|
5-orthoplex Honeycomb
In the geometry of hyperbolic 5-space, the 5-orthoplex honeycomb is one of five paracompact regular space-filling tessellations (or honeycombs). It is called ''paracompact'' because it has infinite vertex figures, with all vertices as ideal points at infinity. With Schläfli symbol , it has three 5-orthoplexes around each cell. It is dual to the 24-cell honeycomb honeycomb. Related honeycombs It is related to the regular Euclidean 4-space 16-cell honeycomb, , with 16-cell (4-orthoplex) facets, and the regular 4-polytope 24-cell, with octahedral (3-orthoplex) cell, and cube , with (2-orthoplex) square faces. See also * List of regular polytopes References *Coxeter, ''Regular Polytopes'', 3rd. ed., Dover Publications, 1973. . (Tables I and II: Regular polytopes and honeycombs, pp. 294–296) *Coxeter Harold Scott MacDonald "Donald" Coxeter, (9 February 1907 – 31 March 2003) was a British and later also Canadian geometer. He is regarded as one of the greatest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Regular Polytopes
This article lists the regular polytopes and regular polytope compounds in Euclidean, spherical and hyperbolic spaces. The Schläfli symbol describes every regular tessellation of an ''n''-sphere, Euclidean and hyperbolic spaces. A Schläfli symbol describing an ''n''-polytope equivalently describes a tessellation of an (''n'' − 1)-sphere. In addition, the symmetry of a regular polytope or tessellation is expressed as a Coxeter group, which Coxeter expressed identically to the Schläfli symbol, except delimiting by square brackets, a notation that is called Coxeter notation. Another related symbol is the Coxeter-Dynkin diagram which represents a symmetry group with no rings, and the represents regular polytope or tessellation with a ring on the first node. For example, the cube has Schläfli symbol , and with its octahedral symmetry, ,3or , it is represented by Coxeter diagram . The regular polytopes are grouped by dimension and subgrouped by convex, nonconve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16-cell Honeycomb
In four-dimensional Euclidean geometry, the 16-cell honeycomb is one of the three regular space-filling tessellations (or honeycombs), represented by Schläfli symbol , and constructed by a 4-dimensional packing of 16-cell facets, three around every face. Its dual is the 24-cell honeycomb. Its vertex figure is a 24-cell. The vertex arrangement is called the B4, D4, or F4 lattice. Alternate names * Hexadecachoric tetracomb/honeycomb * Demitesseractic tetracomb/honeycomb Coordinates Vertices can be placed at all integer coordinates (i,j,k,l), such that the sum of the coordinates is even. D4 lattice The vertex arrangement of the 16-cell honeycomb is called the D4 lattice or F4 lattice. The vertices of this lattice are the centers of the 3-spheres in the densest known packing of equal spheres in 4-space; its kissing number is 24, which is also the same as the kissing number in R4, as proved by Oleg Musin in 2003. The related D lattice (also called D) can be constructed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Regular Polytopes
This article lists the regular polytopes and regular polytope compounds in Euclidean, spherical and hyperbolic spaces. The Schläfli symbol describes every regular tessellation of an ''n''-sphere, Euclidean and hyperbolic spaces. A Schläfli symbol describing an ''n''-polytope equivalently describes a tessellation of an (''n'' − 1)-sphere. In addition, the symmetry of a regular polytope or tessellation is expressed as a Coxeter group, which Coxeter expressed identically to the Schläfli symbol, except delimiting by square brackets, a notation that is called Coxeter notation. Another related symbol is the Coxeter-Dynkin diagram which represents a symmetry group with no rings, and the represents regular polytope or tessellation with a ring on the first node. For example, the cube has Schläfli symbol , and with its octahedral symmetry, ,3or , it is represented by Coxeter diagram . The regular polytopes are grouped by dimension and subgrouped by convex, nonconve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
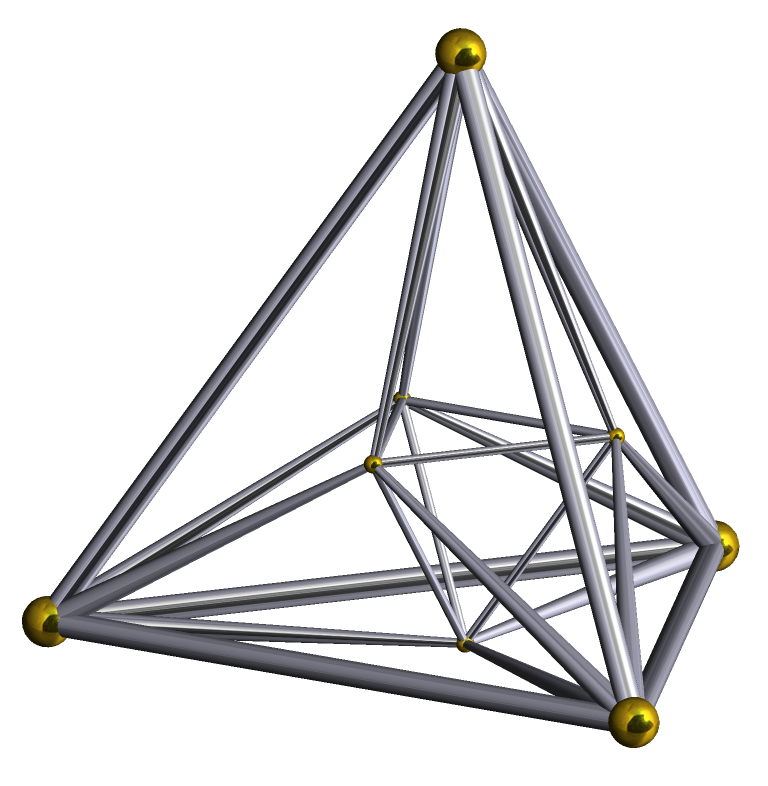
16-cell
In geometry, the 16-cell is the regular convex 4-polytope (four-dimensional analogue of a Platonic solid) with Schläfli symbol . It is one of the six regular convex 4-polytopes first described by the Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli in the mid-19th century. It is also called C16, hexadecachoron, or hexdecahedroid .Matila Ghyka, ''The Geometry of Art and Life'' (1977), p.68 It is a part of an infinite family of polytopes, called cross-polytopes or ''orthoplexes'', and is analogous to the octahedron in three dimensions. It is Coxeter's \beta_4 polytope. Conway's name for a cross-polytope is orthoplex, for '' orthant complex''. The dual polytope is the tesseract (4-cube), which it can be combined with to form a compound figure. The 16-cell has 16 cells as the tesseract has 16 vertices. Geometry The 16-cell is the second in the sequence of 6 convex regular 4-polytopes (in order of size and complexity). Each of its 4 successor convex regular 4-polytopes can be constructed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual Polytope
In geometry, every polyhedron is associated with a second dual structure, where the vertices of one correspond to the faces of the other, and the edges between pairs of vertices of one correspond to the edges between pairs of faces of the other. Such dual figures remain combinatorial or abstract polyhedra, but not all can also be constructed as geometric polyhedra. Starting with any given polyhedron, the dual of its dual is the original polyhedron. Duality preserves the symmetries of a polyhedron. Therefore, for many classes of polyhedra defined by their symmetries, the duals belong to a corresponding symmetry class. For example, the regular polyhedrathe (convex) Platonic solids and (star) Kepler–Poinsot polyhedraform dual pairs, where the regular tetrahedron is self-dual. The dual of an isogonal polyhedron (one in which any two vertices are equivalent under symmetries of the polyhedron) is an isohedral polyhedron (one in which any two faces are equivalent .., and vice vers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Point
In hyperbolic geometry, an ideal point, omega point or point at infinity is a well-defined point outside the hyperbolic plane or space. Given a line ''l'' and a point ''P'' not on ''l'', right- and left- limiting parallels to ''l'' through ''P'' converge to ''l'' at ''ideal points''. Unlike the projective case, ideal points form a boundary, not a submanifold. So, these lines do not intersect at an ideal point and such points, although well-defined, do not belong to the hyperbolic space itself. The ideal points together form the Cayley absolute or boundary of a hyperbolic geometry. For instance, the unit circle forms the Cayley absolute of the Poincaré disk model and the Klein disk model. While the real line forms the Cayley absolute of the Poincaré half-plane model . Pasch's axiom and the exterior angle theorem still hold for an omega triangle, defined by two points in hyperbolic space and an omega point. Properties * The hyperbolic distance between an ideal point an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex Figures
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off. Definitions Take some corner or vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines across the connected faces, joining adjacent points around the face. When done, these lines form a complete circuit, i.e. a polygon, around the vertex. This polygon is the vertex figure. More precise formal definitions can vary quite widely, according to circumstance. For example Coxeter (e.g. 1948, 1954) varies his definition as convenient for the current area of discussion. Most of the following definitions of a vertex figure apply equally well to infinite tilings or, by extension, to space-filling tessellation with polytope cells and other higher-dimensional polytopes. As a flat slice Make a slice through the corner of the polyhedron, cutting through all the edges connected to the vertex. The cut surface is the vertex figure. This i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honeycomb (geometry)
In geometry, a honeycomb is a ''space filling'' or '' close packing'' of polyhedral or higher-dimensional ''cells'', so that there are no gaps. It is an example of the more general mathematical ''tiling'' or ''tessellation'' in any number of dimensions. Its dimension can be clarified as ''n''-honeycomb for a honeycomb of ''n''-dimensional space. Honeycombs are usually constructed in ordinary Euclidean ("flat") space. They may also be constructed in non-Euclidean spaces, such as hyperbolic honeycombs. Any finite uniform polytope can be projected to its circumsphere to form a uniform honeycomb in spherical space. Classification There are infinitely many honeycombs, which have only been partially classified. The more regular ones have attracted the most interest, while a rich and varied assortment of others continue to be discovered. The simplest honeycombs to build are formed from stacked layers or ''slabs'' of prisms based on some tessellations of the plane. In particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tessellation
A tessellation or tiling is the covering of a surface, often a plane, using one or more geometric shapes, called ''tiles'', with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellation can be generalized to higher dimensions and a variety of geometries. A periodic tiling has a repeating pattern. Some special kinds include ''regular tilings'' with regular polygonal tiles all of the same shape, and ''semiregular tilings'' with regular tiles of more than one shape and with every corner identically arranged. The patterns formed by periodic tilings can be categorized into 17 wallpaper groups. A tiling that lacks a repeating pattern is called "non-periodic". An ''aperiodic tiling'' uses a small set of tile shapes that cannot form a repeating pattern. A ''tessellation of space'', also known as a space filling or honeycomb, can be defined in the geometry of higher dimensions. A real physical tessellation is a tiling made of materials such as cemented ceramic squares or hexagons. Such t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Polytope
In mathematics, a regular polytope is a polytope whose symmetry group acts transitively on its flags, thus giving it the highest degree of symmetry. All its elements or -faces (for all , where is the dimension of the polytope) — cells, faces and so on — are also transitive on the symmetries of the polytope, and are regular polytopes of dimension . Regular polytopes are the generalized analog in any number of dimensions of regular polygons (for example, the square or the regular pentagon) and regular polyhedra (for example, the cube). The strong symmetry of the regular polytopes gives them an aesthetic quality that interests both non-mathematicians and mathematicians. Classically, a regular polytope in dimensions may be defined as having regular facets (-faces) and regular vertex figures. These two conditions are sufficient to ensure that all faces are alike and all vertices are alike. Note, however, that this definition does not work for abstract polytopes. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Space
In mathematics, hyperbolic space of dimension n is the unique simply connected, n-dimensional Riemannian manifold of constant sectional curvature equal to -1. It is homogeneous, and satisfies the stronger property of being a symmetric space. There are many ways to construct it as an open subset of \mathbb R^n with an explicitly written Riemannian metric; such constructions are referred to as models. Hyperbolic 2-space, H2, which was the first instance studied, is also called the hyperbolic plane. It is also sometimes referred to as Lobachevsky space or Bolyai–Lobachevsky space after the names of the author who first published on the topic of hyperbolic geometry. Sometimes the qualificative "real" is added to differentiate it from complex hyperbolic spaces, quaternionic hyperbolic spaces and the octononic hyperbolic plane which are the other symmetric spaces of negative curvature. Hyperbolic space serves as the prototype of a Gromov hyperbolic space which is a far-reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a '' geometer''. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point, line, plane, distance, angle, surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts. During the 19th century several discoveries enlarged dramatically the scope of geometry. One of the oldest such discoveries is Carl Friedrich Gauss' ("remarkable theorem") that asserts roughly that the Gaussian curvature of a surface is independent from any specific embedding in a Euclidean space. This implies that surfaces can be studied ''intrinsically'', that is, as stand-alone spaces, and has been expanded into the theory of manifolds and Riemannian geometry. Later in the 19th century, it appeared that geom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |