|
4-2-1 Engine Exhaust System
In an internal combustion engine, the geometry of the exhaust system can be optimised ("tuned") to maximise the power output of the engine. Tuned exhausts are designed so that reflected pressure waves arrive at the exhaust port at a particular time in the combustion cycle. Two-stroke engines Expansion chambers In two-stroke engines where the exhaust port is opened by being uncovered by the piston (rather than by a separate valve), a tuned exhaust system usually consists of an expansion chamber. The expansion chamber is designed to produce a negative pressure wave to assist in filling the cylinder with the next intake charge, and then to produce a positive pressure wave which reduces the amount of fresh intake charge that escapes through the exhaust port (''port blocking''). Uniflow scavenging An alternate design of two-stroke engines is where the exhaust port is opened/closed using a poppet valve and the intake port is piston-controlled (opened by being uncovered by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
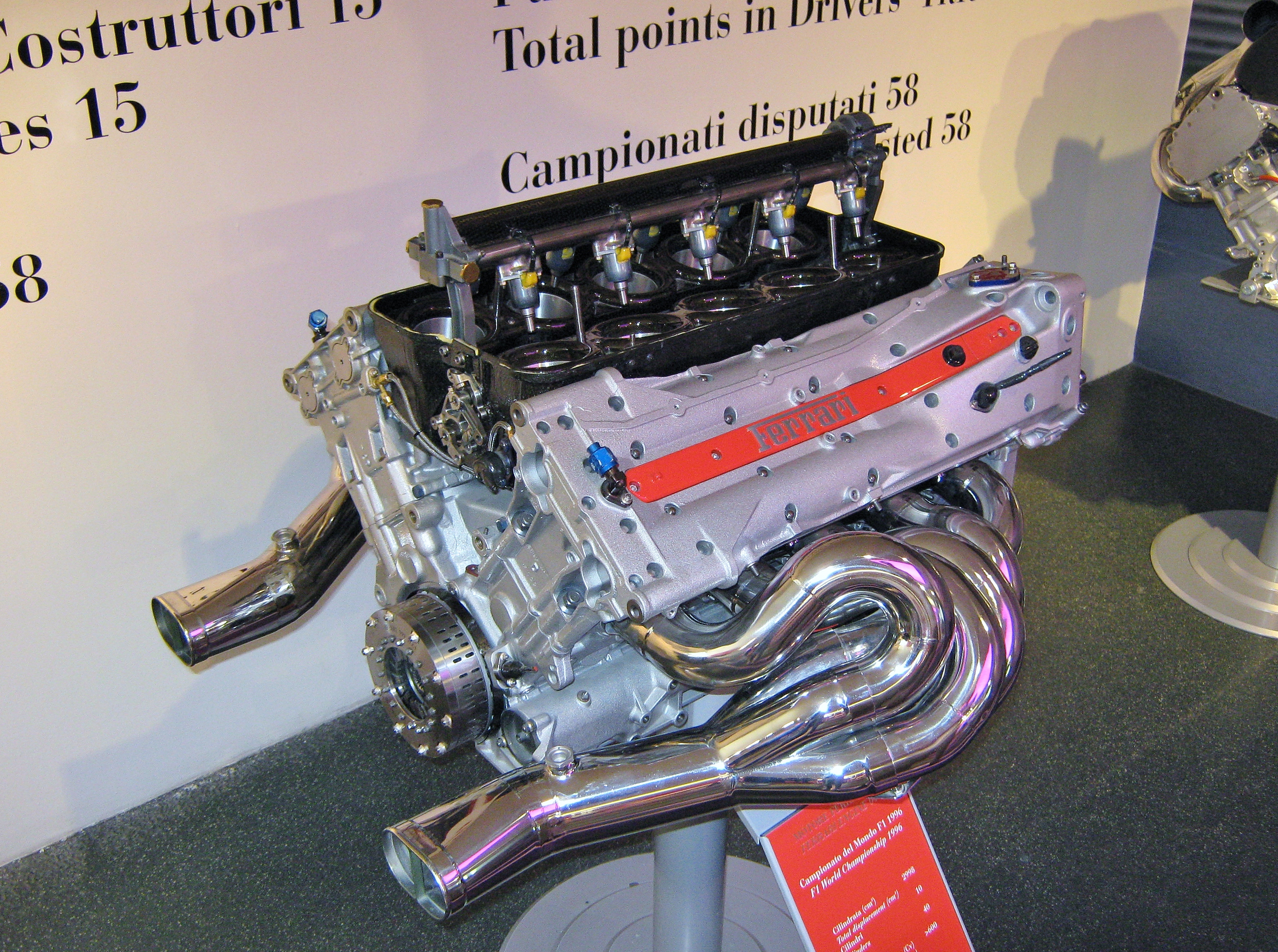
Ferrari V10 - Galleria Ferrari Di Maranello
Ferrari S.p.A. (; ) is an Italian luxury sports car manufacturer based in Maranello. Founded in 1939 by Enzo Ferrari (1898–1988), the company built its first car in 1940, adopted its current name in 1945, and began to produce its current line of road cars in 1947. Ferrari became a public company in 1960, and from 1963 to 2014 it was a subsidiary of Fiat S.p.A. It was spun off from Fiat's successor entity, Fiat Chrysler Automobiles, in 2016. The company currently offers a large model range which includes several supercars, grand tourers, and one SUV. Many early Ferraris, dating to the 1950s and 1960s, count among the most expensive cars ever sold at auction. Throughout its history, the company has been noted for its continued participation in racing, especially in Formula One, where its team, Scuderia Ferrari, is the series' single oldest and most successful. Scuderia Ferrari has raced since 1929, first in Grand Prix events and later in Formula One, where it holds m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragster (car)
A dragster is a specialized competition automobile used in drag racing. Dragsters, also commonly called "diggers", can be broadly placed in three categories, based on the fuel they use: gasoline, methanol, and nitromethane. They are most commonly single-engined, though twin-engined and quad-engined designs did race in the 1950s and 1960s. The design of dragsters evolved from the front-engined rail (named for the exposed frame rails) of the earliest days of drag racing, into the "slingshot" (with the driver between or behind the rear tires, or "slicks") of the early to middle 1960s, to the "modern" type common in the 1970s. Depending on the class they run in, dragsters can be injected or supercharged (or turbocharged), with a variety of possible engines. The engines are most often derived from automobiles'; some early examples used surplus aircraft engines. Today, they may also be electric. Dragsters are distinct from "bodied" cars such as funny cars and gassers, as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scavenging (automotive)
Scavenging is the process of replacing the exhaust gas in a cylinder of an internal combustion engine with the fresh air–fuel mixture (or fresh air, in the case of direct-injection engines) for the next cycle. If scavenging is incomplete, the remaining exhaust gases can cause improper combustion for the next cycle, leading to reduced power output. Scavenging is equally important for both two-stroke and four-stroke engine A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either directi ...s. Most modern four-stroke engines use crossflow cylinder heads and valve timing overlap to scavenge the cylinders. Modern two-stroke engines use either Schnuerle scavenging (also known as "loop scavenging") or uniflow scavenging. The scavenge or scavenging port refers to that port through which clean air ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exhaust System
An exhaust system is used to guide reaction exhaust gases away from a controlled combustion inside an engine or stove. The entire system conveys burnt gases from the engine and includes one or more exhaust pipes. Depending on the overall system design, the exhaust gas may flow through one or more of the following: * Cylinder head and exhaust manifold *A turbocharger to increase engine power. *A catalytic converter to reduce air pollution. *A muffler (North America) / silencer (UK/India), to reduce noise. Design criteria An exhaust pipe must be carefully designed to carry toxic and noxious gases away from the users of the machine. Indoor generators and furnaces can quickly fill an enclosed space with poisonous exhaust gases such as hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, if they are not properly vented to the outdoors. Also, the gases from most machines are scorching; the pipe must be heat-resistant and not pass through or near anything that can burn or be da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kadenacy Effect
The Kadenacy effect is an effect of pressure-waves in gases. It is named after Michel Kadenacy who obtained a French patent for an engine utilizing the effect in 1933. There are also European and US patents. In simple terms, the momentum of the exhaust gas leaving the cylinder of an internal combustion engine creates a pressure-drop in the cylinder which assists the flow of a fresh charge of air, or fuel-air mixture, into the cylinder. The effect can be maximized by careful design of the inlet and exhaust passages. Uses The Kadenacy effect has been utilized in pulse jet engines and in two-stroke piston engines and is important in the design of high-performance motorcycle engines. Pulse jets Two-stroke engines In a two-stroke engine the pressure-drop resulting from the Kadenacy effect assists the flow of a fresh fuel-air mixture charge into the cylinder. However, the Kadenacy effect alone is not sufficient and must be boosted in some way. In small engines this is done by crankcas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exhaust Pulse Pressure Charging
Exhaust pulse pressure charging (EPPC) is a system for supercharging two-stroke diesel engines of the loop-scavenge type. Loop-scavenge engines cannot be pressure-charged in the same way as uniflow engines or four-stroke engines because the inlet and exhaust ports are open at the same time. Overview The engine usually has a Roots blower to provide air for scavenging and this is arranged to deliver excess air so that air follows the exhaust gases into the exhaust manifold. Some of this air is then forced back into the cylinder by a rise in pressure in the exhaust manifold resulting from the exhaust pulse from another cylinder. For additional pressure charging a turbocharger may be fitted, in series with the Roots blower, but a turbocharger cannot be used alone as it would not provide enough air for scavenging at low speeds. Examples Exhaust pulse pressure charging was used by Crossley in these diesel locomotive engines: * the HST-Vee 8, used in the British Rail Class 28, the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expansion Chamber
On a two-stroke engine A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a Thermodynamic power cycle, power cycle with two strokes of the piston, one up and one down, in one revolution of the crankshaft in contrast to a f ..., an expansion chamber or tuned pipe is a tuned exhaust system used to enhance its power (physics), power output by improving its volumetric efficiency. History Expansion chambers were invented and successfully manufactured by Limbach, a German engineer, in 1938, to economize fuel in two stroke engines. Germany was running short of petrol, which was at that stage produced using coal and sewage transformation. An unexpected bonus was that the two stroke engines using tuned exhausts produced far more power than if running with a normal silencer. After the end of the second world war, some time passed before the concept was re-developed by East German Walter Kaaden during the Cold War. They first appeared i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake air, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. Turbochargers are distinguished from superchargers in that a turbocharger is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gases, whereas a is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft). However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. History Prior to the inv ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Band
The power band of an internal combustion engine or electric motor is the range of operating speeds under which the engine or motor is able to output the most power, that is, the maximum energy per unit of time. This usually means that maximum acceleration can be achieved inside this band (often at the cost of lower efficiency). While engines and motors have a large range of operating speeds, the power band is usually a much smaller range of engine speed, only half or less of the total engine speed range (electric motors are an exception—see the section on electric motors below). Specifically, power band is the range of RPM around peak power output. The power band of an internal combustion gasoline automobile engine typically starts at midrange engine speeds (around 4,000 RPM) where maximum torque is produced, and ends below the redline after reaching maximum power (typically between 6,200 RPM and 6,800 RPM). Diesel engines in cars and small trucks may develop maximum torq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firing Order
The firing order of an internal combustion engine is the sequence of ignition for the cylinders. In a spark ignition (e.g. gasoline/petrol) engine, the firing order corresponds to the order in which the spark plugs are operated. In a diesel engine, the firing order corresponds to the order in which fuel is injected into each cylinder. Four-stroke engines must also time the valve openings relative to the firing order, as the valves do not open and close on every stroke. Firing order affects the vibration, sound and evenness of power output from the engine and heavily influences crankshaft design. Cylinder numbering Numbering systems for car engines The numbering system for cylinders is generally based on the cylinder numbers increasing from the front to the rear of an engine (See engine orientation below). However, there are differences between manufacturers in how this is applied; some commonly used systems are as listed below. Straight engine In a straight engine the cylin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scavenging (engine)
Scavenging is the process of replacing the exhaust gas in a cylinder of an internal combustion engine with the fresh air–fuel mixture (or fresh air, in the case of direct-injection engines) for the next cycle. If scavenging is incomplete, the remaining exhaust gases can cause improper combustion for the next cycle, leading to reduced power output. Scavenging is equally important for both two-stroke and four-stroke engines. Most modern four-stroke engines use crossflow cylinder heads and valve timing overlap to scavenge the cylinders. Modern two-stroke engines use either Schnuerle scavenging (also known as "loop scavenging") or uniflow scavenging. The scavenge or scavenging port refers to that port through which clean air enters the cylinder, the exhaust port through which the combustible mix leaves. Origins The first engines deliberately designed to encourage scavenging were gas engines built by Crossley Brothers Ltd in the United Kingdom in the early 1890s. These ''Cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder Head
In a piston engine, the cylinder head sits above the cylinders, forming the roof of the combustion chamber. In sidevalve engines the head is a simple plate of metal containing the spark plugs and possibly heat dissipation fins. In more modern overhead valve and overhead camshaft engines, the head is a more complicated metal block that also contains the inlet and exhaust passages, and often coolant passages, valvetrain components, and fuel injectors. Number of cylinder heads A piston engine typically has one cylinder head per bank of cylinders. Most modern engines with a "straight" (inline) layout today use a single cylinder head that serves all the cylinders. Engines with a "V" layout or "flat" layout typically use two cylinder heads (one for each cylinder bank), however a small number of 'narrow-angle' V engines (such as the Volkswagen VR5 and VR6 engines) use a single cylinder head spanning the two banks. Most radial engines have one head for each cylind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |