|
5-hydroxytryptamine
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. In the CNS, serotonin regulates mood, appetite, and sleep. Most of the body's serotonin—about 90%—is synthesized in the gastrointestinal tract by enterochromaffin cells, where it regulates intestinal movements. It is also produced in smaller amounts in the brainstem's raphe nuclei, the skin's Merkel cells, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells, and taste receptor cells of the tongue. Once secreted, serotonin is taken up by platelets in the blood, which release it during clotting to promote vasoconstriction and platelet aggregation. Around 8% of the body's serotonin is stored in platelets, and 1–2% is found in the CNS. Serotonin acts as both a vasoconstrictor and vas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT5 Receptor
5-Hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 5A, also known as HTR5A, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HTR5A'' gene. Agonists and antagonists for 5-HT receptors, as well as serotonin uptake inhibitors, present promnesic (memory-promoting) and/or anti-amnesic effects under different conditions, and 5-HT receptors are also associated with neural changes. Function The gene described in this record is a member of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor family and encodes a multi-pass membrane protein that functions as a receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine and couples to G proteins, negatively influencing cAMP levels via Gi and Go. This protein has been shown to function in part through the regulation of intracellular Ca2+ mobilization. The 5-HT5A receptor has been shown to be functional in a native expression system. Rodents have been shown to possess two functional 5-HT5 receptor subtypes, 5-HT5A and 5-HT5B, however while humans possess a gene coding for the 5-HT5B subtype, its co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT4 Receptor
5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HTR4'' gene. Function This gene is a member of the family of human serotonin receptors, which are G protein-coupled receptors that stimulate cAMP production in response to serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine). The gene product is a glycosylated transmembrane protein that functions in both the peripheral and central nervous system to modulate the release of various neurotransmitters. Multiple transcript variants encoding proteins with distinct C-terminal sequences have been described, but the full-length nature of some transcript variants has not been determined. Location The receptor is located in the alimentary tract, urinary bladder, heart and adrenal gland as well as the central nervous system (CNS). In the CNS the receptor appears in the putamen, caudate nucleus, nucleus accumbens, globus pallidus, and substantia nigra, and to a lesser extent in the neocortex, raphe, pontine nuclei, and some a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT3 Receptor
The 5-HT3 receptor belongs to the Cys-loop superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs) and therefore differs structurally and functionally from all other 5-HT receptors (5-hydroxytryptamine, or serotonin receptors) which are G-protein-coupled receptor, G protein-coupled receptors. This ion channel is cation-selective and mediates neuronal depolarization and excitation within the Central nervous system, central and Peripheral nervous system, peripheral nervous systems. As with other ligand gated ion channels, the 5-HT3 receptor consists of five subunits arranged around a central ion conducting pore, which is permeable to sodium (Na), potassium (K), and calcium (Ca) ions. Binding of the neurotransmitter 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) to the 5-HT3 receptor opens the channel, which, in turn, leads to an excitatory response in neurons. The rapidly activating, desensitizing, inward current is predominantly carried by sodium and potassium ions. 5-HT3 receptors have a negligible perme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT6 Receptor
The 5HT6 receptor is a subtype of 5HT receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5HT). It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gs and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. ''HTR6'' denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor. Distribution The 5HT6 receptor is expressed almost exclusively in the brain. It is distributed in various areas including, but not limited to, the olfactory tubercle, cerebral cortex ( frontal and entorhinal regions), nucleus accumbens, striatum, caudate nucleus, hippocampus, and the molecular layer of the cerebellum. Based on its abundance in extrapyramidal, limbic, and cortical regions it can be suggested that the 5HT6 receptor plays a role in functions like motor control, emotionality, cognition, and memory. Function Blockade of central 5HT6 receptors has been shown to increase glutamatergic and cholinergic neurotransmission in various brain areas, whereas activation enh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT1 Receptor
The 5-HT1 receptors are a subfamily of the 5-HT serotonin receptors that bind to the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine, or 5-HT). The 5-HT1 subfamily consists of five G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that share 40% to 63% overall sequence homology, including 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, 5-HT1E, and 5-HT1F. Receptors of the 5-HT1 type, specifically, the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1D receptor subtypes, are present on the cell bodies. Receptors of the 5-HT1 type, specifically, the 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptor subtypes, are also present on the nerve terminals. These receptors are broadly distributed throughout the brain and are recognized to play a significant part in regulating synaptic levels of 5-HT. The receptor subfamily is coupled to Gi/Go and mediate inhibitory neurotransmission Neurotransmission (Latin: ''transmissio'' "passage, crossing" from ''transmittere'' "send, let through") is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT7 Receptor
The 5-HT7 receptor is a member of the GPCR superfamily of cell surface receptors and is activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). The 5-HT7 receptor is coupled to Gs (stimulates the production of the intracellular signaling molecule cAMP) and is expressed in a variety of human tissues, particularly in the brain, the gastrointestinal tract, and in various blood vessels. This receptor has been a drug development target for the treatment of several clinical disorders. The 5-HT7 receptor is encoded by the ''HTR7'' gene, which in humans is transcribed into 3 different splice variants. Function When the 5-HT7 receptor is activated by serotonin, it sets off a cascade of events starting with release of the stimulatory G protein Gs from the GPCR complex. Gs in turn activates adenylate cyclase which increases intracellular levels of the second messenger cAMP. The 5-HT7 receptor plays a role in smooth muscle relaxation within the vasculature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HTP
5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), used medically as oxitriptan, is a naturally occurring amino acid and chemical precursor as well as a metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitter serotonin. 5-HTP can be manufactured and used as a drug and supplement with the '' oxitriptan''. Brand names include Cincofarm, Levothym, Levotonine, Oxyfan, Telesol, Tript-OH, and Triptum. As a drug, it is used in the treatment of depression and for certain other indications. Production 5-HTP is produced from the amino acid tryptophan through the action of the enzyme tryptophan hydroxylase. Tryptophan hydroxylase is one of the biopterin-dependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylases. Production of 5-HTP is the rate-limiting step in 5-HT (serotonin) synthesis. 5-HTP is normally rapidly converted to 5-HT by amino acid decarboxylase. Metabolism 5-HTP is decarboxylated to serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine or 5-HT) by the enzyme aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase with the help of vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
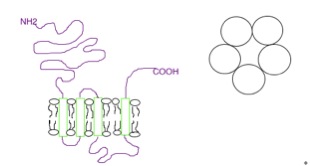
5-HT2 Receptor
The 5-HT2 receptors are a subfamily of 5-HT receptors that bind the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). The 5-HT2 subfamily consists of three G protein-coupled receptor G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related ...s (GPCRs) which are coupled to Gq/G11 and mediate excitatory neurotransmission, including 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C. For more information, please see the respective main articles of the individual subtypes: * 5-HT2A receptor * 5-HT2B receptor * 5-HT2C receptor See also * 5-HT1 receptor * 5-HT3 receptor * 5-HT4 receptor * 5-HT5 receptor * 5-HT6 receptor * 5-HT7 receptor * 5-HT2 antagonists References {{Serotonergics Serotonin receptors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterochromaffin Cell
Enterochromaffin (EC) cells (also known as Kulchitsky cells) are a type of enteroendocrine cell, and neuroendocrine cell. They reside alongside the epithelium lining the lumen of the digestive tract and play a crucial role in gastrointestinal regulation, particularly intestinal motility and secretion. They were discovered by Nikolai Kulchitsky. EC cells modulate neuron signalling in the enteric nervous system (ENS) via the secretion of the neurotransmitter serotonin and other peptides. As enteric afferent and efferent nerves do not protrude into the intestinal lumen, EC cells act as a form of sensory transduction. However, recent research has shown the direct vagal connection to a specialized entero-endocrine cell, the neuropod cell. ECs known as neuropod cells rapidly relay signals from gut to brain via a direct communication with vagal and primary sensory neurons. Serotonin in the ENS acts in synergy with other digestive hormones to regulate sensory and motor gastrointestina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myenteric
The myenteric plexus (or Auerbach's plexus) provides motor innervation to both layers of the muscular layer of the gut, having both parasympathetic and sympathetic input (although present ganglion cell bodies belong to parasympathetic innervation, fibers from sympathetic innervation also reach the plexus), whereas the submucous plexus provides secretomotor innervation to the mucosa nearest the lumen of the gut. It arises from cells in the vagal trigone also known as the nucleus ala cinerea, the parasympathetic nucleus of origin for the tenth cranial nerve (vagus nerve), located in the medulla oblongata. The fibers are carried by both the anterior and posterior vagal nerves. The myenteric plexus is the major nerve supply to the gastrointestinal tract and controls GI tract motility. According to preclinical studies, 30% of myenteric plexus' neurons are enteric sensory neurons, thus Auerbach's plexus has also a sensory component. Structure A part of the enteric nervous system, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic L-amino Acid Decarboxylase
Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC or AAAD), also known as DOPA decarboxylase (DDC), tryptophan decarboxylase, and 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase, is a lyase enzyme (), located in region 7p12.2-p12.1. Mechanism The enzyme uses pyridoxal phosphate (PLP), the active form of vitamin B6, as a cofactor. PLP is essential to the mechanism of decarboxylation in AADC. In the active enzyme, PLP is bound to lysine-303 of AADC as a Schiff base. Upon substrate binding, Lys-303 is displaced by the substrate's amine. This positions the carboxylate of the substrate within the active site such that decarboxylation is favored. Decarboxylation of the substrate produces a quinonoid intermediate, which is subsequently protonated to produce a Schiff base adduct of PLP and the decarboxylated product. Lys-303 can then regenerate the original Schiff base, releasing the product while retaining PLP. Probing this PLP-catalyzed decarboxylation, it has been discovered that there is a differenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
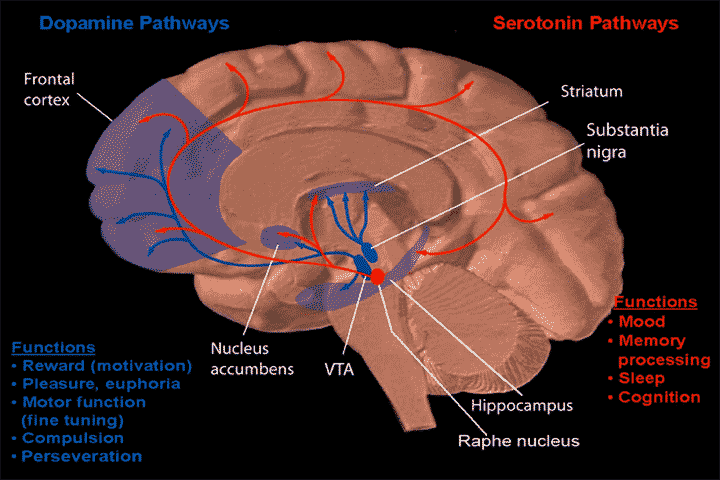
Raphe Nuclei
The raphe nuclei (, "seam") are a moderate-size cluster of nuclei found in the brain stem. They have 5-HT1 receptors which are coupled with Gi/Go-protein-inhibiting adenyl cyclase. They function as autoreceptors in the brain and decrease the release of serotonin. The anxiolytic drug Buspirone acts as partial agonist against these receptors. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants are believed to act in these nuclei, as well as at their targets. Anatomy The raphe nuclei are traditionally considered to be the medial portion of the reticular formation, and appear as a ridge of cells in the center and most medial portion of the brain stem. In order from caudal to rostral, the raphe nuclei are known as the '' nucleus raphe obscurus'', the '' nucleus raphe pallidus'', the '' nucleus raphe magnus'', the '' nucleus raphe pontis'', the '' median raphe nucleus'', ''dorsal raphe nucleus'', ''caudal linear nucleus''. In the first systematic examination of the raph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |