|
7.7 Cm Kanone In Haubitzelafette
The 7.7 cm Kanone in Haubitzlafette (7.7 cm gun on howitzer carriage) was a field gun used by Germany in World War I. It consisted of the barrel of the 7.7 cm FK 96 n.A. mounted on the carriage of the 10.5 cm Feldhaubitze 98/09 in an attempt to get more elevation and range than the old 7.7 cm FK 96 n.A.. The Allies captured one example on 17 April 1916, but it is uncertain just how many were made or if they remained in service once the 7.7 cm FK 16 was introduced. The problem of range was addressed in the 7.7 cm FK 16 by adopting a longer barrel, increasing the size of the propellant chamber, changing the rifling pattern and increasing the elevation of the carriage. References World War I artillery of Germany 77 mm artillery {{artillery-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Gun
A field gun is a field artillery piece. Originally the term referred to smaller guns that could accompany a field army on the march, that when in combat could be moved about the battlefield in response to changing circumstances (field artillery), as opposed to guns installed in a fort (Royal Garrison Artillery, garrison artillery or coastal artillery), or to siege cannons and mortar (weapon), mortars which are too large to be moved quickly, and would be used only in a prolonged siege. Perhaps the most famous use of the field gun in terms of advanced tactics was Napoleon Bonaparte's use of very large wheels on the guns that allowed them to be moved quickly even during a battle. By moving the guns from point to point during a battle, enemy formations could be broken up to be handled by the infantry or cavalry wherever they were massing, dramatically increasing the overall effectiveness of the attack. World War I As the evolution of artillery continued, almost all guns of any siz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheinmetall
Rheinmetall AG () is a German automotive and arms manufacturer, headquartered in Düsseldorf, Germany. The group was promoted to the DAX, Germany's leading stock market index, in March 2023. It is the largest German and fifth largest European arms manufacturer, and produces a variety of armored fighting vehicles and armored personnel carriers, in both wheeled and tracked versions. Its name is derived from the German-language words ''Rhein'' and ''Metall'', translating to "Rhine-metal" when combined. History Founding and early growth In April 1889, the Hörder Bergwerks- und Hütten-Verein founded the Rheinische Metallwaren- und Maschinenfabrik Aktiengesellschaft under General Director Josef Massenez, to produce ammunition for the German Empire. The Thuringian engineer Heinrich Ehrhardt (1840-1928) oversaw the construction of the Rheinmetall plant in Düsseldorf and managed it until 1920. He made many of his patents and inventions available to the company and contributed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shell (projectile)
A shell, in a modern military context, is a projectile whose payload contains an explosive, incendiary device, incendiary, or other chemical filling. Originally it was called a bombshell, but "shell" has come to be unambiguous in a military context. A shell can hold a tracer ammunition, tracer. All explosive- and incendiary-filled projectiles, particularly for mortar (weapon), mortars, were originally called ''grenades'', derived from the French language, French word for pomegranate, so called because of the similarity of shape and that the multi-seeded fruit resembles the powder-filled, fragmentizing bomb. Words cognate with ''grenade'' are still used for an artillery or mortar projectile in some European languages. Shells are usually large-caliber projectiles fired by artillery, armored fighting vehicle, armoured fighting vehicles (e.g. tanks, assault guns, and mortar carriers), warships, and autocannons. The shape is usually a cylinder (geometry), cylinder topped by an o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
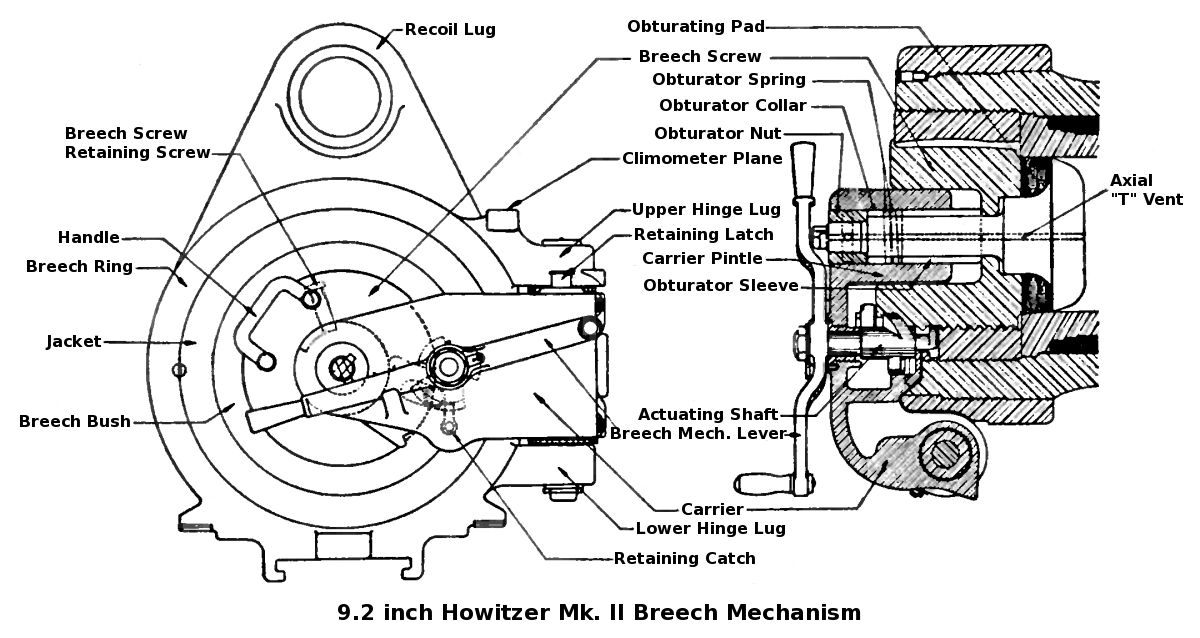
Rifled Breech Loader
A rifled breech loader (RBL) is an artillery piece which, unlike the smoothbore cannon and rifled muzzle loader which preceded it, has rifling in the barrel and is loaded from the breech-loading weapon, breech at the rear of the gun. The spin imparted by the gun's rifling gives projectiles directional stability and increased range. Loading from the rear of the gun leaves the crew less exposed to enemy fire, allows smaller gun emplacements or turrets, and allows a faster rate of fire. These rapidly improving breech systems and the powerful new guns they facilitated led to an arms race in fortification and ironclad warship design that led to the battleship class of HMS Dreadnought (1906), HMS ''Dreadnought'' and continued until the start of World War I. Overview The major problem to be solved with breechloading artillery was obturation: the sealing of the breech after firing to ensure that none of the gases generated by the burning of the propellant (initially gunpowder) escaped r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of British Ordnance Terms
This article explains terms used for the British Armed Forces' Materiel, ordnance (weapons) and ammunition. The terms may have different meanings depending on their usage in another country's military. BD Between decks: applies to a naval gun mounting in which part of the rotating mass is below the deck, and part of it is above the deck. This allows for a lower profile for a gun turret, turret, meaning that the turrets need not be superfiring (i.e. they can be mounted on the same deck and not obstruct each other at high angles of elevation). BL The term BL, in its general sense, stood for breech loading, and contrasted with muzzle loading. The shell was loaded via the breech (i.e. the gunner's end of the barrel, which opened) followed by the propellant charge, and the breech mechanism was closed to seal the chamber. Breech loading, in its formal British ordnance sense, served to identify the gun as the type of Rifled breech-loader, rifled breechloading gun for which the powder c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Carriage
A gun carriage is a frame or a mount that supports the gun barrel of an artillery piece, allowing it to be maneuvered and fired. These platforms often had wheels so that the artillery pieces could be moved more easily. Gun carriages are also used on ships to facilitate the movement and aiming of large cannons and guns. These are also used in the funeral procession of any higher authority of any state and country. Early guns The earliest guns were laid directly onto the ground, with earth being piled up under the muzzle end of the barrel to increase the elevation. As the size of guns increased, they began to be attached to heavy wooden frames or beds that were held down by stakes. These began to be replaced by wheeled carriages in the early 16th century. Smoothbore gun carriages From the 16th to the mid-19th century, the main form of artillery remained the smoothbore cannon. By this time, the trunnion (a short axle protruding from either side of the gun barrel) had been devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I Artillery Of Germany
The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique, while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object, while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts. In scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "the totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon, or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |