|
4-6-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and two trailing wheels on one axle. The locomotive became almost globally known as a Pacific type after a locomotive built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in Philadelphia was shipped across the Pacific Ocean to New Zealand. Overview The introduction of the design in 1901 has been described as "a veritable milestone in locomotive progress". On many railways worldwide, Pacific steam locomotives provided the motive power for express passenger trains throughout much of the early to mid-20th century, before either being superseded by larger types in the late 1940s and 1950s, or replaced by electric or diesel-electric locomotives during the 1950s and 1960s. Nevertheless, new Pacific designs continued to be built until the mid-1950s. The type is generally considered to be an enlargement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-6-4
, under the Whyte notation for the classification of locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels and four trailing wheels. In France where the type was first used, it is known as the Baltic while it became known as the Hudson in most of North America. Overview Tender locomotives The 4-6-4 tender locomotive was first introduced in 1911 and throughout the 1920s to 1940s, the wheel arrangement was widely used in North America and to a lesser extent in the rest of the world. The type combined the basic design principles of the 4-6-2 type with an improved boiler and larger firebox that necessitated additional support at the rear of the locomotive. In general, the available tractive effort differed little from that of the 4-6-2, but the steam-raising ability was increased, giving more power at speed. The 4-6-4 was best suited to high-speed running across flat terrain. Since the type had fewer driving wheels than car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
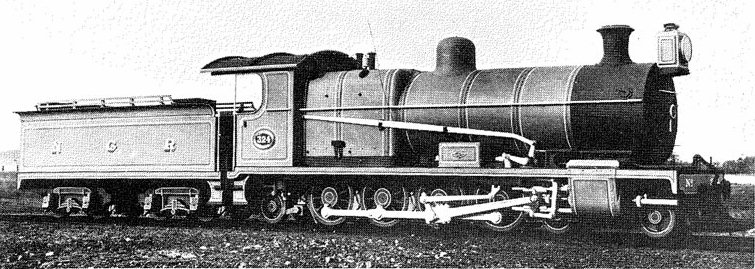
South African Class 5A 4-6-2
The South African Railways Class 5A 4-6-2 of 1903 was a steam locomotive from the pre- Union era in the Cape of Good Hope. In 1903, the Cape Government Railways placed two Karoo Class steam locomotives with a Pacific type wheel arrangement in passenger service. In 1912, when they were assimilated into the South African Railways, they were renumbered and designated Class 5A.Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1944). ''The Locomotive in South Africa – A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter II – The Cape Government Railways'' (Continued). South African Railways and Harbours Magazine, February 1944. pp. 97-101.Classification of S.A.R. Engines with Renumbering Lists, issued by the Chief Mechanical Engineer's Office, Pretoria, January 1912, pp. 8, 12, 14, 34 (Reprinted in April 1987 by SATS Museum, R.3125-6/9/11-1000) Design The Karoo Class of the Cape Government Railways (CGR) was the first tender locomotive with a Pacific type wheel arrangement to be introduced in Afric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-6-0
A 4-6-0 steam locomotive, under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, has four leading wheels on two axles in a leading bogie and six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles with the absence of trailing wheels. In the mid-19th century, this wheel arrangement became the second-most-popular configuration for new steam locomotives in the United States, where this type is commonly referred to as a ten-wheeler.White, John H., Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York, NY: Dover Publications. p. 57. As locomotives pulling trains of lightweight all-wood passenger cars from the 1890 to the 1920s, they were exceptionally stable at near speeds on the New York Central's New York-to-Chicago Water Level Route and on the Reading Railroad's line from Camden to Atlantic City, New Jersey. Overview Tender locomotives During the second half of the nineteenth and first half of the twen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whyte Notation
The Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twentieth century following a December 1900 editorial in ''American Engineer and Railroad Journal''. The notation was adopted and remains in use in North America and the United Kingdom to describe the wheel arrangements of steam locomotives, but for modern locomotives, multiple units and trams it has been supplanted by the UIC system in Europe and by the AAR system (essentially a simplification of the UIC system) in North America. However, geared steam locomotives do not use the notation. They are classified by their model and their number of trucks. Structure of the system Basic form The notation in its basic form counts the number of leading wheels, then the number of driving wheels, and finally the number of trailing wheels, numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels, eight powered and coupled driving wheels and two trailing wheels. This type of steam locomotive is commonly known as the Mountain type, though the New York Central Railroad used the name Mohawk for their 4-8-2s. Overview The Colony of Natal in South Africa and New Zealand were innovators of the Mountain wheel arrangement. The Natal Government Railways (NGR) placed in service the first tank engines with the 4-8-2 arrangement, and the NGR was also first to modify tender locomotives to use a 4-8-2 wheel arrangement. The New Zealand Railways Department (NZR) introduced the first tender locomotives designed and built as 4-8-2. In 1888, the Natal Government Railways placed the first five of its eventual one hundred Class D tank locomotives in service. The locomotive was designed by William Milne, the locomotive superintendent of the NGR from 1877 to 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, Fuel oil, oil or, rarely, Wood fuel, wood) to heat water in the locomotive's Boiler (power generation), boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels. In most locomotives, the steam is admitted alternately to each end of its Steam locomotive components, cylinders in which pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive's main wheels. Fuel and water supplies are usually carried with the locomotive, either on the locomotive itself or in a Tender (rail), tender coupled to it. #Variations, Variations in this general design include electrically powered boilers, turbines in place of pistons, and using steam generated externally. Steam locomotives were first developed in the United Kingdom of Great Britain an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Beattie
Alfred Luther Beattie (1852 – 2 May 1920), typically referred to as A. L. Beattie, was a pioneering locomotive engineer. Born in Yorkshire, England,The Rock, September 2010 http://www.stpeterscaversham.org.nz/The%20Rock/1009.pdf he gained fame as the Chief Mechanical Engineer of the New Zealand Railways Department (NZR) between 1900 and 1913. During this time, Beattie designed the Q class, the first 4-6-2 (''Pacific'') steam locomotive class in the world, and he was also one of the earliest people to use other wheel arrangements. Early life Born in 1852, his birth was registered in Hunslet as Alfred Luther Betty. He arrived in New Zealand at Port Chalmers in 1876, when he joined NZR. In February 1897, Beattie was given the position of Locomotive Engineer at Addington Workshops in Christchurch.McGavin, ''Steam Locomotives of New Zealand'', pg. 53. Unlike in some countries, where "locomotive engineer" is the title of regular train drivers, the title in New Zealand then refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NZR Q Class (1901)
The NZR Q class was an important steam locomotive class not only in the history of New Zealand's railway network but also in worldwide railways in general. Designed by New Zealand Government Railways' (NZR) Chief Mechanical Engineer A. L. Beattie and ordered from the Baldwin Locomotive Works in 1901, they were the first locomotives in the world to be built with the wheel arrangement of 4-6-2. This wheel arrangement came to be known as the ''Pacific'' type after the voyage the completed locomotives made across the Pacific Ocean to New Zealand. A few instances of the 4-6-2 wheel arrangement are known to have existed prior to 1901, but these were all reconstructions of locomotives that were originally built with a different wheel arrangement, thereby making the thirteen members of the Q class the first "true" Pacifics in the world. The Pacific style went on to become arguably the most famous wheel arrangement in the world. Design The Q class's design stems from the requirement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LNER Class A4 4468 Mallard
LNER Class A4 4468 ''Mallard'' is a 4-6-2 ("Pacific") steam locomotive built in 1938 for operation on the London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) at Doncaster Works to a design of Nigel Gresley. Its streamlined, wind tunnel tested design allowed it to haul long-distance express passenger services at high speeds. On 3 July 1938, ''Mallard'' broke the world speed record for steam locomotives at , which still stands today. While in British Railways days regular steam-hauled rail services in the UK were officially limited to a 'line speed', before the war, the A4s had to run significantly above just to keep schedule on trains such as the ''Silver Jubilee'' and '' The Coronation'', with the engines reaching 100 mph on many occasions. ''Mallard'' covered almost one and a half million miles (2.4 million km) before it was retired in 1963. The locomotive is long and weighs 165 long tons (168 tonnes, 369,600 lbs), including the tender. It is painted in LNER garter blue with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-6-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels, six coupled driving wheels and two trailing wheels. This arrangement is commonly called a Prairie. Overview The majority of American 2-6-2s were tender locomotives, but in Europe tank locomotives, described as , were more common. The first 2-6-2 tender locomotives for a North American customer were built by Brooks Locomotive Works in 1900 for the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad, for use on the Midwestern prairies. The type was thus nicknamed the Prairie in North American practice. This name was often also used for British locomotives with this wheel arrangement. As with the 2-10-2, the major problem with the 2-6-2 is that these engines have a symmetrical wheel layout, with the centre of gravity almost over the centre driving wheel. The reciprocation rods, when working near the centre of gravity, induce severe side-to-side nosing which results ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-4-2 (locomotive)
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, represents a configuration of a four-wheeled leading bogie, four powered and coupled driving wheels, and two trailing wheels supporting part of the weight of the boiler and firebox. This allows a larger firebox and boiler than the configuration. This wheel arrangement is commonly known as the Atlantic type, although it is also sometimes called a Milwaukee or 4-4-2 Milwaukee, after the Milwaukee Road, which employed it in high speed passenger service. Overview While the wheel arrangement and type name Atlantic would come to fame in the fast passenger service competition between railroads in the United States by mid-1895, the tank locomotive version of the Atlantic type first made its appearance in the United Kingdom in 1880, when William Adams designed the 1 Class T of the London, Tilbury and Southend Railway (LT&SR). The is the tank locomotive equivalent of a 4-4-0 American type t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheel Arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement or wheel configuration is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed under a locomotive. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and connections, with the adopted notations varying by country. Within a given country, different notations may also be employed for different kinds of locomotives, such as steam, electric, and diesel powered. Especially in steam days, wheel arrangement was an important attribute of a locomotive because there were many different types of layout adopted, each wheel being optimised for a different use (often with only some being actually "driven"). Modern diesel and electric locomotives are much more uniform, usually with all axles driven. Major notation schemes The main notations are the Whyte notation (based on counting the wheels), the AAR wheel arrangement notation (based on counting either the axles or the bogies), and the UIC classifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |