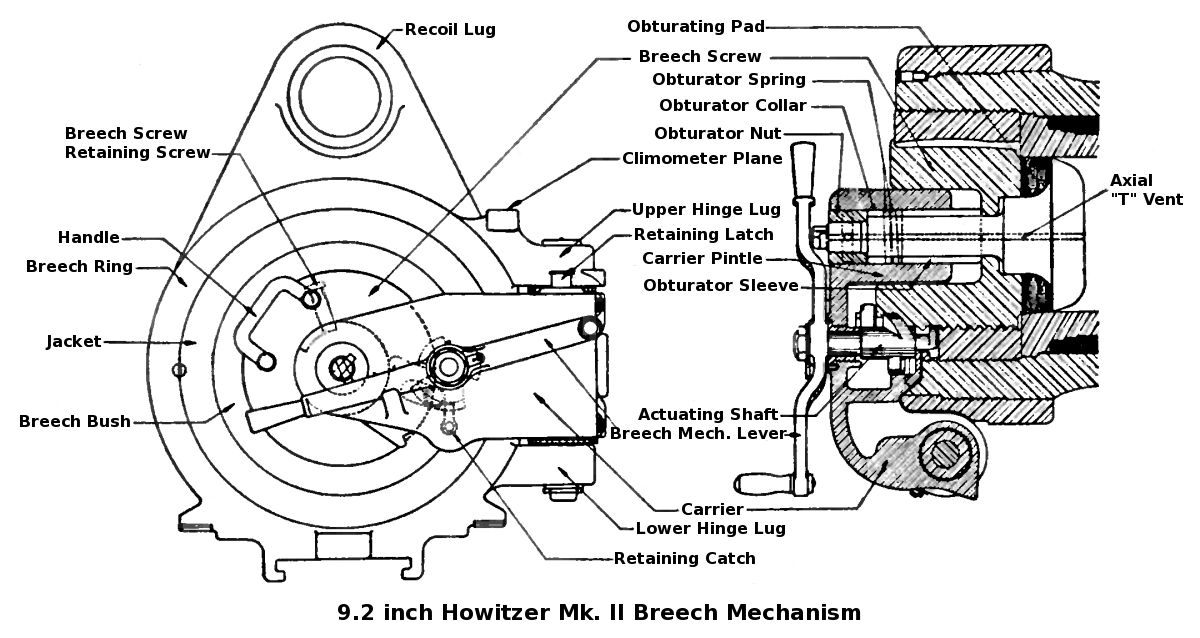
|
7.5 Cm Pak 50
The 7.5 cm Panzerabwehrkanone 50 or 7.5 cm Pak 50 was an anti-tank gun, produced in limited numbers by Germany, towards the end of World War II. History The 7.5 cm Pak 50 was developed during 1944 and details are scarce. The rationale for the guns might have been to produce a lighter, more portable and easily concealable version of the Pak 40. Despite its ''Panzerabwehrkanone'' designation, it may have been a dual-purpose gun with both anti-tank and ''Infanteriegeschütz'' or Infantry support gun roles. Design The Pak 50 consisted of a shortened 7.5 cm Pak 40 barrel and recoil mechanism mounted on the carriage of the earlier 5 cm Pak 38. The carriage was a split-trail design with spoked metal wheels and solid rubber tires. There was also a curved two-layer gun shield and the breech was a semi-automatic horizontal sliding wedge. Once fired the breech would open and eject the spent casing and it remained open until the next round was loaded and the breech was closed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-tank Gun
An anti-tank gun is a form of artillery designed to destroy tanks and other armoured fighting vehicles, normally from a static defensive position. The development of specialized anti-tank munitions and anti-tank guns was prompted by the appearance of tanks during World War I. To destroy hostile tanks, artillerymen often used field guns depressed to fire directly at their targets, but this practice expended too much valuable ammunition and was of increasingly limited effectiveness as tank armor became thicker. The first dedicated anti-tank artillery began appearing in the 1920s, and by World War II was a common appearance in many European armies. To penetrate armor, they fired specialized ammunition from longer barrels to achieve a higher muzzle velocity than field guns. Most anti-tank guns were developed in the 1930s as improvements in tanks were noted, and nearly every major arms manufacturer produced one type or another. Anti-tank guns deployed during World War II were often mann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct-fire
Direct fire or line-of-sight fire refers to firing of a ranged weapon whose projectile is launched directly at a target within the line-of-sight of the user. The firing weapon must have a sighting device and an unobstructed view to the target, which means no obstacles or friendly units can be between it and the target. A weapon engaged in direct fire conversely exposes itself to direct return fire from the target.p.49, Bailey This is in contrast to indirect fire, which refers to firing a projectile on a curved ballistic trajectory or delivering self-accelerated munitions capable of long range and various degrees of homing abilities to alter the flight path. Indirect fire does not need a direct line-of-sight to the target because the shots are normally directed by a forward observer. As such, indirect-fire weapons can shoot over obstacles or friendly units and the weapons can be concealed from counter-battery fire. Description Examples of direct-fire weapons include most anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II Anti-tank Guns Of Germany
The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique, while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object, while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts. In scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "the totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon, or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
75 Mm Artillery
75 may refer to: * 75 (number) * one of the years 75 BC, AD 75, 1975, 2075 * ''75'' (album), an album by Joe Zawinul * 75 Eurydike, a main-belt asteroid Vehicles * Alfa Romeo 75, a compact executive sedan * Tatra 75, a mid-size car * Various Rover models: ** Rover 75, an executive car ** Rover 75, a saloon ** Rover 75, a large family car See also * * * * Canon de 75 modèle 1897 (the 75, or, French 75) * M75 (other) * List of highways numbered 75 {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-explosive Anti-tank Warhead
High-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) is the effect of a shaped charge explosive that uses the Munroe effect to penetrate heavy armor. The warhead functions by having an explosive charge collapse a metal liner inside the warhead into a high-velocity shaped charge jet; this is capable of penetrating armor steel to a depth of seven or more times the diameter of the charge (charge diameters, CD). The shaped charge jet armor penetration effect is purely kinetic in nature; the round has no explosive or incendiary effect on the armor. Unlike standard armor-piercing rounds, a HEAT warhead's penetration performance is unaffected by the projectile's velocity, allowing them to be fired by lower-powered weapons that generate less recoil. The performance of HEAT weapons has nothing to do with thermal effects, with HEAT being simply an acronym. History HEAT warheads were developed during World War II, from extensive research and development into shaped charge warheads. Shaped charge war ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armor-piercing Shell
Armour-piercing ammunition (AP) is a type of projectile designed to penetrate armour protection, most often including naval armour, body armour, and vehicle armour. The first, major application of armour-piercing projectiles was to defeat the thick armour carried on many warships and cause damage to their lightly armoured interiors. From the 1920s onwards, armour-piercing weapons were required for anti-tank warfare. AP rounds smaller than 20 mm are intended for lightly armoured targets such as body armour, bulletproof glass, and lightly armoured vehicles. As tank armour improved during World War II, anti-vehicle rounds began to use a smaller but dense penetrating body within a larger shell, firing at a very-high muzzle velocity. Modern penetrators are long rods of dense material like tungsten or depleted uranium (DU) that further improve the terminal ballistics. Penetration In the context of weaponry, ''penetration'' is the ability of a weapon or projectile to pierc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of British Ordnance Terms
This article explains terms used for the British Armed Forces' Materiel, ordnance (weapons) and ammunition. The terms may have different meanings depending on their usage in another country's military. BD Between decks: applies to a naval gun mounting in which part of the rotating mass is below the deck, and part of it is above the deck. This allows for a lower profile for a gun turret, turret, meaning that the turrets need not be superfiring (i.e. they can be mounted on the same deck and not obstruct each other at high angles of elevation). BL The term BL, in its general sense, stood for breech loading, and contrasted with muzzle loading. The shell was loaded via the breech (i.e. the gunner's end of the barrel, which opened) followed by the propellant charge, and the breech mechanism was closed to seal the chamber. Breech loading, in its formal British ordnance sense, served to identify the gun as the type of Rifled breech-loader, rifled breechloading gun for which the powder c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indirect-fire
Indirect fire is aiming and firing a projectile without relying on a direct line of sight between the gun and its target, as in the case of direct fire. Aiming is performed by calculating azimuth and inclination, and may include correcting aim by observing the fall of shot and calculating new angles. Description Indirect fire is most commonly used by field artillery and mortars (although field artillery was originally and until after World War I a direct fire weapon, hence the bullet-shields fitted to the carriages of guns such as the famous M1897 75 mm). It is also used with missiles, howitzers, rocket artillery, multiple rocket launchers, cruise missiles, ballistic missiles, naval guns against shore targets, sometimes with machine guns, and has been used with tank and anti-tank guns and by anti-aircraft guns against surface targets. There are two dimensions in aiming a weapon: * In the horizontal plane (azimuth); and * In the vertical plane (elevation), which is gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muzzle Brake
A muzzle brake or recoil compensator is a device connected to, or a feature integral (ported barrel) to the construction of, the muzzle or barrel of a firearm or cannon that is intended to redirect a portion of propellant gases to counter recoil and unwanted muzzle rise. Barrels with an integral muzzle brake are often said to be ported. The concept of a muzzle brake was first introduced for artillery. It was a common feature on many anti-tank guns, especially those mounted on tanks, in order to reduce the area needed to take up the strokes of recoil and kickback. They have been used in various forms for rifles and pistols to help control recoil and the rising of the barrel that normally occurs after firing. They are used on pistols for practical pistol competitions, and are usually called compensators in this context.STI article o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rifled Breech Loader
A rifled breech loader (RBL) is an artillery piece which, unlike the smoothbore cannon and rifled muzzle loader which preceded it, has rifling in the barrel and is loaded from the breech-loading weapon, breech at the rear of the gun. The spin imparted by the gun's rifling gives projectiles directional stability and increased range. Loading from the rear of the gun leaves the crew less exposed to enemy fire, allows smaller gun emplacements or turrets, and allows a faster rate of fire. These rapidly improving breech systems and the powerful new guns they facilitated led to an arms race in fortification and ironclad warship design that led to the battleship class of HMS Dreadnought (1906), HMS ''Dreadnought'' and continued until the start of World War I. Overview The major problem to be solved with breechloading artillery was obturation: the sealing of the breech after firing to ensure that none of the gases generated by the burning of the propellant (initially gunpowder) escaped r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Shield
A U.S. Marine manning an M240 machine gun equipped with a gun shield A gun shield is a flat (or sometimes curved) piece of armor designed to be mounted on a crew-served weapon such as a machine gun, automatic grenade launcher, or artillery piece. Military Some mounted machine guns and artillery pieces are equipped with metal armor plates to protect the gunners from small arms fire and shrapnel from explosions. They were fitted to some armored fighting vehicles and patrol boats during the Vietnam War. Gun shields fell out of widespread use after the Vietnam War, but they have seen a resurgence in popularity during the 1980s and 1990s. Israeli military analysts began urging the use of gun shields, pointing to the grave risk to soldiers exposed to fire from automatic weapons. In particular, it was noted that many casualties were hit in areas not protected by body armor or a helmet, such as the neck or face. The United States Armed Forces began using gun shields in the earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5 Cm Pak 38
The 5 cm Pak 38 (L/60) (''5 cm Panzerabwehrkanone 38 (L/60)'') was a German anti-tank gun of 50 mm calibre. It was developed in 1938 by Rheinmetall-Borsig AG as a successor to the 3.7 cm Pak 36, and was in turn followed by the 7.5 cm Pak 40. The unique curved gun-shield design differed from most WWII anti-tank guns which had either one flat or two angled and one flat gun-shield plates for ease of manufacturing. Development After the Spanish Civil War, the German authorities started to think that a new anti-tank gun would be needed, even though the 3.7 cm Pak 36 had proven to be very successful. They asked Rheinmetall-Borsig to produce a new and more capable AT-gun. They first designed the Pak 37 in 1935, but the German authorities did not approve it because of its low capabilities. Rheinmetall-Borsig were forced to create a new gun with a longer - L/60 - barrel which was approved for mass production in 1939 under the designation Pak 38. Variants The original ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |