|
A62 Road (England)
The A62 road in Northern England runs between the cities of Leeds in West Yorkshire and Manchester in Greater Manchester covering a distance of . It passes through Heckmondwike, Huddersfield, Failsworth and Oldham. Route The A62 begins at a junction with the A58 road as Gelderd Road in Leeds. It runs through West Yorkshire, passing through Birstall, West Yorkshire, Birstall, Heckmondwike, Liversedge, Huddersfield, Linthwaite, Slaithwaite, and Marsden, West Yorkshire, Marsden. It crosses the Pennines at Standedge, and continues through Saddleworth and into Oldham. From there, the A62 runs into Manchester as Oldham Street and Oldham Road through Failsworth, ending at the Manchester Inner Ring Road. History It is paralleled at some distance by part of the M62 motorway, M62 Trans-Pennine motorway. Before the M62 was built, the A62 was the main trans-Pennine road between Oldham and Huddersfield. The M62 is numbered after the A62 and now takes most of the long-distance traffic betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A62 Road Map
A6, A 6 or A-6 can refer to: Arts and entertainment *A6, a mutated flu virus in the short story " Night Surf" by Stephen King *A-6, a renamed version of the US Security Group in the 1997 comic book movie '' Spawn'' Electronics and software *A6 record, a type of DNS record * Apple A6, a System-on-a-chip ARM processor *Hanlin eReader A6, an ebook reader *Samsung Galaxy A6, a smartphone by Samsung Military *A6, the designation for air force headquarters staff concerned with signals, communications, or information technology **In the United Kingdom, the A6 Air CIS (Computers & Information Systems) branch, also known as JFACHQ, UK Joint Force Air Component Headquarters *A 6, a Swedish artillery regiment * Grumman A-6 Intruder, a twin-engine, mid-wing all-weather US Navy medium attack aircraft manufactured by Grumman, in service from 1962 to 1997 Science and technology Biology *British NVC community A6 (Ceratophyllum submersum community), a British Isles plants community *Noradrenergi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linthwaite
Linthwaite (known as ''Linfit'' in the local community) is a village in Kirklees, West Yorkshire, England. Historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire, it is situated west of Huddersfield, on the A62 in the Colne Valley. The village together with Blackmoorfoot had a population of 3,835 according to the 2001 census. The River Colne, Huddersfield Narrow Canal, the Huddersfield to Manchester railway line and A62 main road all pass near to the village. After they were constructed, textile mills were then built to produce cloth making use of the river. This led to the growth of the village. Linthwaite Hall on Linfit Fold was built around 1600. Currently, it is a busy village with five pubs, including the Sair Inn, a traditional pub, formerly known as the 'New Inn' and now one of the few 'own brew' pubs still in the country. It won the CAMRA National Pub of the Year Award in 1997. Linthwaite is believed to be given where the surname Dyson started in 1316. Blackmoorfoot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roads In England
The United Kingdom has a network of roads, of varied quality and capacity, totalling about . Road distances are shown in miles or yards and UK speed limits are indicated in miles per hour (mph) or by the use of the national speed limit (NSL) symbol. Some vehicle categories have various lower maximum limits enforced by speed limiters. A unified numbering system is in place for Great Britain, whilst in Northern Ireland, there is no available explanation for the allocation of road numbers. The earliest specifically engineered roads were built during the British Iron Age. The road network was expanded during the Roman occupation. Some of these roads still remain to this day. New roads were added in the Middle Ages and from the 17th century onwards. Whilst control has been transferred between local and central bodies, current management and development of the road network is shared between local authorities, the devolved administrations of Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport In Manchester
The transport infrastructure of Greater Manchester is built up of numerous transport modes and forms an integral part of the structure of Greater Manchester and North West England – the most populated region outside of South East England which had approximately 301 million annual passenger journeys using either buses, planes, trains or trams in 2014. Its position as a national city of commerce, education and cultural importance means the city has one of the largest and most thorough transport infrastructures which is heavily relied upon by its 2.8 million inhabitants in the Greater Manchester conurbation and further afield in the North West region. Public transport comes under the jurisdiction of Transport for Greater Manchester. Greater Manchester has a higher percentage of the motorway network than any other county. According to the ''Guinness Book of World Records'', it has the most traffic lanes side by side (17), spread across several parallel carriageways – the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M62 Motorway
The M62 is a west–east trans-Pennine motorway in Northern England, connecting Liverpool and Hull via Manchester, Bradford, Leeds and Wakefield; of the route is shared with the M60 orbital motorway around Manchester. The road is part of the unsigned Euroroutes E20 ( Shannon to Saint Petersburg) and E22 ( Holyhead to Ishim). The motorway, which was first proposed in the 1930s, and conceived as two separate routes, was opened in stages between 1971 and 1976, with construction beginning at Pole Moor near Huddersfield and finishing at that time in Tarbock on the outskirts of Liverpool. The motorway absorbed the northern end of the Stretford- Eccles bypass, which was built between 1957 and 1960. Adjusted for inflation to 2007, its construction cost approximately £765 million. The motorway has an average daily traffic flow of 144,000 vehicles in West Yorkshire, and has several sections prone to gridlock, in particular, between Leeds and Huddersfield and the M60 secti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester Inner Ring Road
Manchester and Salford Inner Relief Route is a ring road in Greater Manchester, England. It is the product of the amalgamation of several major roads around Manchester and Salford city centres to form a circular route. It was completed in 2004 with the opening of a final section to Trinity Way. A major component of the ring road is the Mancunian Way motorway to the south of Manchester city centre. When it was built, it was planned to be the first of many such inner-city elevated roads. The road is a pivotal part of the ring road for east–west traffic across the southern part of the city centre. The principal section of Trinity Way opened in 1987 easing congestion on Deansgate and opening a route north-west of the city centre. Improvements were made to Great Ancoats Street, north-east of the city centre, making it mostly dual carriageway. Great Ancoats Street (to the north and east), Trinity Way (to the north and west) and the Mancunian Way (to the south) almost formed a cir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oldham Street
Oldham Street is in Manchester city centre and forms part of the city's historic Northern Quarter district. The Northern Quarter is dominated by buildings that were built before World War II. The street runs from Piccadilly to Great Ancoats Street on the edge of Ancoats, beyond which it continues northwards as Oldham Road, the A62. The street is part of Manchester which is on a tentative list as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The Methodist Central Hall stands on the east side. Retrieved 2011-04-17. Until the 1970s Oldham Street formed one of the principal shopping areas of Manchester city centre. However the construction of the large indoor [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saddleworth
Saddleworth is a civil parish of the Metropolitan Borough of Oldham in Greater Manchester, England. It comprises several villages and hamlets as well as suburbs of Oldham on the west side of the Pennine hills. Areas include Austerlands, Delph, Denshaw, Diggle, Dobcross, Friezland, Grasscroft, Greenfield, Grotton, Lydgate, Scouthead, Springhead and Uppermill. Saddleworth lies east of Oldham and northeast of Manchester. It is broadly rural and had a population of 25,460 at the 2011 Census, making it one of the larger civil parishes in the United Kingdom. Historically in the West Riding of Yorkshire and following the Industrial Revolution, in the 18th and 19th centuries, Saddleworth became a centre for cotton spinning and weaving. By the end of Queen Victoria's reign, mechanised textile production had become a vital part of the local economy. The Royal George Mill, owned by the Whitehead family, manufactured felt used for pianofortes, billiard tables and flags. Foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standedge
Standedge () is a moorland escarpment in the Pennine Hills of northern England between Marsden, West Yorkshire and Diggle, Greater Manchester. Standedge has been a major moorland crossing point since Roman times and possibly earlier. From east to west, Standedge is crossed by five generations of road crossing, the earliest a Roman road from York to Chester and the latest the A62 road. The Huddersfield Narrow Canal and the railway line from Leeds to Manchester pass underground in the Standedge Tunnels. The Pennine Way long-distance footpath passes through Standedge in a north–south direction along the Pennines. Much of Standedge is in the National Trust's Marsden Moor Estate. Administratively, Standedge is split between Kirklees and Oldham. Surface crossings The earliest known crossing of Standedge is the Roman road connecting the Roman forts at Slack and Castleshaw, on the way from York to Chester. The road is believed to have been built in AD 80. Its course was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
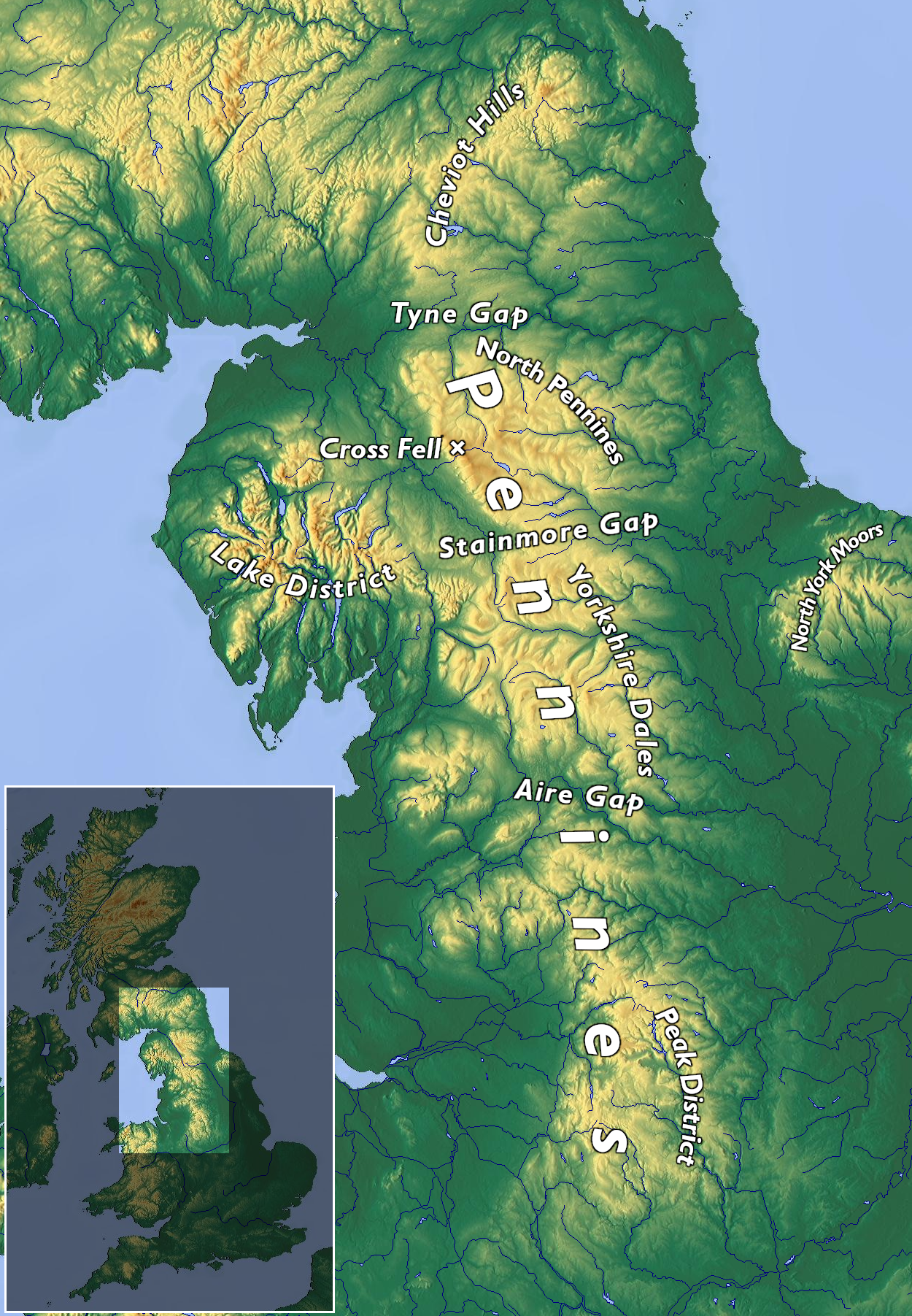
Pennines
The Pennines (), also known as the Pennine Chain or Pennine Hills, are a range of uplands running between three regions of Northern England: North West England on the west, North East England and Yorkshire and the Humber on the east. Commonly described as the " backbone of England", the range stretches northwards from the Peak District at the southern end, through the South Pennines, Yorkshire Dales and North Pennines to the Tyne Gap, which separates the range from the Border Moors and Cheviot Hills across the Anglo-Scottish border, although some definitions include them. South of the Aire Gap is a western spur into east Lancashire, comprising the Rossendale Fells, West Pennine Moors and the Bowland Fells in North Lancashire. The Howgill Fells and Orton Fells in Cumbria are sometimes considered to be Pennine spurs to the west of the range. The Pennines are an important water catchment area with numerous reservoirs in the head streams of the river valleys. The North Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsden, West Yorkshire
Marsden is a large village in the Metropolitan Borough of Kirklees, West Yorkshire, England. It is in the South Pennines close to the Peak District which lies to the south. The village is west of Huddersfield at the confluence of the River Colne and Wessenden Brook. It was an important centre for the production of woollen cloth. In 2020, the village had an estimated population of 3,768. History Marsden grew wealthy in the 19th century from the production of woollen cloth. It is still home to Bank Bottom Mill, later known as Marsden Mill, and home to John Edward Crowther Ltd, formerly one of the largest mills in Yorkshire. The Crowthers moved to Marsden in 1876, beginning a long and profitable association with cloth manufacturing in the town. During the 1930s Bank Bottom Mill covered an area of 14 acres, employed 680 looms, and provided employment for 1,900 workers. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slaithwaite
Slaithwaite , locally ''Slawit'' (Old Norse: Timber-fell clearing), is a village within the Metropolitan Borough of Kirklees, in West Yorkshire, England. Historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire, it lies in the Colne Valley, lying across the River Colne and the Huddersfield Narrow Canal, approximately south-west of Huddersfield. The village has two primary schools; Slaithwaite Church of England School on Holme Lane and Nields Junior, Infant and Nursery School on Nields Road. There is also a small primary school in the nearby hamlet of Wilberlee. The village is serviced by the local Secondary School, Colne Valley High School in Linthwaite approximately 2.5 miles away. The village was voted the best place to live in the North & Northeast in The Times 2022 Best Places To Live annual guide. History Between 1195 and 1205, Roger de Laci, Constable of Chester, gave the manor of Slaithwaite to Henry Teutonicus (Lord Tyas). It remained in the Tyas family until the end o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
