|
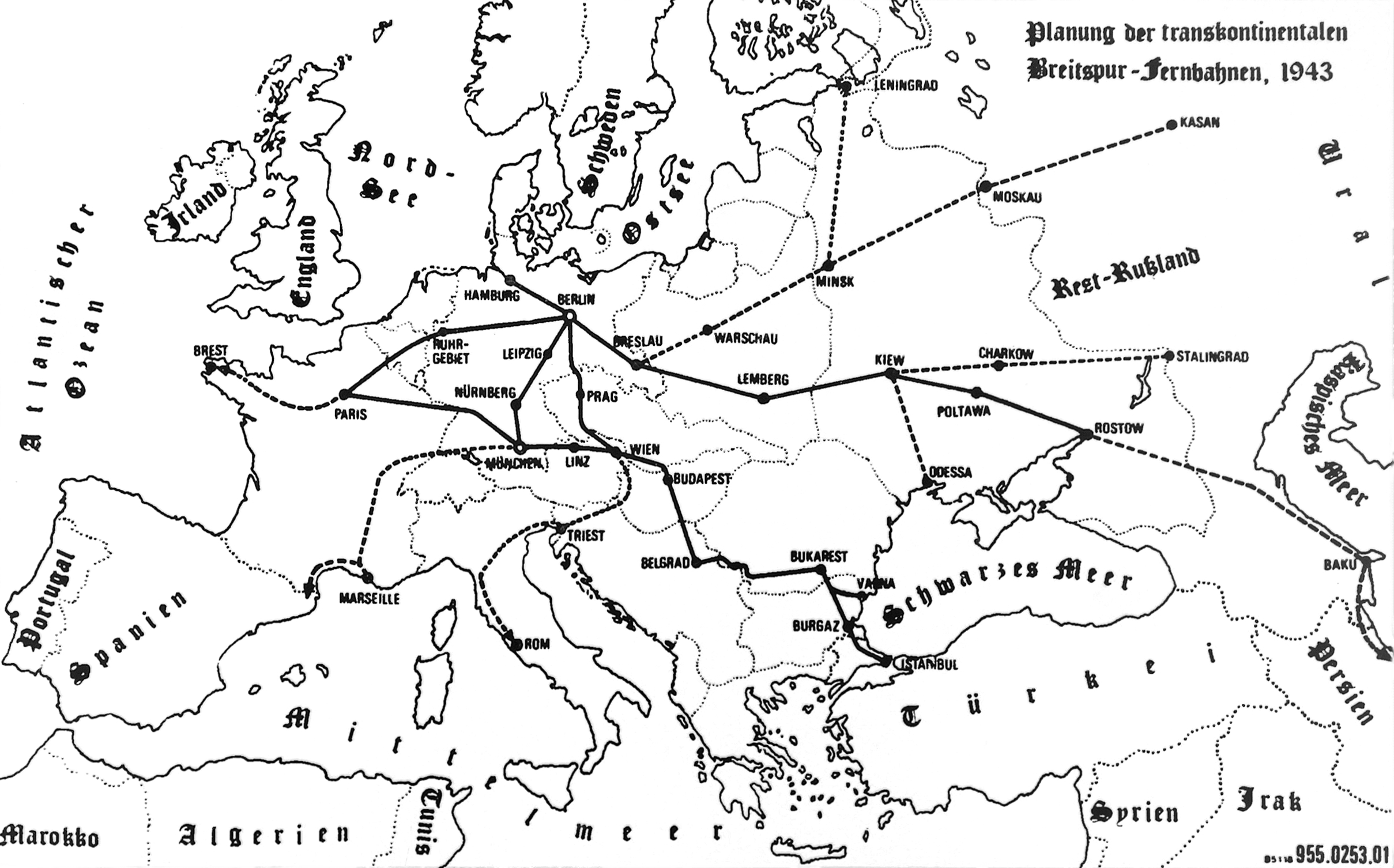
A-A Line
The Arkhangelsk–Astrakhan line, or A–A line for short, was the military goal of Operation Barbarossa. It is also known as the Volga–Arkhangelsk line, as well as (more rarely) the Volga–Arkhangelsk–Astrakhan line. It was first mentioned on 18 December 1940 in ''Führer'' Directive 21 () which enunciated the set goals and conditions of the German invasion of the Soviet Union, describing the attainment of the "general line Volga–Archangelsk" as its overall military objective.. Background The line had its origins in an earlier military study carried out in the summer of 1940 by General Erich Marcks called the ''Operation Draft East''.Kay, Alex J. (2006). Exploitation, Resettlement, Mass Murder: Political and Economic Planning for German Occupation Policy in the Soviet Union, 1940-1941"p. 31 Berghahn Books. This report advocated the occupation of the Soviet Union up to the line "Arkhangelsk- Gorky- Rostov" in order to prevent it from being a threat to Germany in the futu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the German Army (1935–1945), ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previously used term (''Reich Defence'') and was the manifestation of the Nazi regime's efforts to German rearmament, rearm Germany to a greater extent than the Treaty of Versailles permitted. After the Adolf Hitler's rise to power, Nazi rise to power in 1933, one of Adolf Hitler's most overt and bellicose moves was to establish the ''Wehrmacht'', a modern offensively-capable armed force, fulfilling the Nazi regime's long-term goals of regaining lost territory as well as gaining new territory and dominating its neighbours. This required the reinstatement of conscription and massive investment and Military budget, defence spending on the arms industry. The ''Wehrmacht'' formed the heart of Germany's politico-military po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1940 In Germany
Events in the year 1940 in Germany. Incumbents National level Head of State and Chancellor * Adolf Hitler (the Führer) (Nazi Party) Events January * 4 January – World War II: (Axis powers): Luftwaffe General Hermann Göring assumes control of most war industries in Germany. * 10 January – World War II: Mechelen Incident: A German plane carrying secret plans for the invasion of western Europe makes a forced landing in Belgium, leading to mobilization of defense forces in the Low Countries. February * 16 February – World War II: Altmark Incident: The British destroyer pursues the German tanker ''Altmark'' into Jøssingfjord in southwestern Norway. March * 18 March – World War II: Axis powers: Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini meet at Brenner Pass in the Alps and agree to form an alliance against France and the United Kingdom. * 31 March – World War II: Commerce raiding ''hilfskreuzer Atlantis'', leaves the Wadden Sea for what will become the longest warship cruis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1940 In The Soviet Union
Year 194 ( CXCIV) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Septimius and Septimius (or, less frequently, year 947 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 194 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Decimus Clodius Septimius Albinus Caesar became a Roman Consul. * Battle of Issus: Septimius Severus marches with his army (12 legions) to Cilicia, and defeats Pescennius Niger, Roman governor of Syria. Pescennius retreats to Antioch, and is executed by Severus' troops. * Septimius Severus besieges Byzantium (194–196); the city walls suffer extensive damage. Asia * Battle of Yan Province: Warlords Cao Cao and Lü Bu fight for control over Yan Province; the battle lasts for over 100 days. * First year of the ''Xingping'' era during the Han Dynast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrbauer
''Wehrbauer'' (, ''defensive peasant''), plural ''Wehrbauern'', is a German term for settlers living on the marches of a realm who were tasked with holding back foreign invaders until the arrival of proper military reinforcements. In turn, they were granted special liberties. ''Wehrbauern'' in their settlements, known as ''Wehrsiedlungen'' (-en being the plural suffix), were mainly used on the eastern fringes of the Holy Roman Empire and later Austria-Hungary to slow attacks by the Ottoman Empire. This historic term was resurrected and used by the Nazis during the Second World War. Etymology The Habsburg use of "''Wehrbauern''" was the Military Frontier, which was established by Ferdinand I in the 16th century and placed under the jurisdiction of the Croatian Sabor and Croatian Ban since it was carved out of Croatian territory. It acted as a ''cordon sanitaire'' against Ottoman incursions. By the 19th century, it was rendered all but obsolete by the establishment of standi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of The Eastern Front Of World War II
The Eastern Front was a theatre of World War II which primarily involved combat between the nations and allies of Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union. Combat in the Eastern Front began with the two powers remaining peaceful towards each other, with the annexation of countries such as Albania and portions of Poland by Germany and its allies, and the annexation of Finland and the rest of Poland by the Soviet Union. However, in 1941, Nazi Germany invaded the Soviet Union, putting an end to the peacetime. The majority of major battles in the Eastern Theatre from 1941 until the end of the war in 1945 were fought between the two powers. The following timeline indicates major events taking place on the Eastern Front. 1939 * March 14–15: Under German pressure, the Slovaks declare their independence and form a Slovak Republic. The Germans occupy the dismantled Czech lands in violation of the Munich agreement and form the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia. * March 31: France and Great Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generalplan Ost
The (; ), abbreviated GPO, was Nazi Germany's plan for the settlement and "Germanization" of captured territory in Eastern Europe, involving the genocide, extermination and large-scale ethnic cleansing of Slavs, Eastern European Jews, and other indigenous peoples of Eastern Europe categorized as "'' Untermenschen''" in Nazi ideology. The campaign was a precursor to Nazi Germany's planned colonisation of Central and Eastern Europe by Germanic settlers, and it was carried out through systematic massacres, mass starvations, chattel labour, mass rapes, child abductions, and sexual slavery. ''Generalplan Ost'' was only partially implemented during the war in territories occupied by Germany on the Eastern Front during World War II, resulting indirectly and directly in the deaths of millions by shootings, starvation, disease, extermination through labour, and genocide. However, its full implementation was not considered practicable during major military operations, and neve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axis Powers Negotiations On The Division Of Asia
As the Axis powers of Germany, Italy, and Japan cemented their military alliance by mutually declaring war against the United States on December 11, 1941, the Japanese proposed a clear territorial arrangement with the two main European Axis powers concerning the Asian continent.Rich, Norman (1973). ''Hitler's War Aims: Ideology, the Nazi State, and the Course of Expansion''. W.W. Norton & Company Inc., p. 235 On December 15, they presented the Germans with a drafted military convention that would delimit the continent of Asia into two separate "operational spheres" (zones of military responsibility) by a dividing line along the 70th meridian east longitude, going southwards through the Ob River's Arctic estuary, southwards to just east of Khost in Afghanistan and heading into the Indian Ocean just west of Rajkot in India, to split the ''Lebensraum'' land holdings of Germany and the similar '' spazio vitale'' areas of Italy to the west of it, and the Empire of Japan (and the Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Air Fleets In World War II
A list of ''Luftwaffe "Luftflotten"'' (Air Fleets) and their locations between 1939 and 1945. Timeline ImageSize = width:580 height:auto barincrement:20 PlotArea = left:80 bottom:60 top:10 right:40 AlignBars = early DateFormat = dd/mm/yyyy # European date format Period = from:01/01/1939 till:08/05/1945 # TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:1 start:01/01/1939 ScaleMinor = grid:blue unit:month increment:3 start:01/01/1939 PlotData= color:red width:10 bar:Luftflotte1 from:01/02/1939 till:08/05/1945 text: Luftflotte 1 bar:Luftflotte2 from:01/02/1939 till:29/09/1944 text: Luftflotte 2 bar:Luftflotte3 from:01/02/1939 till:26/09/1944 text: Luftflotte 3 bar:Luftflotte4 from:18/03/1939 till:21/04/1945 text: Luftflotte 4 bar:Luftflotte5 from:12/04/1940 till:08/05/1945 text: Luftflotte 5 bar:Luftflotte6 from:05/05/1943 till: 08/05/1945 text: Luftflotte 6 bar:LuftflotteReich from:05/02/1944 till: 08/05/1945 te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ural Bomber
The Ural bomber was the initial aircraft design program/competition to develop a long-range bomber for the Luftwaffe, created and led by General Walther Wever in the early 1930s. Wever died in an air crash on June 3, 1936, and his successor Albert Kesselring continued the project until he left office. Wever, the chief of staff of the newly formed Luftwaffe in 1933, realized the importance that strategic bombing would play in a war. In a war with the Soviet Union, he expected that German forces would not attempt to move very far east of Moscow, which would leave much of Joseph Stalin's recently relocated industry out of reach of existing bombers. Wever proposed using a strategic bomber to target those factories, hampering the Soviet ability to fight, without the need for ground forces to advance. Development Under the Ural bomber program, he engaged in secret talks with Dornier and Junkers, requesting designs for a long-range bomber. They responded with the Dornier Do 19 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have conventionally been considered as a natural barrier between Europe and Asia, bisecting the Eurasian landmass. Mount Elbrus, Europe's highest mountain, is situated in the Western Caucasus area of Russia. On the southern side, the Lesser Caucasus includes the Javakheti Plateau and the Armenian highlands. The Caucasus is divided into the North Caucasus and South Caucasus, although the Western Caucasus also exists as a distinct geographic space within the North Caucasus. The Greater Caucasus mountain range in the north is mostly shared by Russia and Georgia as well as the northernmost parts of Azerbaijan. The Lesser Caucasus mountain range in the south is mostly located on the territory of sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |