|
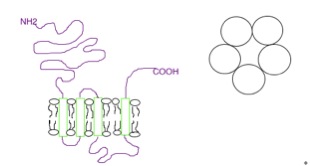
5-HT2A Receptor
The 5-HT2A receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor, 5-HT2 receptor that belongs to the serotonin receptor family and functions as a GPCR, G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is a cell surface receptor that activates multiple intracellular signalling cascades. Like all 5-HT2 receptors, the 5-HT2A receptor is coupled to the Gq protein, Gq/G11 signaling pathway. It is the primary excitatory receptor subtype among the serotonin-responsive GPCRs. The 5-HT2A receptor was initially noted for its central role as the primary target of serotonergic psychedelic drugs such as LSD and psilocybin mushrooms. It later regained research prominence when found to mediate, at least in part, the effects of many antipsychotic drugs, particularly atypical antipsychotic, atypical antipsychotics. Downregulation of post-synaptic 5-HT2A receptors is an adaptive response triggered by chronic administration of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and atypical antipsychotics. Elevated 5-HT2A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT2 Receptor
The 5-HT2 receptors are a subfamily of 5-HT receptors that bind the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). The 5-HT2 subfamily consists of three G protein-coupled receptor G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related ...s (GPCRs) which are coupled to Gq/G11 and mediate excitatory neurotransmission, including 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C. For more information, please see the respective main articles of the individual subtypes: * 5-HT2A receptor * 5-HT2B receptor * 5-HT2C receptor See also * 5-HT1 receptor * 5-HT3 receptor * 5-HT4 receptor * 5-HT5 receptor * 5-HT6 receptor * 5-HT7 receptor * 5-HT2 antagonists References {{Serotonergics Serotonin receptors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gut (zoology)
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore ( osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTR2B
5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor 2B (5-HT2B) also known as serotonin receptor 2B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HTR2B'' gene. 5-HT2B is a member of the 5-HT2 receptor family that binds the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). Like all 5-HT2 receptors, the 5-HT2B receptor is Gq/G11-protein coupled, leading to downstream activation of phospholipase C. Tissue distribution and function First discovered in the stomach of rats, 5-HT2B was challenging to characterize initially because of its structural similarity to the other 5-HT2 receptors, particularly 5-HT2C. The 5-HT2 receptors (of which the 5-HT2B receptor is a subtype) mediate many of the central and peripheral physiologic functions of serotonin. Cardiovascular effects include contraction of blood vessels and shape changes in platelets; central nervous system (CNS) effects include neuronal sensitization to tactile stimuli and mediation of some of the effects of hallucinogenic substituted amphet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 13
Chromosome 13 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 13 spans about 113 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 3.5 and 4% of the total DNA in cell (biology), cells. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 13. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project (Consensus CDS Project, CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes. Gene list The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 13. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right. Diseases and disorders The following diseases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT2C
The 5-HT2C receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). Like all 5-HT2 receptors, it is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gq/G11 and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. ''HTR2C'' denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor, that in humans is located on the X chromosome. As males have one copy of the gene and females have one of the two copies of the gene repressed, polymorphisms at this receptor can affect the two sexes to differing extent. Structure At the cell surface the receptor exists as a homodimer. The crystal structure has been known since 2018. Distribution 5-HT2C receptors are located mainly in the choroid plexus, and in rats is also found in many other brain regions in high concentrations, including parts of the hippocampus, anterior olfactory nucleus, substantia nigra, several brainstem nuclei, amygdala, subthalamic nucleus and Habenula#Lateral habenula, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT2B
5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor 2B (5-HT2B) also known as serotonin receptor 2B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HTR2B'' gene. 5-HT2B is a member of the 5-HT2 receptor family that binds the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). Like all 5-HT2 receptors, the 5-HT2B receptor is Gq/G11-protein coupled, leading to downstream activation of phospholipase C. Tissue distribution and function First discovered in the stomach of rats, 5-HT2B was challenging to characterize initially because of its structural similarity to the other 5-HT2 receptors, particularly 5-HT2C. The 5-HT2 receptors (of which the 5-HT2B receptor is a subtype) mediate many of the central and peripheral physiologic functions of serotonin. Cardiovascular effects include contraction of blood vessels and shape changes in platelets; central nervous system (CNS) effects include neuronal sensitization to tactile stimuli and mediation of some of the effects of hallucinogenic substituted amphet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT3 Receptor
The 5-HT3 receptor belongs to the Cys-loop superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs) and therefore differs structurally and functionally from all other 5-HT receptors (5-hydroxytryptamine, or serotonin receptors) which are G-protein-coupled receptor, G protein-coupled receptors. This ion channel is cation-selective and mediates neuronal depolarization and excitation within the Central nervous system, central and Peripheral nervous system, peripheral nervous systems. As with other ligand gated ion channels, the 5-HT3 receptor consists of five subunits arranged around a central ion conducting pore, which is permeable to sodium (Na), potassium (K), and calcium (Ca) ions. Binding of the neurotransmitter 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) to the 5-HT3 receptor opens the channel, which, in turn, leads to an excitatory response in neurons. The rapidly activating, desensitizing, inward current is predominantly carried by sodium and potassium ions. 5-HT3 receptors have a negligible perme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT1 Receptor
The 5-HT1 receptors are a subfamily of the 5-HT serotonin receptors that bind to the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine, or 5-HT). The 5-HT1 subfamily consists of five G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that share 40% to 63% overall sequence homology, including 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, 5-HT1E, and 5-HT1F. Receptors of the 5-HT1 type, specifically, the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1D receptor subtypes, are present on the cell bodies. Receptors of the 5-HT1 type, specifically, the 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptor subtypes, are also present on the nerve terminals. These receptors are broadly distributed throughout the brain and are recognized to play a significant part in regulating synaptic levels of 5-HT. The receptor subfamily is coupled to Gi/Go and mediate inhibitory neurotransmission Neurotransmission (Latin: ''transmissio'' "passage, crossing" from ''transmittere'' "send, let through") is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysergic Acid Diethylamide
Lysergic acid diethylamide, commonly known as LSD (from German ; often referred to as acid or lucy), is a Semisynthesis, semisynthetic, Hallucinogen, hallucinogenic compound derived from ergot, known for its powerful psychological effects and Serotonin, serotonergic activity. It was historically significant in psychiatry and 1960s counterculture; it is currently legally restricted but experiencing renewed scientific interest and increasing use. When taken orally, LSD has an onset of action within 0.4 to 1.0 hours (range: 0.1–1.8 hours) and a duration of effect lasting 7 to 12 hours (range: 4–22 hours). It is commonly administered via tabs of Blotting paper, blotter paper. LSD is extremely potent, with noticeable effects at doses as low as 20 Microgram, micrograms and is sometimes taken in much smaller amounts for microdosing. Yet no fatal human overdoses have been documented. LSD is mainly used recreationally or for spiritual purposes. LSD can cause mystical experiences. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiperone
Spiperone, also known as spiroperidol and sold under the brand name Spiropitan (( JP)) is a typical antipsychotic of the butyrophenone family related to haloperidol. It is approved for clinical use in Japan as a treatment for schizophrenia. Pharmacology Spiperone interacts with various monoamine receptors. Additionally, spiperone was identified by compound screening to be an activator of Ca2+ activated Cl− channels (CaCCs), thus a potential target for therapy of cystic fibrosis. Derivatives ''N''-Methylspiperone (NMSP) is a derivative of spiperone that is used to study the dopamine and serotonin neurotransmitter system. Labeled with the radioisotope carbon-11, it can be used for positron emission tomography. See also * Spirodecanone References {{Navboxes , title = Pharmacodynamics Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemistry, biochemical and physiology, physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioligand
A radioligand is a microscopic particle which consists of a Radiopharmaceutical, therapeutic radioactive isotope and the cell-targeting compound - the ligand. The ligand is the target binding site, it may be on the surface of the targeted cancer cell for therapeutic purposes. Radioisotopes can occur naturally or be synthesized and produced in a cyclotron/nuclear reactor. The different types of radioisotopes include Y-90, H-3, C-11, Lu-177, Ac-225, Ra-223, In-111, I-131, I-125, etc. Thus, radioligands must be produced in special nuclear reactors for the radioisotope to remain stable. Radioligands can be used to analyze/characterize receptors, to perform binding assays, to help in diagnostic imaging, and to provide targeted cancer therapy. Radiation is a novel method of treating cancer and is effective in short distances along with being unique/personalizable and causing minimal harm to normal surrounding cells. Furthermore, radioligand binding can provide information about receptor-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |