|
760 Naval Air Squadron
760 Naval Air Squadron (760 NAS) is a List of Fleet Air Arm aircraft squadrons, Naval Air Squadron of the Royal Navy's Fleet Air Arm. The squadron first formed in April 1940 as No.1 Fleet Fighter Pool with a variety of aircraft types before standardising in 1941 on the Hawker Sea Hurricane. In this role it disbanded in December 1942. In May 1944 760 NAS briefly reformed as an Anti-Submarine Operational Training Squadron before disbanding into 766 Naval Air Squadron in November. Reformed again as part of No.1 Naval Air Fighter School in April 1945 it converted fighter pilots to the Vought Corsair and then the Supermarine Seafire until 23 January 1946 when it disbanded. 760 Squadron reformed in 1989 at the Air Engineering School at RNAS Lee-on-Solent (HMS ''Daedalus''), providing air engineering training for officers and ratings using old airframes. The school moved to HMS ''Sultan'' at Gosport in 1995. It continues as the Engineering Training Squadron of the Royal Navy Air Enginee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
760 Naval Air Squadron Badge
76 or Seventy-Six may refer to: Common uses * 76 (number) * one of the years 76 BC, AD 76, 1976, 2076 Places * Seventy Six, Kentucky * Seventy-Six, Missouri * Seventy-Six Township, Iowa (other), several places Arts, entertainment, and media * Seventy-Six (novel), ''Seventy-Six'' (novel), an 1823 American novel by John Neal * 76 (album), ''76'' (album), the debut album of Dutch trance producer and DJ Armin van Buuren * '76 (comics), ''76'' (comics), a 2007 comic book limited series by Image Comics * '76 (film), ''76'' (film), a 2016 film starring Ramsey Nouah and Rita Dominic Brands and enterprises * 76 (gas station), gas station chain in the United States Sports * Philadelphia 76ers, NBA team located in Philadelphia Others * 76 Freia, a main-belt asteroid See also * * List of highways numbered 76 {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNAS Yeovilton (HMS Heron)
Royal Naval Air Station Yeovilton, commonly referred to as WAFU central, (HMS ''Heron'') is an airbase of the Royal Navy, sited a few miles north of Yeovil, in the English county of Somerset. It is one of two active Fleet Air Arm bases, the other being RNAS Culdrose. RNAS Yeovilton is currently home to the Royal Navy Wildcat HMA2, along with Army Air Corps Wildcat AH1 helicopters, as well as the Royal Navy's Commando Helicopter Force Merlin HCi3/4/4A and Wildcat AH1 helicopters. The site consists of of airfield sites, plus ranges and minor estates. Royal Naval Air Station (RNAS) Yeovilton is a large multi-role air station, with an annual budget of some £61 million. The airfield is also home to the Fleet Air Arm Museum, and until 2019 the station hosted an annual Air Day in July. History In , the potential of the land at Yeovilton for use as an airfield was spotted by Westland Aircraft's chief test pilot Harald Penrose, and an offer was made to buy the land. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Zeals
Royal Air Force Zeals, or more simply RAF Zeals, is a former Royal Air Force station in Wiltshire, sited to the north of the village of Zeals, next to the village of Stourton and the Stourhead estate. History The station was in operation from 1942 to 1946, and was successively occupied by the Royal Air Force, the United States Army Air Forces and the Royal Navy. From opening until August 1943 the site was used by the RAF as an airfield for Hawker Hurricane and Supermarine Spitfire fighters. Units: *No. 66 Squadron RAF between 24 August and 23 December 1942 with the Spitfire VB & VC * No. 118 Squadron RAF between 24 August and 23 December 1942 with the Spitfire VB * No. 132 (City of Bombay) Squadron RAF between 28 February and 5 April 1943 with the Spitfire VB * No. 174 (Mauritius) Squadron RAF between 12 March and 5 April 1943 with the Hurricane IIB * No. 184 Squadron RAF between 12 March and 5 April 1943 with the Hurricane IID * No. 263 (Fellowship of the Bellows) Squadr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inskip, Lancashire
Inskip is a small village in the Fylde area of Lancashire, England. It is part of the Civil parishes in England, civil parish of Inskip-with-Sowerby. The village is close to the former RNAS Inskip (HMS Nightjar), RNAS Inskip airfield, which still serves the armed forces as a tri-service communication centre. It is home to one of the Royal Air Force Air Cadets training centres. Etymology The first part of the name ''Inskip'' may be the Common Brittonic, Brittonic ''ïnïs'' meaning "island" (Welsh language, Welsh ''ynys''), in place names generally referring to dry land in a marshy flood-prone area. Suffixed may be the Brittonic ''*cib'' meaning any rounded receptacle, presumably with some topographic sense, Old English ''-cy:pe'' or Anglo-Latin ''cuppa'', with the sense "fish-trap" recorded for both. History Inskip was listed in the Domesday Book of 1086 as ''Inscip''. Its area was estimated in that survey to be two carucates of land. From 1281, the manorialism, manor was owned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNAS Inskip (HMS Nightjar)
Royal Naval Air Station Inskip (RNAS Inskip, also known as HMS ''Nightjar''), was a Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm airbase near the village of Inskip, Lancashire, England. It saw considerable aircrew training activity towards the end of the World War II, Second World War. In the 1960s and 70s it was a Royal Navy transmitting station known as HMS ''Inskip''. It is now a military high frequency radio transmitting station known as Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), MOD Inskip. History On 4 June 1942 Admiralty (United Kingdom), the Admiralty acquired of farmland between Preston, Lancashire, Preston and Blackpool from John Stanley, 18th Earl of Derby, Lord Derby. It planned to build an airfield, to be called RNAS Elswick, for the training of Anti-submarine warfare, anti-submarine and two-seat strike crews. The location was chosen because of the relatively quiet airspace in the north-west of England and the proximity of coastal ranges in the Morecambe Bay area. Construction of the runwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Hurricane - Fly Navy Day 2016 (27670763331)
A sea is a large body of salt water. There are particular seas and the sea. The sea commonly refers to the ocean, the interconnected body of seawaters that spans most of Earth. Particular seas are either marginal seas, second-order sections of the oceanic sea (e.g. the Mediterranean Sea), or certain large, nearly landlocked bodies of water. The salinity of water bodies varies widely, being lower near the surface and the mouths of large rivers and higher in the depths of the ocean; however, the relative proportions of dissolved salts vary little across the oceans. The most abundant solid dissolved in seawater is sodium chloride. The water also contains salts of magnesium, calcium, potassium, and mercury, among other elements, some in minute concentrations. A wide variety of organisms, including bacteria, protists, algae, plants, fungi, and animals live in various marine habitats and ecosystems throughout the seas. These range vertically from the sunlit surface and shoreline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navalised Aircraft
A navalised aircraft (or navalized aircraft) is an aircraft that has been specifically designed for naval use, in some cases as a variant of a land-based design. An aircraft based on an aircraft carrier is called carrier-based aircraft. Characteristics A navalised aircraft typically differs from its land-based equivalent by: * The airframe, engine and avionics are marinised against salt water corrosion. * It is designed to be used on a flight deck. For a fixed wing aircraft this typically means catapult attachment points, a tailhook and strengthened undercarriage. Naval helicopters usually have wheels rather than skids and may have mechanisms to attach to the deck. * It is designed to occupy minimum hangar space – for example the wings, tail-boom or rotors may fold. * There is enhanced protection against water ingress (including that from hosing down with fresh water to get rid of salt water). * Equipment such as sensors and weapons are optimised for naval roles. * The avio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Hurricane Variants
The Hawker Hurricane was a British single-seat fighter aircraft designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft. Some models were built in Canada by Canadian Car and Foundry. British variants Hurricane Mk I Hurricane Mk I (Early production) The first Mark I production machines were ready fairly quickly, with deliveries starting in December 1937. These early aircraft featured fabric-covered wings, and a wooden, two bladed, fixed pitch propeller. Initially, the tailwheel was designed to be retractable. Early on it was discovered that the Hurricane needed a larger rudder area to improve the control characteristics during a spin. To this end, the lower part of the rudder was extended and a distinctive ventral "keel" was added to the rear fuselage. The tailwheel was fixed in place. Early Hurricanes lacked armour or self-sealing tanks. They used "ring and bead" gunsights, with the ring being mounted above the instrument panel and the bead mounted on a post above the engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Hurricane
The Hawker Hurricane is a British single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1930s–40s which was designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft Ltd. for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was overshadowed in the public consciousness by the Supermarine Spitfire during the Battle of Britain in 1940, but the Hurricane inflicted 60% of the losses sustained by the ''Luftwaffe'' in the campaign, and fought in all the major theatres of the Second World War. The Hurricane originated from discussions between RAF officials and aircraft designer Sir Sydney Camm about a proposed monoplane derivative of the Hawker Fury biplane in the early 1930s. Despite an institutional preference for biplanes and lack of interest by the Air Ministry, Hawker refined its monoplane proposal, incorporating several innovations which became critical to wartime fighter aircraft, including retractable landing gear and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin engine. The Air Ministry ordered Hawker's ''Interce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brewster F2A Buffalo
The Brewster F2A Buffalo is an American fighter aircraft which saw service early in World War II. Designed and built by the Brewster Aeronautical Corporation, it was one of the first U.S. monoplanes with an arrestor hook and other modifications for aircraft carriers. The Buffalo won a competition against the Grumman F4F Wildcat in 1939 to become the U.S. Navy's first monoplane fighter aircraft. Although superior to the Grumman F3F biplane it replaced, and the early F4Fs,Wheeler 1992, p. 58. the Buffalo was largely obsolete when the United States entered the war, being unstable and overweight, especially when compared to the Japanese Mitsubishi A6M Zero. Several nations, including Finland, Belgium, Britain and the Netherlands, ordered the Buffalo. The Finns were the most successful with their Buffalos, flying them in combat against early Soviet fighters with excellent results.Ethell 1995, p. 212. During the Continuation War of 1941–1944, the B-239s (de-navalized F2A-1s) op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
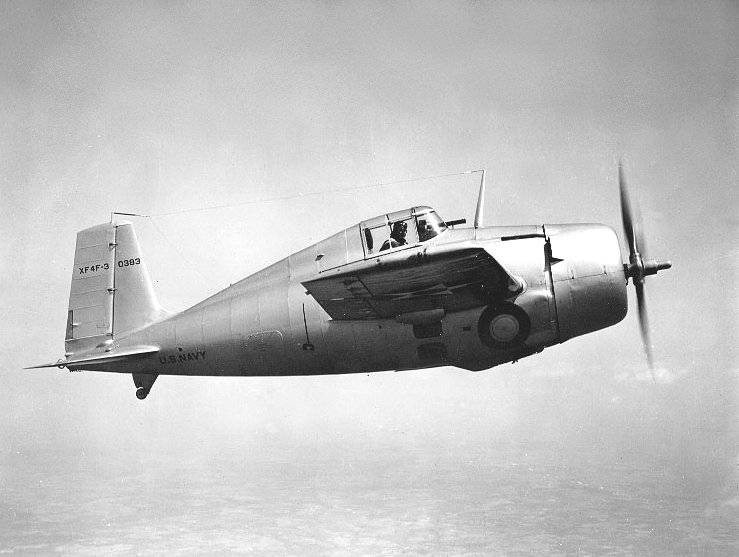
Grumman F4F Wildcat
The Grumman F4F Wildcat is an American carrier-based A carrier-based aircraft (also known as carrier-capable aircraft, carrier-borne aircraft, carrier aircraft or aeronaval aircraft) is a naval aircraft designed for operations from aircraft carriers. Carrier-based aircraft must be able to launch ... fighter aircraft that entered service in 1940 with the United States Navy, and the British Royal Navy where it was initially known as the Martlet. First used by the British in the North Atlantic, the Wildcat was the only effective fighter available to the United States Navy and Marine Corps in the Pacific Theater during the early part of the Second World War. The disappointing Brewster Buffalo was withdrawn in favor of the Wildcat and replaced as aircraft became available. With a top speed of , the Wildcat was outperformed by the faster [], more maneuverable, and longer-ranged Mitsubishi A6M Zero. US Navy pilots, including John Thach, John "Jimmy" Thach, a pioneer of fighter t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairey Fulmar
The Fairey Fulmar is a British carrier-borne reconnaissance aircraft/fighter aircraft which was developed and manufactured by aircraft company Fairey Aviation. It was named after the northern fulmar, a seabird native to the British Isles. The Fulmar served with the Royal Navy's Fleet Air Arm (FAA) during the Second World War. The design of the Fulmar was based on that of the earlier Fairey P.4/34, a land-based light bomber developed during 1936 as a replacement for the Fairey Battle light bomber. Fairey had redesigned the aircraft as a navalised observation/fighter aircraft to satisfy the requirements of Specification O.8/38, for which it was selected. Although its performance (like that of its Battle antecedent) was unspectacular, the Fulmar was a reliable, sturdy aircraft with long range and an effective armament of eight machine guns; the type could also be put into production relatively quickly. On 4 January 1940, the first production aircraft made its first flight a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |