|
20 Nm Process
The "22 nm" node is the process step following 32 nm in CMOS MOSFET semiconductor device fabrication. It was first demonstrated by semiconductor companies for use in RAM in 2008. In 2010, Toshiba began shipping 24 nm flash memory chips, and Samsung Electronics began mass-producing 20 nm flash memory chips. The first consumer-level CPU deliveries using a 22 nm process started in April 2012 with the Intel Ivy Bridge processors. Since at least 1997, "process nodes" have been named purely on a marketing basis, and have no relation to the dimensions on the integrated circuit; neither gate length, metal pitch or gate pitch on a "22nm" device is twenty-two nanometers. The ITRS 2006 Front End Process Update indicates that equivalent physical oxide thickness will not scale below 0.5 nm (about twice the diameter of a silicon atom), which is the expected value at the 22 nm node. This is an indication that CMOS scaling in this area has reached a wall at this poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
32 Nm Process
The "32 nm" node is the step following the "45 nm" process in CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication. "32-nanometre" refers to the average half-pitch (i.e., half the distance between identical features) of a memory cell at this technology level. Toshiba produced commercial 32 GiB NAND flash memory chips with the "32nm" process in 2009. Intel and AMD produced commercial microchips using the "32 nm" process in the early 2010s. IBM and the Common Platform also developed a "32 nm" high-κ metal gate process. Intel began selling its first "32 nm" processors using the Westmere architecture on 7 January 2010. Since at least 1997, "process nodes" have been named purely on a marketing basis, and have no relation to the dimensions on the integrated circuit; neither gate length, nor metal pitch, nor gate pitch on a "32nm" device is thirty-two nanometers. The "28 nm" node is an intermediate half-node die shrink based on the "32 nm" process. The "32 nm" process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Die Shrink
The term die shrink (sometimes optical shrink or process shrink) refers to the List of semiconductor scale examples, scaling of metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) devices. The act of shrinking a Die (integrated circuit), die creates a somewhat identical circuit using a more advanced fabrication process, usually involving an advance of lithographic semiconductor node, nodes. This reduces overall costs for a chip company, as the absence of major architectural changes to the Central processing unit, processor lowers research and development costs while at the same time allowing more processor dies to be manufactured on the same piece of silicon wafer, resulting in less cost per product sold. Die shrinks are the key to lower prices and higher performance at Semiconductor company, semiconductor companies such as Samsung Electronics, Samsung, Intel, TSMC, and SK Hynix, and fabless manufacturers such as Advanced Micro Devices, AMD (including the former ATI Technologies, ATI), Nvidia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
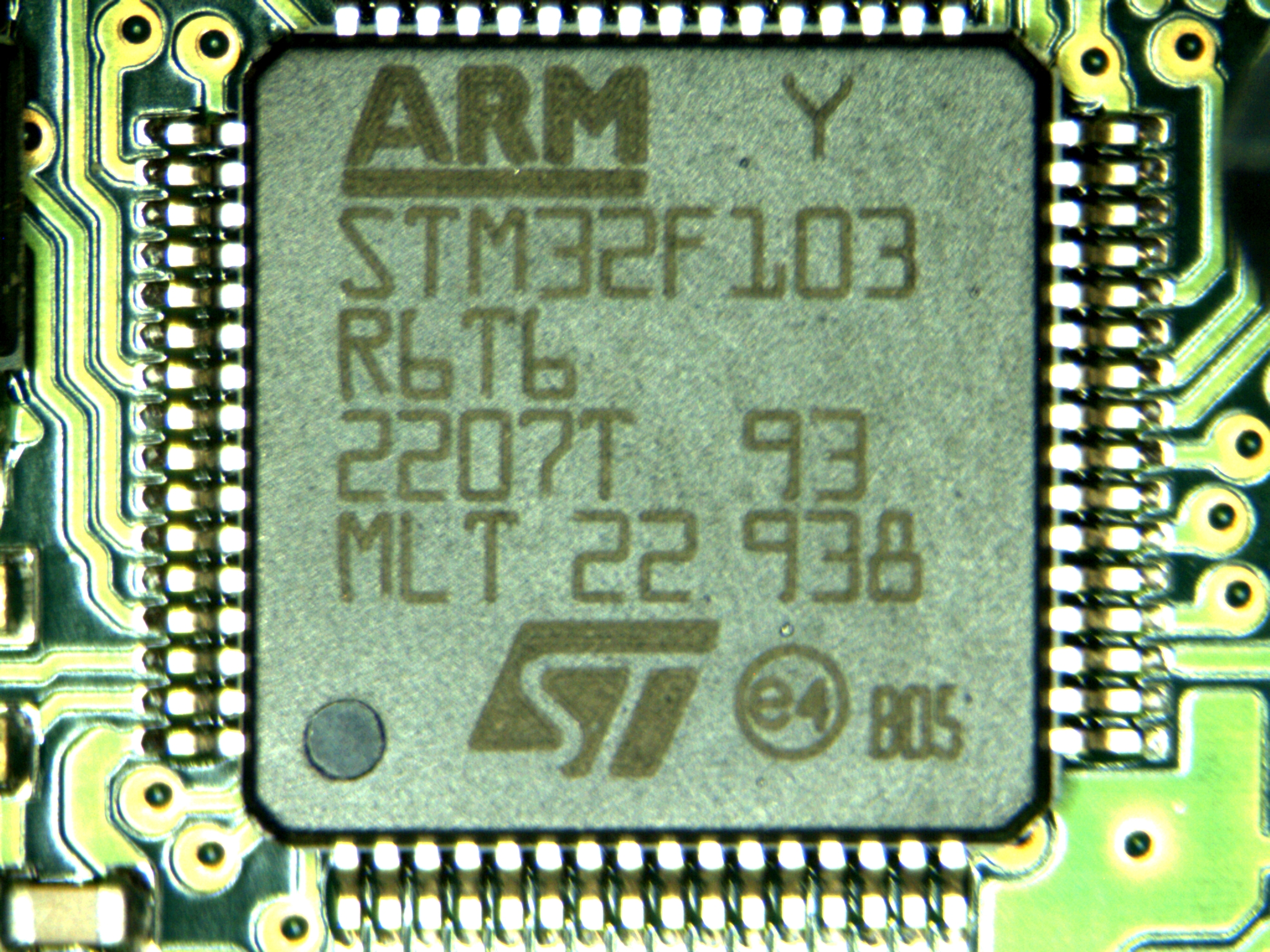
Micron Technology
Micron Technology, Inc. is an American producer of computer memory and computer data storage including dynamic random-access memory, flash memory, and solid-state drives (SSDs). It is headquartered in Boise, Idaho. Micron's consumer products, including the Ballistix line of consumer and gaming memory modules, are marketed under the Crucial brand. Micron and Intel together created IM Flash Technologies, which produced NAND flash memory. It owned Lexar between 2006 and 2017. Micron is the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory. History 1978–1999 Micron was founded in Boise, Idaho, in 1978 by Ward Parkinson, Joe Parkinson, Dennis Wilson, and Doug Pitman as a semiconductor design consulting company. Startup funding was provided by local Idaho businessmen Tom Nicholson, Allen Noble, Rudolph Nelson, and Ron Yanke. Later it received funding from Idaho billionaire J. R. Simplot, whose fortune was made in the potato business. In 1981, the company moved from consulting to manu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel Developer Forum
The Intel Developer Forum (IDF) was a biannual gathering of technologists to discuss Intel products and products based on Intel products. The first IDF was held in 1997. To emphasize the importance of China, the Spring 2007 IDF was held in Beijing instead of San Francisco, and San Francisco and Taipei shared the Fall IDF event in September and October, respectively. Three IDF shows were scheduled in 2008; with the date of IDF San Francisco notably moving to August rather than September. In previous years, events were held in major cities around the world such as San Francisco, Mumbai, Bangalore, Moscow, Cairo, São Paulo, Amsterdam, Munich and Tokyo. On April 17, 2017, Intel announced that it would no longer be hosting IDF. As a result of this announcement, IDF17, which was scheduled for August in San Francisco, was canceled. 2007 events * April 17–18, 2007 – Beijing, China * September 18–20, 2007 – San Francisco, United States * October 15–16, 2007 – Taipei, Taiwan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immersion Lithography
Immersion lithography is a technique used in semiconductor manufacturing to enhance the resolution and accuracy of the lithographic process. It involves using a liquid medium, typically water, between the lens and the wafer during exposure. By using a liquid with a higher refractive index than air, immersion lithography allows for smaller features to be created on the wafer. Immersion lithography replaces the usual air gap between the final lens and the wafer surface with a liquid medium that has a refractive index greater than one. The angular resolution is increased by a factor equal to the refractive index of the liquid. Current immersion lithography tools use highly purified water for this liquid, achieving feature sizes below 45 nanometers. Background The ability to resolve features in optical lithography is directly related to the numerical aperture of the imaging equipment, the numerical aperture being the sine of the maximum refraction angle multiplied by the refracti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometre
The micrometre (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American English), also commonly known by the non-SI term micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI) equalling (SI standard prefix "micro-" = ); that is, one millionth of a metre (or one thousandth of a millimetre, , or about ). The nearest smaller common SI Unit, SI unit is the nanometre, equivalent to one thousandth of a micrometre, one millionth of a millimetre or one billionth of a metre (). The micrometre is a common unit of measurement for wavelengths of infrared radiation as well as sizes of biological cell (biology), cells and bacteria, and for grading wool by the diameter of the fibres. The width of a single human hair ranges from approximately 20 to . Examples Between 1 μm and 10 μm: * 1–10 μm – length of a typical bacterium * 3–8 μm – width of str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wafer (electronics)
In electronics, a wafer (also called a slice or substrate) is a thin slice of semiconductor, such as a crystalline silicon (c-Si, silicium), used for Semiconductor device fabrication, the fabrication of integrated circuits and, in photovoltaics, to manufacture solar cells. The wafer serves as the substrate (materials science), substrate for microelectronic devices built in and upon the wafer. It undergoes many microfabrication processes, such as doping (semiconductor), doping, ion implantation, Etching (microfabrication), etching, thin-film deposition of various materials, and Photolithography, photolithographic patterning. Finally, the individual microcircuits are separated by wafer dicing and Integrated circuit packaging, packaged as an integrated circuit. History In the semiconductor industry, the term wafer appeared in the 1950s to describe a thin round slice of semiconductor material, typically germanium or silicon. The round shape characteristic of these wafers comes f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminal (electronics), terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or Electric current, current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more in miniature form are found embedded in integrated circuits. Because transistors are the key active components in practically all modern electronics, many people consider them one of the 20th century's greatest inventions. Physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld proposed the concept of a field-effect transisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Random Access Memory
Static random-access memory (static RAM or SRAM) is a type of random-access memory (RAM) that uses latching circuitry (flip-flop) to store each bit. SRAM is volatile memory; data is lost when power is removed. The ''static'' qualifier differentiates SRAM from ''dynamic'' random-access memory (DRAM): * SRAM will hold its data permanently in the presence of power, while data in DRAM decays in seconds and thus must be periodically refreshed. * SRAM is faster than DRAM but it is more expensive in terms of silicon area and cost. * Typically, SRAM is used for the cache and internal registers of a CPU while DRAM is used for a computer's main memory. History Semiconductor bipolar SRAM was invented in 1963 by Robert Norman at Fairchild Semiconductor. Metal–oxide–semiconductor SRAM (MOS-SRAM) was invented in 1964 by John Schmidt at Fairchild Semiconductor. The first device was a 64-bit MOS p-channel SRAM. SRAM was the main driver behind any new CMOS-based technology fabrica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
College Of Nanoscale Science And Engineering
The College of Nanotechnology, Science, and Engineering is part of the University at Albany, SUNY in Albany, New York. Founded in 2004 at the University at Albany, SUNY, the college underwent rapid expansion in the late-2000s and early-2010s before merging with the SUNY Institute of Technology in 2014. The college rejoined the University at Albany in 2023. The college was the first college in the United States devoted to nanotechnology. History The College of Nanoscale Science and Engineering was originally established as the School of Nanosciences and Nanoengineering at the University at Albany in 2001 (part of the College of Arts and Sciences). CNSE was accredited as the College of Nanoscale Science and Engineering of the University at Albany in 2004, and in December of that year, awarded its first Ph.D. degrees in nanoscience. In July 2013, SUNY's Board of Trustees approved a memorandum that led to the separation of CNSE from the University at Albany and included the creatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STMicroelectronics
STMicroelectronics Naamloze vennootschap, NV (commonly referred to as ST or STMicro) is a European multinational corporation, multinational semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company. It is the largest of such companies in Europe. It was founded in 1987 from the merger of two state-owned semiconductor corporations: ''Thomson Semiconducteurs'' of United States/France and ''SGS Microelettronica'' of Italy. The company is incorporated in the Netherlands and headquartered in Plan-les-Ouates, Switzerland. Its shares are traded on Euronext Paris, the Borsa Italiana and the New York Stock Exchange. History ST was formed in 1987 by the merger of two government-owned semiconductor companies: Italian SGS Microelettronica (where SGS stands for ''Società Generale Semiconduttori'', "General Semiconductor Company"), and French ''Thomson Semiconducteurs'', the semiconductor arm of Thomson SA, Thomson. SGS Microelettronica originated in 1972 from a previous merger of two compan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freescale
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. was an American semiconductor manufacturer. It was created by the divestiture of the Semiconductor Products Sector of Motorola in 2004. Freescale focused their integrated circuit products on the automotive, embedded and communications markets. It was bought by a private investor group in 2006, and subsequently merged with NXP Semiconductors in 2015. History Divestiture from Motorola and first IPO As of 2003, Motorola Semiconductor Products Sector earned US$5.0 billion in semiconductor sales in 2002 (out of US$27 billion sales for all of Motorola). Motorola announced that their semiconductor division would be divested on October 6, 2003 and would have a temporary name ''SPS Spinco''. Freescale completed its Initial public offering (IPO) on July 16, 2004, at a price of US$13. In its announcement, it estimated the stock price to be US$17.50- 19.50 but following a cooling of the market towards tech stocks, it lowered its price to US$13. Existing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |