|
4-Cyano-4'-pentylbiphenyl
4-Cyano-4'-pentylbiphenyl is a commonly used nematic liquid crystal with the chemical formula C18H19N. It frequently goes by the common name 5CB. 5CB was first synthesized by George William Gray, Ken Harrison, and J.A. Nash at the University of Hull in 1972 and at the time it was the first member of the cyanobiphenyls. The liquid crystal was discovered after Gray's group received a grant from the UK Ministry of Defence to find a liquid crystal that had liquid crystal phases near room temperature with the specific intention of using them in liquid crystal displays. The molecule is about 20 Å long. The liquid crystal 5CB undergoes a phase transition from a crystalline state to a nematic state at 22.5 °C and it goes from a nematic to an isotropic state at 35.0 °C. Production 5CB is produced by modifying biphenyl in a linear manner. First Br2 is added to the biphenyl to introduce a bromine atom to the end of the moiety. Next aluminium chloride and C4H9COCl is added ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George William Gray
George William Gray (4 September 1926 – 12 May 2013) was a Professor of Organic Chemistry at the University of Hull who was instrumental in developing the long-lasting materials which made liquid crystal displays possible. He created and systematically developed liquid crystal materials science, and established a method of practical molecular design. Gray was recipient of the 1995 Kyoto Prize in Advanced Technology. Education and career Born in Denny, Scotland, Gray was educated at the University of Glasgow and while working as an assistant lecturer at the University College in Hull (then part of the University of London) obtained his PhD in 1953. He developed his academic career at the college, which became the University of Hull in 1954, from 1946 to 1990. He was appointed senior lecturer in 1960, Professor of Organic Chemistry in 1974, and GF Grant Professor of Chemistry in 1984. He remained an Emeritus Professor at Hull. In 1990 he joined the chemical company Merck, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
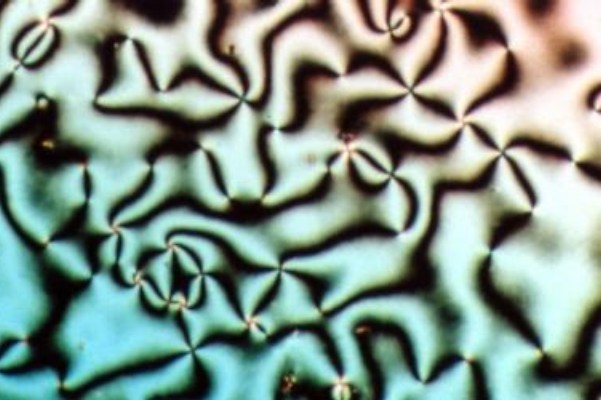
Liquid Crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal can flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a common direction as in a solid. There are many types of LC Phase (matter), phases, which can be distinguished by their Optics, optical properties (such as Texture (crystalline), textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. An LC material may not always be in an LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapour). Liquid crystals can be divided into three main types: thermotropic, lyotropic, and #Metallotropic liquid crystals, metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Hull
The University of Hull is a public research university in Kingston upon Hull, a city in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It was founded in 1927 as University College Hull. The main university campus is located in Hull and is home to the Hull York Medical School, a joint initiative with the University of York. Students are served by Hull University Union. The first chancellor of the university was Michael Willoughby, 11th Baron Middleton, Lord Middleton (1954–1969), followed by Henry Cohen, 1st Baron Cohen of Birkenhead, Lord Cohen (1970–1977), Richard Wilberforce, Baron Wilberforce, Lord Wilberforce (1978–1994), Robert Armstrong, Baron Armstrong of Ilminster, Lord Armstrong (1994–2006) and Virginia Bottomley (Baroness Bottomley of Nettlestone) (2006–2023). Alan Johnson was installed as the current chancellor in July 2023. History University College The foundation stone of University College Hull, then an external college of the University of London, was laid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Defence (United Kingdom)
The Ministry of Defence (MOD or MoD) is a Departments of the Government of the United Kingdom, ministerial department of the Government of the United Kingdom. It is responsible for implementing the defence policy set by the government and serves as the headquarters of the British Armed Forces. The MOD states that its principal objectives are to defend the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and its interests and to strengthen international peace and stability. The MOD also manages day-to-day running of the armed forces, contingency planning and defence procurement. The expenditure, administration and policy of the MOD are scrutinised by the Defence Select Committee, except for Defence Intelligence which instead falls under the Intelligence and Security Committee of Parliament. History During the 1920s and 1930s, British civil servants and politicians, looking back at the performance of the state during World War I, concluded that there was a need for greater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angstrom
The angstrom (; ) is a unit of length equal to m; that is, one ten-billionth of a metre, a hundred-millionth of a centimetre, 0.1 nanometre, or 100 picometres. The unit is named after the Swedish physicist Anders Jonas Ångström (1814–1874). It was originally spelled with Swedish letters, as Ångström and later as ångström (). The latter spelling is still listed in some dictionaries, but is now rare in English texts. Some popular US dictionaries list only the spelling ''angstrom''. The unit's symbol is Å, which is a letter of the Swedish alphabet, regardless of how the unit is spelled. However, "A" or "A.U." may be used in less formal contexts or typographically limited media. The angstrom is often used in the natural sciences and technology to express sizes of atoms, molecules, microscopic biological structures, and lengths of chemical bonds, arrangement of atoms in crystals, wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, and dimensions of integrated circuit part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Chloride
Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It forms a hexahydrate with the formula , containing six water molecules of hydration. Both the anhydrous form and the hexahydrate are colourless crystals, but samples are often contaminated with iron(III) chloride, giving them a yellow colour. The anhydrous form is commercially important. It has a low melting and boiling point. It is mainly produced and consumed in the production of aluminium, but large amounts are also used in other areas of the chemical industry. The compound is often cited as a Lewis acid. It is an inorganic compound that reversibly changes from a polymer to a monomer at mild temperature. Structure Anhydrous adopts three structures, depending on the temperature and the state (solid, liquid, gas). Solid has a sheet-like layered structure with cubic close-packed chloride ions. In this framework, the Al centres exhibit octahedral coordination geom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash. Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which utilize its caustic nature and its reactivity toward acids. An estimated 700,000 to 800,000 tonnes were produced in 2005. KOH is noteworthy as the precursor to most soft and liquid soaps, as well as numerous potassium-containing chemicals. It is a white solid that is dangerously corrosive. Properties and structure KOH exhibits high thermal stability. Because of this high stability and relatively low melting point, it is often melt-cast as pellets or rods, forms that have low surface area and convenient handling properties. These pellets become tacky in air because KOH is hygroscopic. Most commercial samples are ca. 90% pure, the remainder being water and carbonates. Its dissolution in water is strongly exothermic. Concentrated aqueous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper(I) Cyanide
Copper(I) cyanide (cuprous cyanide) is an inorganic compound with the formula CuCN. This off-white solid occurs in two polymorphs; impure samples can be green due to the presence of Cu(II) impurities. The compound is useful as a catalyst, in electroplating copper, and as a reagent in the preparation of nitriles.H. Wayne Richardson "Copper Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. Structure Copper cyanide is a coordination polymer. It exists in two polymorphs both of which contain - u-CN chains made from linear copper(I) centres linked by cyanide bridges. In the high-temperature polymorph, HT-CuCN, which is isostructural with AgCN, the linear chains pack on a hexagonal lattice and adjacent chains are off set by +/- 1/3 ''c'', Figure 1. In the low-temperature polymorph, LT-CuCN, the chains deviate from linearity and pack into rippled layers which pack in an AB fashion with chains in adjacent layers rotated by 49 °, Figure 2. File ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylformamide
Dimethylformamide, DMF is an organic compound with the chemical formula . Its structure is . Commonly abbreviated as DMF (although this initialism is sometimes used for 2,5-dimethylfuran, dimethylfuran, or dimethyl fumarate), this colourless liquid is Miscibility, miscible with Water (molecule), water and the majority of organic liquids. DMF is a common solvent for chemical reactions. Dimethylformamide is odorless, but chemical purity, technical-grade or degraded samples often have a fishy smell due to impurity of dimethylamine. Dimethylamine degradation impurities can be removed by Sparging (chemistry), sparging samples with an inert gas such as argon or by sonication, sonicating the samples under reduced pressure. As its name indicates, it is structurally related to formamide, having two methyl groups in the place of the two hydrogens. DMF is a polar molecule, polar (hydrophilic) aprotic solvent with a high boiling point. It facilitates reactions that follow polar mechanisms, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthesis Of 5CB
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to: Science Chemistry and biochemistry *Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors **Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organic compounds ***Total synthesis, the complete organic synthesis of complex organic compounds, usually without the aid of biological processes ***Convergent synthesis or linear synthesis, a strategy to improve the efficiency of multi-step chemical syntheses **Dehydration synthesis, a chemical synthesis resulting in the loss of a water molecule *Biosynthesis, the creation of an organic compound in a living organism, usually aided by enzymes **Photosynthesis, a biochemical reaction using a carbon molecule to produce an organic molecule, using sunlight as a catalyst **Chemosynthesis, the synthesis of biological compounds into organic waste, using methane or an oxidized molecule as a catalyst **Amino acid synthesis, the synthesis of an amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Crystals
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal can flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a common direction as in a solid. There are many types of LC phases, which can be distinguished by their optical properties (such as textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. An LC material may not always be in an LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapour). Liquid crystals can be divided into three main types: thermotropic, lyotropic, and metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the LC phase as temperature changes. Lyotropic LCs exhibit phase transitions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Crystal Displays
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other Electro-optic modulator, electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers to display information. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but instead use a backlight or Reflector (photography), reflector to produce images in color or Monochrome monitor, monochrome. LCDs are available to display arbitrary images (as in a general-purpose computer display) or fixed images with low information content, which can be displayed or hidden: preset words, digits, and seven-segment displays (as in a digital clock) are all examples of devices with these displays. They use the same basic technology, except that arbitrary images are made from a matrix of small pixels, while other displays have larger elements. LCDs are used in a wide range of applications, including LCD televisions, computer monitors, Dashboard, instrument panels, flight instrument ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |