|
21-hydroxylase
Steroid 21-hydroxylase is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CYP21A2'' gene. The protein is an enzyme that hydroxylates steroids at the C21 position on the molecule. Naming conventions for enzymes are based on the substrate acted upon and the chemical process performed. Biochemically, this enzyme is involved in the biosynthesis of the adrenal gland hormones aldosterone and cortisol, which are important in blood pressure regulation, sodium homeostasis and blood sugar control. The enzyme converts progesterone and 17α-hydroxyprogesterone into 11-deoxycorticosterone and 11-deoxycortisol, respectively, within metabolic pathways which in humans ultimately lead to aldosterone and cortisol creation—deficiency in the enzyme may cause congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Steroid 21-hydroxylase is a member of the cytochrome P450 family of monooxygenase enzymes that use an iron-containing heme cofactor to oxidize substrates. In humans, the enzyme is localized in endoplasmic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Due To 21-hydroxylase Deficiency
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency (CAH) is a genetic disorder characterized by impaired production of cortisol in the adrenal glands. It is classified as an inherited metabolic disorder. CAH is an autosomal recessive condition since it results from inheriting two copies of the faulty '' CYP21A2'' gene responsible for 21-hydroxylase enzyme deficiency. The most common forms of CAH are: ''classical'' form, usually diagnosed at birth, and ''nonclassical'', late onset form, typically diagnosed during childhood or adolescence, although it can also be identified in adulthood when seeking medical help for fertility concerns or other related issues, such as PCOS or menstrual irregularities. Carriers for the alleles of the nonclassical forms may have no symptoms, such form of CAH is sometimes called ''cryptic'' form. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency in all its forms accounts for over 95% of diagnosed cases of all types of conge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progesterone
Progesterone (; P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the major progestogen in the body. Progesterone has a variety of important functions in the body. It is also a crucial metabolic intermediate in the production of other endogenous steroids, including the sex hormones and the corticosteroids, and plays an important role in brain function as a neurosteroid. In addition to its role as a natural hormone, progesterone is also used as a medication, such as in combination with estrogen for contraception, to reduce the risk of Uterine cancer, uterine or cervical cancer, in hormone replacement therapy, and in feminizing hormone therapy. It was first prescribed in 1934. Biological activity Progesterone is the most important progestogen in the body. As a potent agonist of the progesterone receptor, nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signal transduction, signaling molecules. Examples include the lipid cholesterol, sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, anabolic steroids, and the anti-inflammatory corticosteroid drug dexamethasone. Hundreds of steroids are found in Fungus, fungi, plants, and animals. All steroids are manufactured in cells from a sterols, sterol: Cholesterol, cholesterol (animals), lanosterol (opisthokonts), or cycloartenol (plants). All three of these molecules are produced via Cyclic compound, cyclization of the triterpene squalene. Structure The steroid nucleus (parent structure, core structure) is called gonane (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene). It is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays a central role in the homeostatic regulation of blood pressure, plasma sodium (Na+), and potassium (K+) levels. It does so primarily by acting on the mineralocorticoid receptors in the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the nephron. It influences the reabsorption of sodium and excretion of potassium (from and into the tubular fluids, respectively) of the kidney, thereby indirectly influencing water retention or loss, blood pressure, and blood volume.Marieb Human Anatomy & Physiology 9th edition, chapter:16, page:629, question number:14 When dysregulated, aldosterone is pathogenic and contributes to the development and progression of cardiovascular and kidney disease. Aldosterone has exactly the opposite function of the atrial nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenal Cortex
The adrenal cortex is the outer region and also the largest part of the adrenal gland. It is divided into three separate zones: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. Each zone is responsible for producing specific hormones. It is also a secondary site of androgen synthesis. Layers The adrenal cortex comprises three main zones, or layers that are regulated by distinct hormones as noted below. This ''anatomic zonation'' can be appreciated at the microscopic level, where each zone can be recognized and distinguished from one another based on structural and anatomic characteristics. Zona glomerulosa The outermost layer, the zona glomerulosa is the main site for the production of aldosterone, a mineralocorticoid. The synthesis and secretion of aldosterone are mainly regulated by the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system. The zona glomerulosa cells express a specific enzyme aldosterone synthase (also known as CYP11B2). Aldosterone is largely responsible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monooxygenase
Monooxygenases are enzymes that incorporate one hydroxyl group (−OH) into substrates in many metabolic pathways. In this reaction, the two atoms of dioxygen are reduced to one hydroxyl group and one H2O molecule by the concomitant oxidation of NAD(P)H. One important subset of the monooxygenases, the cytochrome P450 omega hydroxylases, is used by cells to metabolize arachidonic acid (i.e. eicosatetraenoic acid) to the cell signaling molecules, 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid or to reduce or totally inactivate the activate signaling molecules for example by hydroxylating leukotriene B4 to 20-hydroxy-leukotriene B5, 5-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid to 5,20-dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, 5-oxo-eicosatetraenoic acid to 5-oxo-20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid to 12,20-dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids to 20-hydroxy-epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Classification They are classified as oxidoreductase enzymes that catalyze an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heme
Heme (American English), or haem (Commonwealth English, both pronounced /Help:IPA/English, hi:m/ ), is a ring-shaped iron-containing molecule that commonly serves as a Ligand (biochemistry), ligand of various proteins, more notably as a Prosthetic group, component of hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. It is composed of four pyrrole rings with 2 Vinyl group, vinyl and 2 propionic acid side chains. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver. Heme plays a critical role in multiple different redox reactions in mammals, due to its ability to carry the oxygen molecule. Reactions include oxidative metabolism (cytochrome c oxidase, succinate dehydrogenase), xenobiotic detoxification via cytochrome P450 pathways (including Drug metabolism, metabolism of some drugs), gas sensing (Guanylate cyclase, guanyl cyclases, nitric oxide synthase), and microRNA processing (DGCR8). Heme is a coordination complex "consisting of an iron ion coordinated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Cofactor
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound or metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's role as a catalyst (a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction). Cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations. The rates at which these happen are characterized in an area of study called enzyme kinetics. Cofactors typically differ from ligands in that they often derive their function by remaining bound. Cofactors can be classified into two types: inorganic ions and complex organic molecules called coenzymes. Coenzymes are mostly derived from vitamins and other organic essential nutrients in small amounts. (Some scientists limit the use of the term "cofactor" for inorganic substances; both types are included here.) Coenzymes are further divided into two types. The first is called a "prosthetic group", which consists of a coenzyme that is tightly (or even covalently and, therefore, permanently) bound to a protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a part of a transportation system of the eukaryote, eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. The word endoplasmic means "within the cytoplasm", and reticulum is Latin for "little net". It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa. There are two types of ER that share many of the same proteins and engage in certain common activities such as the synthesis of certain lipids and cholesterol. Different types of Cell (biology), cells contain different ratios of the two types of ER dependin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archives Of Neurology
''JAMA Neurology'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal published by the American Medical Association. It was established in 1960 as ''Archives of Neurology'' and obtained its current name in 2013. The journal publishes research on the nervous system as well as the various mechanisms of neurological disease. Its editor-in-chief is S. Andrew Josephson. Naming History Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Index Medicus/MEDLINE/PubMed. According to ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal's 2021 impact factor is 29.907, ranking it 3rd out of 212 titles in the category "Clinical Neurology". See also *List of American Medical Association journals There are thirteen medical journals published by the JAMA Network, a division of the American Medical Association (AMA). The ''Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA)'', along with ''JAMA Network Open'' and eleven specialty journals, co ... References External links * Neurology journal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, and metabolism. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines. Almost all List of life sciences, areas of the life sciences are being uncovered and developed through biochemical methodology and research.#Voet, Voet (2005), p. 3. Biochemistry focuses on understanding the chemical basis that allows biomolecule, biological molecules to give rise to the processes that occur within living Cell (biology), cells and between cells,#Karp, Karp (2009), p. 2. in turn relating greatly to the understanding of tissue (biology), tissues and organ (anatomy), organs as well as organism structure and function.#Miller, Miller (2012). p. 62. Biochemistry is closely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
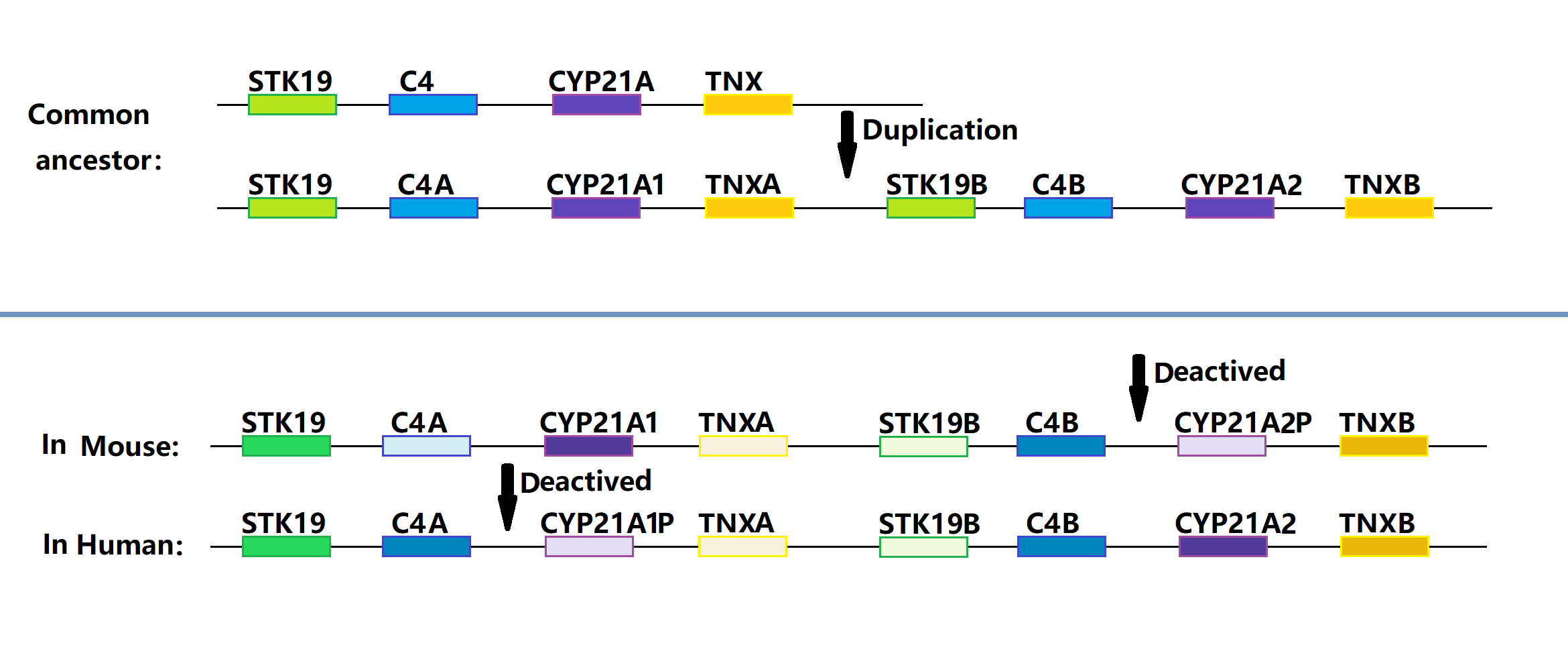
Pseudogene
Pseudogenes are nonfunctional segments of DNA that resemble functional genes. Pseudogenes can be formed from both protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. In the case of protein-coding genes, most pseudogenes arise as superfluous copies of functional genes, either directly by gene duplication or indirectly by Reverse transcriptase, reverse transcription of an mRNA transcript. Pseudogenes are usually identified when genome sequence analysis finds gene-like sequences that lack regulatory sequences or are incapable of producing a functional product. Pseudogenes are a type of junk DNA. Most non-bacterial genomes contain many pseudogenes, often as many as functional genes. This is not surprising, since various biological processes are expected to accidentally create pseudogenes, and there are no specialized mechanisms to remove them from genomes. Eventually pseudogenes may be deleted from their genomes by chance of DNA replication or DNA repair errors, or they may accumulate so many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |