|
807
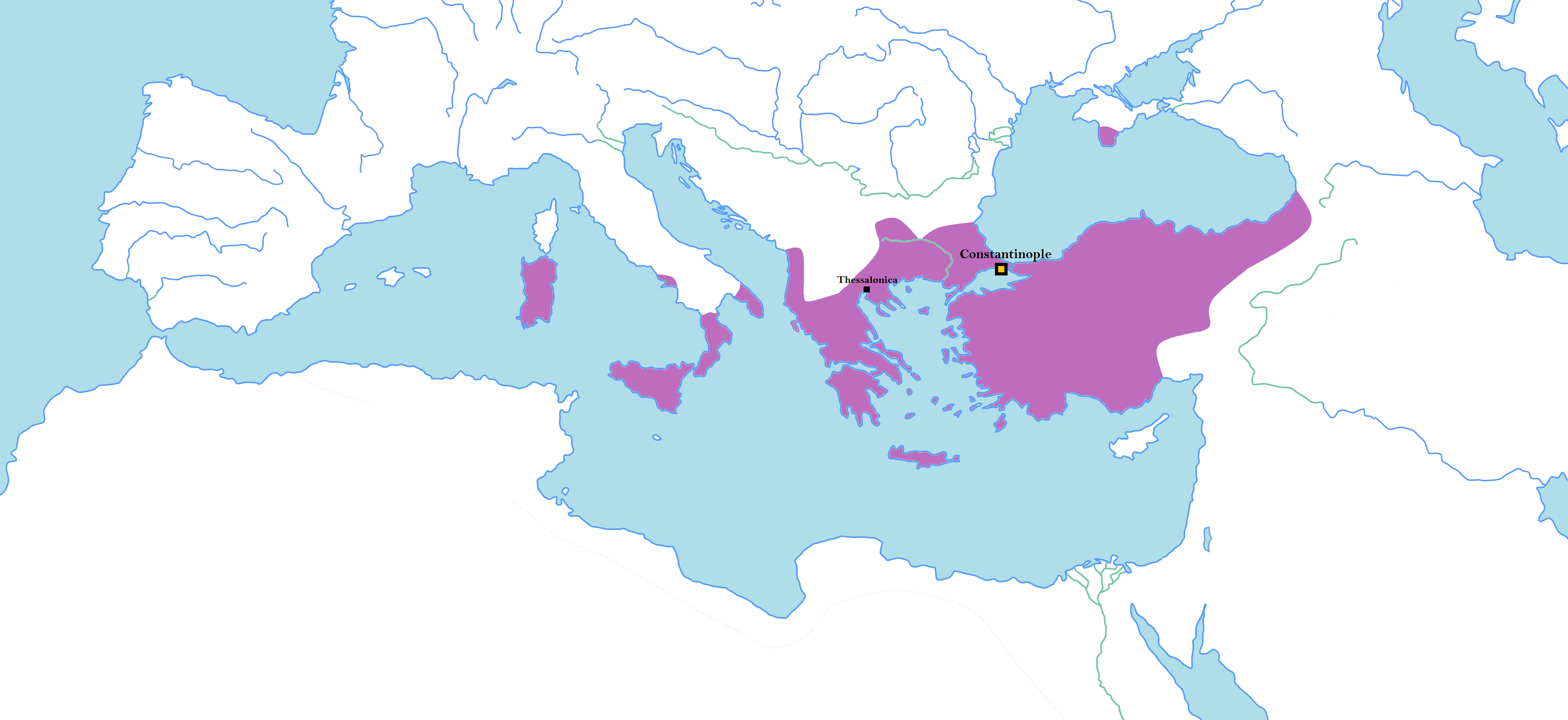
__NOTOC__ Year 807 ( DCCCVII) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar, the 807th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 807th year of the 1st millennium, the 7th year of the 9th century, and the 8th year of the 800s decade. Events By place Abbasid Empire and Byzantine Empire * Emperor Nikephoros I is forced to sue for peace, on condition of paying 50,000 ''nomismata'' to Caliph Harun al-Rashid, and agrees to a yearly tribute. Nikephoros promises not to rebuild the dismantled forts. Rashid recalls his forces from various sieges, and evacuates Byzantine territory.. * An Abbasid fleet under Humayd ibn Ma'yuf al-Hajuri raids the Peloponnese, Rhodes and Myra. Europe * Al-Andalus (modern Spain): An uprising occurs in the city of Mérida against the Umayyad Emirate of Córdoba. * Siege of Patras: This marks the end of independent rule by the South Slavs in the Peloponnese (or 805). Britain * The Vikings land on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Europe and the fourth-most populous European Union member state. Spanning across the majority of the Iberian Peninsula, its territory also includes the Canary Islands, in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands, in the Western Mediterranean Sea, and the Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, in mainland Africa. Peninsular Spain is bordered to the north by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; to the east and south by the Mediterranean Sea and Gibraltar; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Spain's capital and List of largest cities in Spain, largest city is Madrid, and other major List of metropolitan areas in Spain, urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Patras (805 Or 807)
The siege of Patras in 805 or 807 was undertaken by the local Slavic tribes of the Peloponnese, reportedly with aid from an Arab fleet. The siege's failure, attributed to the miraculous intervention of the city's patron, Saint Andrew, marked the consolidation of Byzantine control over the Peloponnese peninsula after two centuries of Slavic occupation over its western half. It also marked the beginning of the ascendancy of the Metropolis of Patras in the peninsula's ecclesiastical affairs. Background The Byzantine Empire's military position in the Balkans collapsed in the early 7th century as a result of disastrous military ventures against the Persians and then the Arabs in the East, which forced the effective abandonment of the Danube '' limes'' and opened the way for large-scale penetration and settlement of the Balkan hinterland by various Slavic tribes. The Slavs raided as far as southern Greece and the coasts of Asia Minor. Most of the region's cities were sacked or aband ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of lands which the state conquered. In the case of alliances, lesser parties may pay tribute to more powerful parties as a sign of allegiance. Tributes are different from taxes, as they are not collected in the same regularly routine manner that taxes are. Further, with tributes, a recognition of political submission by the payer to the payee is uniquely required. Overview The Aztec Empire is another example, as it received tribute from the various city-states and provinces that it conquered. Ancient China received tribute from various states such as Japan, Korea, Vietnam, Cambodia, Borneo, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Myanmar and Central Asia. Aztec Empire Tributes as a form of government The Aztecs used tributes as a means for maintaining control over con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 Common Era, CE), from whom the Abbasid dynasty, dynasty takes its name. After overthrowing the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 anno Hegirae, AH), they ruled as caliphs based in modern-day Iraq, with Baghdad being their capital for most of their history. The Abbasid Revolution had its origins and first successes in the easterly region of Greater Khorasan, Khurasan, far from the Levantine center of Umayyad influence. The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad as the new capital. Baghdad became the center of Science in the medieval Islamic world, science, Islamic culture, culture, Abbasid art, arts, and List of invent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most of the peninsula as well as Septimania under Umayyad rule. These boundaries changed through a series of conquests Western historiography has traditionally characterized as the ''Reconquista'',"Para los autores árabes medievales, el término Al-Andalus designa la totalidad de las zonas conquistadas – siquiera temporalmente – por tropas arabo-musulmanas en territorios actualmente pertenecientes a Portugal, España y Francia" ("For medieval Arab authors, Al-Andalus designated all the conquered areas – even temporarily – by Arab-Muslim troops in territories now belonging to Spain, Portugal and France"), García de Cortázar, José Ángel. ''V Semana de Estudios Medievales: Nájera, 1 al 5 de agosto de 1994'', Gobie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harun Ar-Rashid
Abū Jaʿfar Hārūn ibn Muḥammad ar-Rāshīd (), or simply Hārūn ibn al-Mahdī (; or 766 – 24 March 809), famously known as Hārūn al-Rāshīd (), was the fifth Abbasid caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate, reigning from September 786 until his death in March 809. His reign is traditionally regarded to be the beginning of the Islamic Golden Age. His epithet ''al-Rashid'' translates to "the Just", "the Upright", or "the Rightly-Guided". Harun established the legendary library Bayt al-Hikma ("House of Wisdom") in Baghdad in present-day Iraq, and during his rule Baghdad began to flourish as a world center of knowledge, culture and trade. During his rule, the family of Barmakids, which played a deciding role in establishing the Abbasid Caliphate, declined gradually. In 796, he moved his court and government to Raqqa in present-day Syria. Domestically, Harun pursued policies similar to those of his father Al-Mahdi. He released many of the Umayyads and 'Alids his brother Al-Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros I
Nikephoros I (; 750 – 26 July 811), also known as Nicephorus I, was Byzantine emperor from 802 to 811. He was General Logothete (finance minister) under Empress Irene, but later overthrew her to seize the throne for himself. Prior to becoming emperor, he was sometimes referred to as "the Logothete" () and "Genikos" or "Genicus" (), in recognition of his previous role as General Logothete. During his reign, Nikephoros engaged in military campaigns against both the Arabs and the Bulgarians, although the outcomes were varied. While leading an invasion into Bulgaria, he suffered a defeat and was killed at the Battle of Pliska. Background According to several sources outside the Byzantine context, such as Michael the Syrian, al-Tabari, and Mas'udi, there is a tradition that suggests Nikephoros had Ghassanid Arab origins and that he descended from the final Ghassanid ruler Jabala ibn al-Ayham. Al-Tabari assets that he obtained this information from Byzantine sources, althou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vikings
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden), who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9–22. They also voyaged as far as the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean, North Africa, the Middle East, Greenland, and Vinland (present-day Newfoundland in Canada, North America). In their countries of origin, and some of the countries they raided and settled in, this period is popularly known as the Viking Age, and the term "Viking" also commonly includes the inhabitants of the Scandinavian homelands as a whole. The Vikings had a profound impact on the Early Middle Ages, early medieval history of Northern Europe, northern and Eastern Europe, including the political and social development of England (and the English language) and parts of France, and established the embryo of Russia in Kievan Rus'. Expert sailors and navigators of their cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which separates the Gulf of Corinth from the Saronic Gulf. From the late Middle Ages until the 19th century, the peninsula was known as the Morea, a name still in colloquial use in its demotic form. The peninsula is divided among three administrative regions: most belongs to the Peloponnese region, with smaller parts belonging to the West Greece and Attica regions. Geography The Peloponnese is a peninsula located at the southern tip of the mainland, in area, and constitutes the southernmost part of mainland Greece. It is connected to the mainland by the Isthmus of Corinth, where the Corinth Canal was constructed in 1893. However, it is also connected to the mainland by several bridges across the canal, including two submers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Slavs
South Slavs are Slavic people who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, Hungary, Romania, and the Black Sea, the South Slavs today include Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes. In the 20th century, the country of Yugoslavia (from Serbo-Croatian, literally meaning "South Slavia" or "South Slavdom") united a majority of the South Slavic peoples and lands—with the exception of Bulgarians and Bulgaria—into a single state. The Pan-Slavic concept of ''Yugoslavia'' emerged in late 17th-century Croatia, at the time part of the Habsburg monarchy, and gained prominence through the 19th-century Illyrian movement. The Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, renamed the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929, was proclaimed on 1 December 1918, following the unification of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodes
Rhodes (; ) is the largest of the Dodecanese islands of Greece and is their historical capital; it is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, ninth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes (regional unit), Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the South Aegean Administrative regions of Greece, administrative region. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is the Rhodes (city), city of Rhodes, which had 50,636 inhabitants in 2011. In 2022, the island had a population of 125,113 people. It is located northeast of Crete and southeast of Athens. Rhodes has several nicknames, such as "Island of the Sun" due to its patron sun god Helios, "The Pearl Island", and "The Island of the Knights", named after the Knights Hospitaller, Knights of Saint John of Jerusalem, who ruled the island from 1310 to 1522. Historically, Rhodes was famous for the Colossus of Rhodes, one of the Sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emirate Of Córdoba
An emirate is a territory ruled by an emir, a title used by monarchs or high officeholders in the Muslim world. From a historical point of view, an emirate is a political-religious unit smaller than a caliphate. It can be considered equivalent to a principality in non-Muslim contexts. Currently in the world, there are two emirates that are independent states (Kuwait and Qatar), one state ruled by an unrecognised emirate (Afghanistan), and a state that consists of a federation of seven emirates (the United Arab Emirates). A great number of previously independent emirates around the world are now part of larger states. Etymology Etymologically, emirate or amirate ( ' plural: ' is the quality, dignity, office, or territorial competence of any emir (prince, commander, governor, etc.). In English, the term is pronounced or in British English and or in American English. Types Monarchies The United Arab Emirates is a federal state that comprises seven federal emirates, each ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |