDRAM in 2007. DDR2 DIMMs are neither forward compatible with DDR3 nor backward compatible with DDR. In addition to double pumping the data bus as in DDR SDRAM (transferring data on the rising and falling edges of the bus clock signal), DDR2 allows higher bus speed and requires lower power by running the internal clock at half the speed of the data bus. The two factors combine to produce a total of four data transfers per internal clock cycle. Since the DDR2 internal clock runs at half the DDR external clock rate, DDR2 memory operating at the same external data bus clock rate as DDR results in DDR2 being able to provide the same bandwidth but with better latency. Alter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
65 Nm
The 65 nm process is an advanced lithographic node used in volume CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor fabrication. Printed linewidths (i.e. transistor gate lengths) can reach as low as 25 nm on a nominally 65 nm process, while the pitch between two lines may be greater than 130 nm. Process node For comparison, cellular ribosomes are about 20 nm end-to-end. A crystal of bulk silicon has a lattice constant of 0.543 nm, so such transistors are on the order of 100 atoms across. By September 2007, Intel, AMD, IBM, UMC and Chartered were also producing 65 nm chips. While feature sizes may be drawn as 65 nm or less, the wavelengths of light used for lithography are 193 nm and 248 nm. Fabrication of sub-wavelength features requires special imaging technologies, such as optical proximity correction and phase-shifting masks. The cost of these techniques adds substantially to the cost of manufacturing sub-wavelength semiconductor products, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
AMD Mobile Platform
The AMD mobile platform is an open platform for laptops from Advanced Micro Devices, AMD. Though little marketing was done on this platform, it has been competing with the Centrino platform in the segment to gain more marketshare. Each platform has its own specification, catching up the latest technology developments. Since the acquisition of ATI, AMD began to include Mobility Radeon GPUs and AMD chipsets as part of the requirements of the mobile platform; the first of such platforms is the AMD mobile platform#Puma platform, ''Puma'' platform. Open platform approach In February 2007, AMD had announced the "Better by Design" initiative to continue the success of the open platform approach for desktop back in early 2003 after the launch of Athlon 64 processors with a lack of chipset being developed by AMD, and open the platform to chipset vendors such as VIA Technologies, VIA, Silicon Integrated Systems, SiS, Nvidia, NVIDIA and from AMD subsidiary ATI Technologies, ATI. The initiativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
AMD K10
The AMD Family 10h, or K10, is a microprocessor microarchitecture by AMD based on the K8 microarchitecture. The first third-generation Opteron products for servers were launched on September 10, 2007, with the Phenom processors for desktops following and launching on November 11, 2007, as the immediate successors to the K8 series of processors (Athlon 64, Opteron, 64-bit Sempron). Nomenclature It appears that AMD has not used K-nomenclature (which originally stood for "Kryptonite" in the K5 processor) from the time after the use of the codename ''K8'' for the AMD K8 or Athlon 64 processor family, since no K-nomenclature naming convention beyond K8 has appeared in official AMD documents and press releases after the beginning of 2005. The name "''K8L''" was first coined by Charlie Demerjian in 2005, at the time a writer at ''The Inquirer'', and was used by the wider IT community as a convenient shorthand while according to AMD official documents, the processor family was terme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
AMD K8
The AMD K8 Hammer, also code-named SledgeHammer, is a computer processor microarchitecture designed by AMD as the successor to the AMD K7 Athlon microarchitecture. The K8 was the first implementation of the AMD64 64-bit extension to the x86 instruction set architecture. Features Processors Processors based on the K8 core include: * Athlon 64 - first 64-bit consumer desktop * Athlon 64 X2 - first dual-core ('X2') desktop ** Athlon X2 - later model dual-core desktop with '64' omitted * Athlon 64 FX - enthusiast desktop (multipliers unlocked) * Sempron - low-end, low-cost desktop * Opteron - server market * Turion 64 - mobile computing market * Turion 64 X2 - dual-core mobile processor The K8 core is very similar to the K7. The most radical change is the integration of the AMD64 instructions and an on-chip memory controller. The memory controller drastically reduces memory latency and is largely responsible for most of the performance gains from K7 to K8. Nomenclat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Turion Ultra Logo , family of AMD 64-bit processors
{{disambig ...
Turion may refer to: * Turion (botany), winter bud in aquatic species * AMD Turion AMD Turion is the brand name AMD applies to its x86-64 low-power consumption mobile processors codenamed ''K8L''. The Turion 64 and Turion 64 X2/Ultra processors compete with Intel's mobile processors, initially the '' Pentium M'' and the In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Codename
A code name, codename, call sign, or cryptonym is a code word or name used, sometimes clandestinely, to refer to another name, word, project, or person. Code names are often used for military purposes, or in espionage. They may also be used in industrial counter-espionage to protect secret projects and the like from business rivals, or to give names to projects whose marketing name has not yet been determined. Another reason for the use of names and phrases in the military is that they transmit with a lower level of cumulative errors over a walkie-talkie or radio link than actual names. Origins Achaemenid Empire The Achaemenid Empire under Darius I employed a network of spies called the King’s Eye or the King’s Ear. These agents operated under anonymity, and “King’s Eye” was not a specific person but rather a code name for the intelligence network that reported directly to the king. Punic Wars The Carthaginian general Hannibal Barca reportedly used coded re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |