|
7K (other)
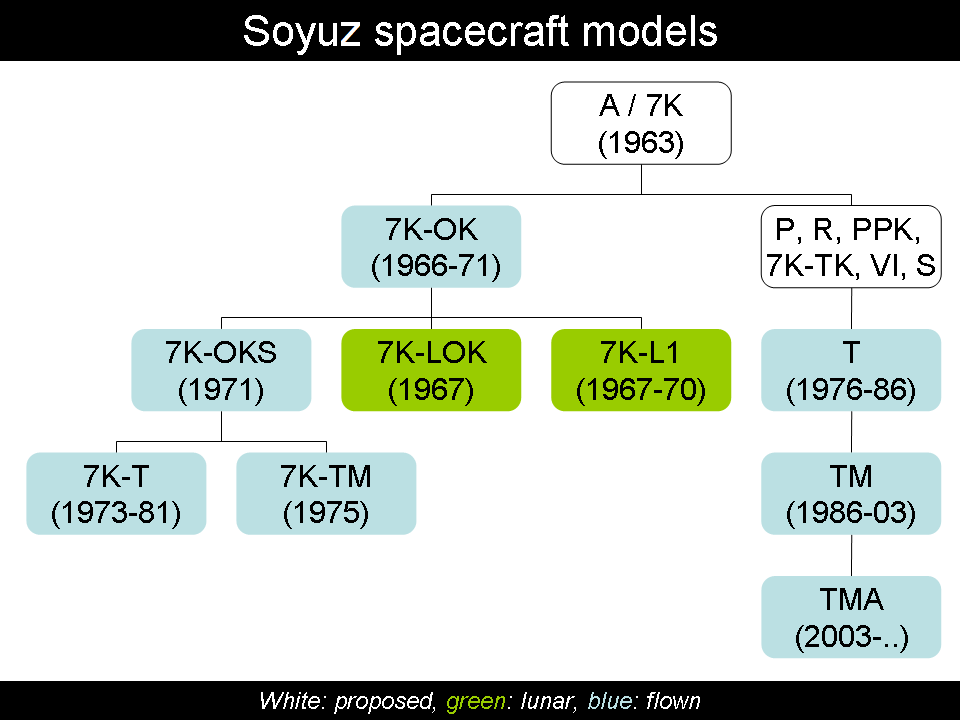
7K or 7-K may refer to: * 7000 (number) * The year 7000, in the 7th millennium *Gnome-Rhône 7K *Soyuz 7K-L1 * Soyuz 7K-L1 No.4L *Soyuz 7K-L1 No.5L *Soyuz 7K-L3 *Soyuz 7K-OK *Soyuz 7K-OKS *Soyuz 7K-T *Progress 7K-TG *Soyuz 7K-TM *A-7K, model of LTV A-7 Corsair II *7K, model of Toyota K engine *7K, the production code for the 1988 ''Doctor Who'' serial ''Silver Nemesis ''Silver Nemesis'' is the third serial of the 25th season of the British science fiction television series ''Doctor Who''. It was first broadcast in the United Kingdom on BBC1 in three weekly parts from 23 November (the 25th anniversary) to 7 ...'' See also * * * 7000 (other) * K7 (other) {{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7000 (number)
7000 (seven thousand) is the natural number following 6999 and preceding 7001. Selected numbers in the range 7001–7999 7001 to 7099 * 7021 – triangular number * 7043 – Sophie Germain prime * 7056 = 842 * 7057 – cuban prime of the form ''x'' = ''y'' + 1, super-prime * 7073 – Leyland number * 7079 – Sophie Germain prime, safe prime 7100 to 7199 * 7103 – Sophie Germain prime, sexy prime with 7109 * 7106 – octahedral number * 7109 – super-prime, sexy prime with 7103 * 7121 – Sophie Germain prime * 7140 – triangular number, also a pronic number and hence = 3570 is also a triangular number, tetrahedral number * 7141 - sum of the first 58 primes, star number * 7151 – Sophie Germain prime * 7155 – number of 19-bead necklaces (turning over is allowed) where complements are equivalent * 7187 – safe prime * 7192 – weird number * 7193 – Sophie Germain prime, super-prime 7200 to 7299 * 7200 – pentagonal pyramidal number * 7211 – Sophie Germain prime * 7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th Millennium
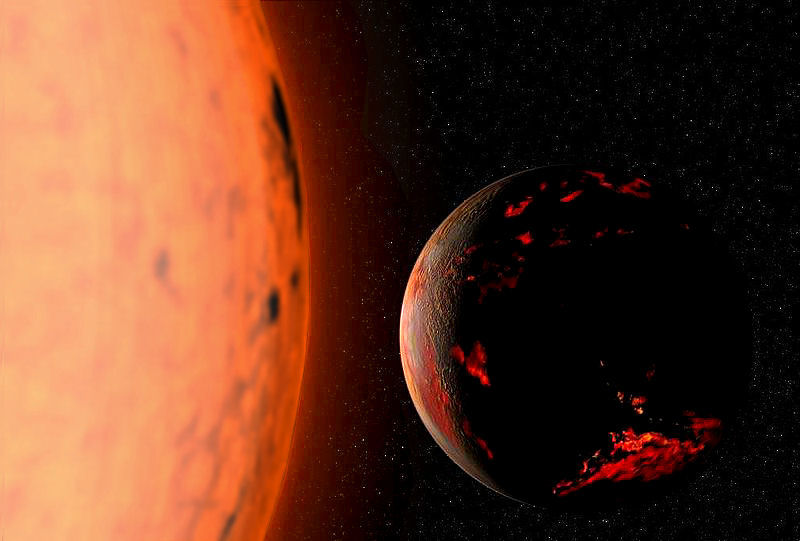
While the future cannot be predicted with certainty, present understanding in various scientific fields allows for the prediction of some far-future events, if only in the broadest outline. These fields include astrophysics, which studies how planets and stars form, interact and die; particle physics, which has revealed how matter behaves at the smallest scales; evolutionary biology, which studies how life evolves over time; plate tectonics, which shows how continents shift over millennia; and sociology, which examines how human societies and cultures evolve. These timelines begin at the start of the 4th millennium in 3001 CE, and continue until the furthest and most remote reaches of future time. They include alternative future events that address unresolved scientific questions, such as whether humans will become extinct, whether the Earth survives when the Sun expands to become a red giant and whether proton decay will be the eventual end of all matter in the universe. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnome-Rhône 7K
The Gnome-Rhône 7K Titan Major was a seven-cylinder 370 hp (270 kW) air-cooled radial engine, that started life as an enlarged Bristol Titan, Gnome-Rhône 5K with two extra cylinders. Development The Gnome-Rhône 5K was itself a licensed version of the Bristol Titan. The 7K is very comparable to the Bristol Neptune seven-cylinder engine since they used the same technology.Gunston 1989, p.74. The 7K was followed by the larger and more powerful nine-cylinder 550 hp (405 kW) Gnome-Rhône 9K Mistral. Gnome-Rhône later responded to the need for a more powerful engine by developing the 7K into a two-row version that became the Gnome-Rhône Mistral Major, Gnome-Rhône14K Mistral Major. Variants ;IAM K7:Licence production in Yugoslavia by Industrija Aeroplanskih Motora- Rakovica (IAM). ;IAR 7K:Licence production in Romania by Industria Aeronautică Română (IAR). Applications Specifications (7Kd) See also References Notes Bibliography * Gunston, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz 7K-L1
Soyuz 7K-L1 "Zond" spacecraft was designed to launch cosmonaut, cosmonauts from the Earth to circle the Moon without going into lunar orbit in the context of the Soviet crewed lunar programs, Soviet crewed Moon-flyby program in the Moon race. It was based on the Soyuz 7K-OK. Several modifications reduced vehicle mass and increased circumlunar capability. The most notable modifications were the replacement of the orbital module with a support cone and a high-gain parabolic antenna, the removal of a reserve parachute, and the addition of the gyro platform and star navigation sensors for the far space navigation. The spacecraft was capable of carrying two cosmonauts. At the start of flight testing, there were serious reliability problems with the new Proton rocket, the 7K-L1, and the Soyuz 7K-OK that the L1 was based on. History Chief Designer Sergei Korolev had originally envisioned a crewed lunar spacecraft launched in pieces by R-7 boosters and assembled in Earth orbit. The de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz 7K-L1 No
Soyuz is a transliteration of the Cyrillic text Союз (Russian and Ukrainian, 'Union'). It can refer to any union, such as a trade union (''profsoyuz'') or the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (Сою́з Сове́тских Социалисти́ческих Респу́блик, ''Soyuz Sovetskikh Sotsialisticheskikh Respublik''). As terminological shorthand "soyuz" by itself was often used interchangeably with each of the slightly longer terms Сове́тский Сою́з (''Sovetskiy Soyuz'', 'Soviet Union'). It was also a shorthand for the citizenry as a whole. Soyuz is also the designated name of various projects the country commissioned during the Space Race. Space program uses * Soyuz programme, a human spaceflight program initiated by the Soviet Union, continued by the Russian Federation * Soyuz (spacecraft), used in that program * Soyuz (rocket), initially used to launch that spacecraft * Soyuz (rocket family), derivatives of that rocket design * Soyuz Launc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz 7K-L3
The Soyuz 7K-LOK, or simply LOK ( meaning "Lunar Orbital Craft") was a Soviet crewed spacecraft designed to take humans from Earth to orbit the Moon, developed in parallel to the 7K-L1. The LOK would carry two cosmonauts, acting as a mother ship for the LK lander which would land one crew member to the surface. It was part of the N1-L3 programme which also included the LK lander and the N1 rocket. Design Like the 7K-OK model, the 7K-LOK was divided into three sections, an ellipsoid Orbital Module, the "headlight"-shaped Descent Module, and a cylindrical equipment module. Like the 7K-OK, the 7K-LOK was capable of physically docking with another spacecraft, but lacked the transfer tunnel used on the Apollo (spacecraft), thus forcing the cosmonaut to make a spacewalk from the 7K-LOK's orbital module to the LK Lander using the new Krechet space suit (the predecessor to the Orlan space suits used today on the International Space Station). Another change to the 7K-LOK was th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz 7K-OK
Soyuz 7K-OK was the first generation of Soyuz spacecraft and was flown between 1967 and 1971. The 7K-OK was used for the first ferry flights to the Salyut space station program, beginning a long history of space station service that continues with the International Space Station (ISS). , the 7K-OK was responsible for the only fatalities of the Soyuz programme, with Soyuz 1 in 1967 (sole crew-member killed by parachute failure) and Soyuz 11 in 1971 (three crew killed by depressurisation during reentry). The first uncrewed automated docking in the history of spaceflight was achieved between 7K-OK spacecraft Kosmos 186 and Kosmos 188 in 1967. Additional firsts include the first docking between two crewed spacecraft ( Soyuz 4 and Soyuz 5), the longest crewed flight involving only one spacecraft (the 18-day flight of Soyuz 9 in 1970), and the first successful transfer of crew to the first space station in the history of space flight ( Soyuz 11 and Salyut 1 in 1971). Descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz 7K-OKS
Soyuz 7K-OKS (also known as Soyuz 7KT-OK) is a version of the Soyuz spacecraft and was the first spacecraft designed for space station flights. Its only crewed flights were conducted in 1971, with Soyuz 10 and Soyuz 11. Design The two craft of the Soyuz 7K-OKS generation were modified from the original Soyuz 7K-OK. The new "probe and drogue" docking mechanism, which was first used by these two missions, featured an internal docking hatch that allowed for the first time internal transfer between Soviet spacecraft. This "probe and drogue" docking mechanism introduced with Soyuz 7K-OKS is still in use today at the International Space Station (ISS). The external toroidal fuel tank, a holdover from the original lunar mission models of the Soyuz, was dropped from the 7K-OKS since it was unneeded for Earth orbital flights. Flights The Soyuz 7K-OKS flew only twice, Soyuz 10 and Soyuz 11. On its maiden flight, the Soyuz 7K-OKS successfully launched into Earth orbit, but faile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz 7K-T
The second generation of the Soyuz spacecraft, the ''Soyuz 7K-T'', comprised Soyuz 12 through Soyuz 40 (1973–1981). In the wake of the Soyuz 11 tragedy, the spacecraft was redesigned to accommodate two cosmonauts who would wear pressure suits at all times during launch, docking, undocking, and reentry. The place of the third cosmonaut was taken by extra life-support systems. Finally, the 7K-T, being intended purely as a space station ferry, had no solar panels, instead sporting two large whip antennas in their place. As a result, it relied on batteries which only provided enough power for two days of standalone flight. The idea was that the Soyuz would recharge while docked with a Salyut space station, but in the event of a docking or other mission failure (which ended up happening on several occasions), the crew was forced to power off everything except communications and life support systems until they could reenter. Two test flights of the 7K-T were conducted prior to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress 7K-TG
Progress 7K-TG (, GRAU index 11F615A15), was a Soviet uncrewed spacecraft used to resupply space stations in low Earth orbit. Forty three flew, delivering cargo to Salyut 6, Salyut 7, and Mir. It was the first version of the Progress spacecraft to fly, and spawned later derivatives including the Progress-M which replaced it, and the later Progress-M1. The Progress 7K-TG spacecraft was derived from the crewed Soyuz 7K-T ferry spacecraft, which had been designed for the Salyut programme. The descent module of the Soyuz spacecraft was replaced with a new section designated ''Otsek Komponentov Dozapravki'', or OKD. This contained fuel tanks and pumps used for refuelling the space station that it docked with. Like the Soyuz 7K-T, the Progress was not equipped with solar panels, and instead relied on batteries for power. Early spacecraft had a design life of 33 days, including three in free flight, and the rest docked with a space station. Later spacecraft flew longer missions, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz 7K-TM
The 1975 Apollo–Soyuz Test Project version of the Soyuz spacecraft (Soyuz 7K-TM) served as a technological bridge to the third generation Soyuz-T (T - транспортный, ''Transportnyi'' meaning transport) spacecraft (1976–1986). The Soyuz ASTP spacecraft was designed for use during the Apollo Soyuz Test Project as Soyuz 19. It featured design changes to increase compatibility with the American craft. The Soyuz ASTP featured new solar panels for increased mission length, an APAS-75 docking mechanism instead of the standard male mechanism, and modifications to the environmental control system to lower the cabin pressure to 0.68 atmospheres (69 kPa) prior to docking with Apollo. The ASTP Soyuz backup craft flew as the Soyuz 22 mission, replacing the docking port with a camera. Missions There are only five spaceflights of the Soyuz 7K-TM spacecraft, mostly in support for the joint US-Soviet Apollo–Soyuz Apollo–Soyuz was the first crewed international Spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LTV A-7 Corsair II
The LTV A-7 Corsair II is an American carrier-capable subsonic light attack aircraft designed and manufactured by Ling-Temco-Vought (LTV). The A-7 was developed during the early 1960s as replacement for the Douglas A-4 Skyhawk. Its design was derived from the Vought F-8 Crusader; in comparison with the F-8, the A-7 is both smaller and restricted to subsonic speeds, its airframe being simpler and cheaper to produce. Following a competitive bid by Vought in response to the United States Navy's (USN) ''VAL'' (Heavier-than-air, Attack, Light) requirement, an initial contract for the type was issued on 8 February 1964. Development was rapid, first flying on 26 September 1965 and entering squadron service with the USN on 1 February 1967; by the end of that year, A-7s were being deployed overseas for the Vietnam War. Initially adopted by USN, the A-7 proved attractive to other services, soon being adopted by the United States Air Force (USAF) and the Air National Guard (ANG) to replac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |