|
AC-to-AC Converter
A solid-state AC-to-AC converter converts an Alternating current, AC waveform to another AC waveform, where the output voltage and frequency can be set arbitrarily. Categories Referring to Fig 1, AC-AC converters can be categorized as follows: * Indirect AC-AC (or AC/DC-AC) converters (i.e., with rectifier, DC link and inverter), such as those used in Variable-frequency drive, variable frequency drives * Cycloconverters * Hybrid matrix converters * Matrix converters (MC) *Voltage controller, AC voltage controllers DC link converters There are two types of converters with DC link: * Voltage-source inverter (VSI) converters (Fig. 2): In VSI converters, the rectifier consists of a diode-bridge and the DC link consists of a shunt capacitor. * Current-source inverter (CSI) converters (Fig. 3): In CSI converters, the rectifier consists of a phase-controlled switching device bridge and the DC link consists of 1 or 2 series inductors between one or both legs of the connection between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternating Current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form of electrical energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen appliances, televisions, Fan (machine), fans and electric lamps into a wall socket. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', respectively, as when they modify ''Electric current, current'' or ''voltage''. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave, whose positive half-period corresponds with positive direction of the current and vice versa (the full period is called a ''wave cycle, cycle''). "Alternating current" most commonly refers to power distribution, but a wide range of other appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon-controlled Rectifier
A silicon controlled rectifier or semiconductor controlled rectifier (SCR) is a four-layer solid-state current-controlling device. The name "silicon controlled rectifier" is General Electric's trade name for a type of thyristor. The principle of four-layer p–n–p–n switching was developed by Moll, Tanenbaum, Goldey, and Holonyak of Bell Laboratories in 1956. The practical demonstration of silicon controlled switching and detailed theoretical behavior of a device in agreement with the experimental results was presented by Dr Ian M. Mackintosh of Bell Laboratories in January 1958. The SCR was developed by a team of power engineers led by Gordon Hall and commercialized by Frank W. "Bill" Gutzwiller in 1957. Some sources define silicon-controlled rectifiers and thyristors as synonymous while other sources define silicon-controlled rectifiers as a proper subset of the set of thyristors; the latter being devices with at least four layers of alternating n- and p-type mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Changer
A frequency changer or frequency converter is Electronics, electronic or electromechanical equipment that converts alternating current (Alternating current, AC) of one frequency to alternating current of another frequency. The equipment may also change the voltage, but if it does, that is incidental to its principal purpose, since voltage conversion of alternating current is much easier to achieve than frequency conversion. Traditionally, these were electromechanical machines called a motor-generator set. There were also mercury arc rectifiers or vacuum tubes in use. With the advent of solid state electronics, it has become possible to build completely electronic frequency changers. These usually consist of a rectifier stage (producing direct current) which is then inverted to produce AC of the desired frequency. The inverter (electrical), inverter may use thyristors, Integrated gate-commutated thyristor, IGCTs or Insulated-gate bipolar transistor, IGBTs. If voltage conversion is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparse Matrix Converter
The Sparse Matrix Converter is an AC/AC converter A solid-state AC-to-AC converter converts an AC waveform to another AC waveform, where the output voltage and frequency can be set arbitrarily. Categories Referring to Fig 1, AC-AC converters can be categorized as follows: * Indirect AC-AC (or ... which offers a reduced number of components, a low-complexity modulation scheme, and low realization effort. Invented in 2001 by Prof Johann W. Kolar , sparse matrix converters avoid the multi step commutation procedure of the conventional matrix converter, improving system reliability in industrial operations. Its principal application is in highly compact integrated AC drives. Characteristics *Quasi-Direct AC-AC conversion with no DC link energy storage elements *Sinusoidal input current in phase with mains voltage *Zero DC link current commutation scheme resulting in lower modulation complexity and very high reliability *Low complexity of power circuit / power modules available * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix Converters
Matrix (: matrices or matrixes) or MATRIX may refer to: Science and mathematics * Matrix (mathematics), a rectangular array of numbers, symbols or expressions * Matrix (logic), part of a formula in prenex normal form * Matrix (biology), the material in between a eukaryotic organism's cells * Matrix (chemical analysis), the non-analyte components of a sample * Matrix (geology), the fine-grained material in which larger objects are embedded * Matrix (composite), the constituent of a composite material * Hair matrix, produces hair * Nail matrix, part of the nail in anatomy Technology * Matrix (mass spectrometry), a compound that promotes the formation of ions * Matrix (numismatics), a tool used in coin manufacturing * Matrix (printing), a mould for casting letters * Matrix (protocol), an open standard for real-time communication * Matrix (record production), or master, a disc used in the production of phonograph records ** Matrix number, of a gramophone record * Diode matrix, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indirect Matrix Converter
Indirect, the opposite of direct, may refer to: *Indirect approach, a battle strategy *Indirect DNA damage, caused by UV-photons *Indirect agonist or indirect-acting agonist, a substance that enhances the release or action of an endogenous neurotransmitter *Indirect speech, a form of speech *Indirect costs, costs that are not directly accountable to a particular function or product *Indirect self-reference, describes an object referring to itself indirectly *Indirect effect, a principle of European Community Law *Indirect finance, where borrowers borrow funds from the financial market through indirect means *Indirection In computer programming, an indirection (also called a reference) is a way of referring to something using a name, reference, or container instead of the value itself. The most common form of indirection is the act of manipulating a value through ..., the ability to reference something in computer programming * Indirect transmission, infections passing from one hos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Matrix Converter
A solid-state AC-to-AC converter converts an AC waveform to another AC waveform, where the output voltage and frequency can be set arbitrarily. Categories Referring to Fig 1, AC-AC converters can be categorized as follows: * Indirect AC-AC (or AC/DC-AC) converters (i.e., with rectifier, DC link and inverter), such as those used in variable frequency drives * Cycloconverters * Hybrid matrix converters * Matrix converters (MC) * AC voltage controllers DC link converters There are two types of converters with DC link: * Voltage-source inverter (VSI) converters (Fig. 2): In VSI converters, the rectifier consists of a diode-bridge and the DC link consists of a shunt capacitor. * Current-source inverter (CSI) converters (Fig. 3): In CSI converters, the rectifier consists of a phase-controlled switching device bridge and the DC link consists of 1 or 2 series inductors between one or both legs of the connection between rectifier and inverter. Any dynamic braking operation required ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel ( aggregate) together. Cement mixed with fine aggregate produces mortar for masonry, or with sand and gravel, produces concrete. Concrete is the most widely used material in existence and is behind only water as the planet's most-consumed resource. Cements used in construction are usually inorganic, often lime- or calcium silicate-based, and are either hydraulic or less commonly non-hydraulic, depending on the ability of the cement to set in the presence of water (see hydraulic and non-hydraulic lime plaster). Hydraulic cements (e.g., Portland cement) set and become adhesive through a chemical reaction between the dry ingredients and water. The chemical reaction results in mineral hydrates that are not very water-soluble. This allows setting in wet conditions or u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
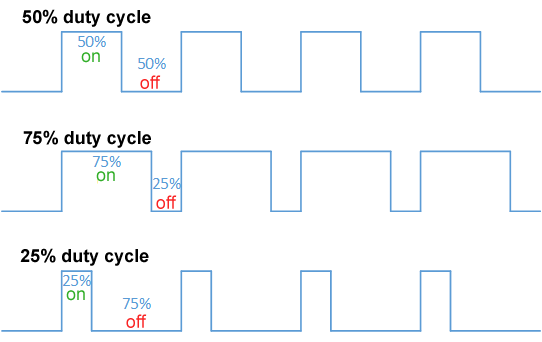
Pulse-width Modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), also known as pulse-duration modulation (PDM) or pulse-length modulation (PLM), is any method of representing a signal as a rectangular wave with a varying duty cycle (and for some methods also a varying period). PWM is useful for controlling the average power or amplitude delivered by an electrical signal. The average value of voltage (and current) fed to the load is controlled by switching the supply between 0 and 100% at a rate faster than it takes the load to change significantly. The longer the switch is on, the higher the total power supplied to the load. Along with maximum power point tracking (MPPT), it is one of the primary methods of controlling the output of solar panels to that which can be utilized by a battery. PWM is particularly suited for running inertial loads such as motors, which are not as easily affected by this discrete switching. The goal of PWM is to control a load; however, the PWM switching frequency must be sele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waveform
In electronics, acoustics, and related fields, the waveform of a signal is the shape of its Graph of a function, graph as a function of time, independent of its time and Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude Scale (ratio), scales and of any displacement in time.David Crecraft, David Gorham, ''Electronics'', 2nd ed., , CRC Press, 2002, p. 62 ''Periodic waveforms'' repeat regularly at a constant wave period, period. The term can also be used for non-periodic or aperiodic signals, like chirps and pulse (signal processing), pulses. In electronics, the term is usually applied to time-varying voltages, electric current, currents, or electromagnetic fields. In acoustics, it is usually applied to steady periodic sounds — variations of air pressure, pressure in air or other media. In these cases, the waveform is an attribute that is independent of the frequency, amplitude, or phase shift of the signal. The waveform of an electrical signal can be visualized with an oscilloscope or an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braking Chopper
Braking choppers, sometimes also referred to as Braking units, are used in the DC voltage intermediate circuits of frequency converters to control voltage when the load feeds energy back to the intermediate circuit. This arises, for example, when a magnetized Electric motor, motor is being rotated by an overhauling load and so functions as a Electrical generator, generator feeding power to the DC voltage intermediate circuit.R. Krishnan, 2001 "Electric Motor Drives: Modeling, Analysis, and Control", Prentice Hall They are an application of the chopper (electronics), chopper principle, using the on-off control of a switching device. Operation A braking chopper is an magnetical switch that limits the DC bus voltage by switching the braking energy to a resistor where the braking energy is converted to heat. Braking choppers are automatically activated when the actual DC bus voltage exceeds a specified level depending on the nominal voltage of the variable-frequency drive Benefits * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |