|
2008–14 Irish Protests
The anti-austerity movement in Ireland saw major demonstrations from 2008 (the year of the Irish economic downturn) to 2015. The protests began during October 2008 after the Fianna Fáil–Green Party coalition of the 30th Dáil oversaw the implementation of the bank guarantee, and were given further impetus by the late 2010 intervention of the European Union/European Central Bank/International Monetary Fund troika and the collapse of that government early the following year. Protests continued during the Fine Gael– Labour coalition of the 31st Dáil. Background The post-2008 Irish economic downturn coincided with a series of banking scandals, followed the 1990s and 2000s Celtic Tiger period of rapid real economic growth fuelled by foreign direct investment, a subsequent property bubble which rendered the real economy uncompetitive, and an expansion in bank lending in the early 2000s. An initial slowdown in economic growth amid the international 2008 financial crisis grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euro Area Crisis
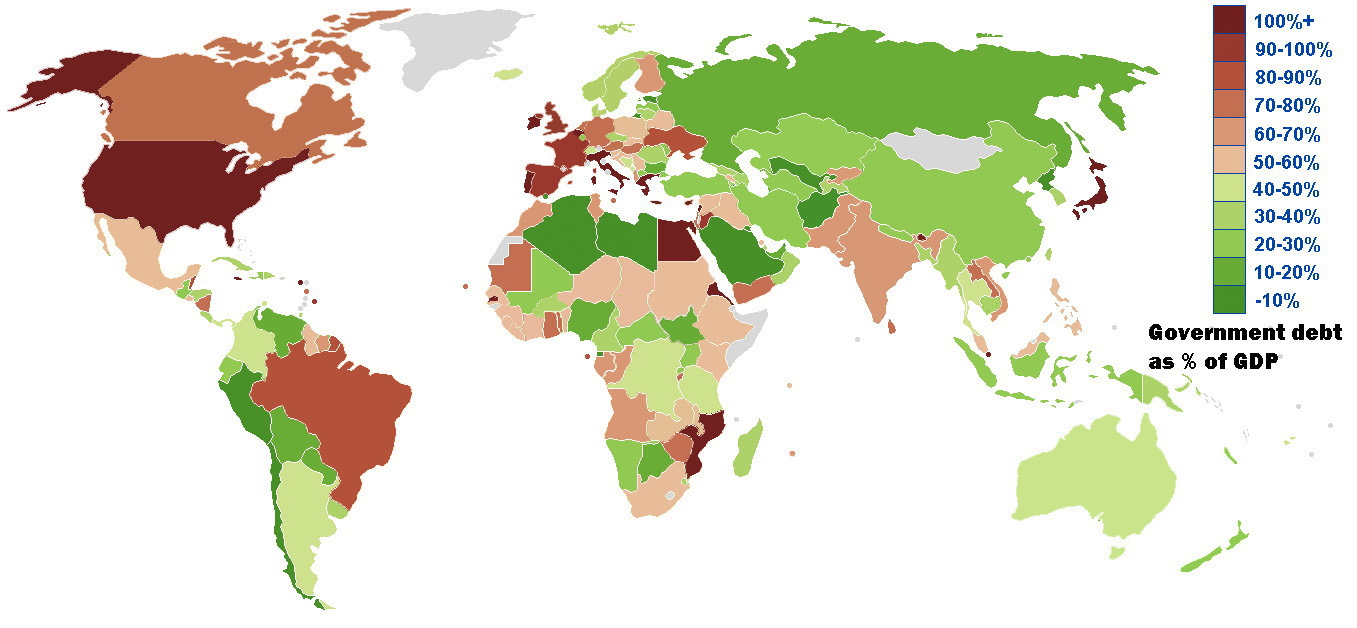
The euro area crisis, often also referred to as the eurozone crisis, European debt crisis, or European sovereign debt crisis, was a multi-year debt crisis and financial crisis in the European Union (EU) from 2009 until, in Greece, 2018. The eurozone member states of Greece, Portugal, Ireland, and Cyprus were unable to repay or refinance their government debt or to bailout fragile banks under their national supervision and needed assistance from other eurozone countries, the European Central Bank (ECB), and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). The crisis included the Greek government-debt crisis, the 2008–2014 Spanish financial crisis, the 2010–2014 Portuguese financial crisis, the post-2008 Irish banking crisis and the post-2008 Irish economic downturn, as well as the 2012–2013 Cypriot financial crisis. The crisis contributed to changes in leadership in Greece, Ireland, France, Italy, Portugal, Spain, Slovenia, Slovakia, Belgium, and the Netherlands as well as in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fine Gael
Fine Gael ( ; ; ) is a centre-right, liberal-conservative, Christian democratic political party in Ireland. Fine Gael is currently the third-largest party in the Republic of Ireland in terms of members of Dáil Éireann. The party had a membership of 25,000 in 2021. Simon Harris succeeded Leo Varadkar as party leader on 24 March 2024. Fine Gael was founded on 8 September 1933, following the merger of its parent party Cumann na nGaedheal, the National Centre Party and the Blueshirts. Its origins lie in the struggle for Irish independence and the pro-Treaty side in the Irish Civil War, with the party claiming the legacy of Michael Collins. In its early years, the party was commonly known as ''Fine Gael – The United Ireland Party'', abbreviated ''UIP'', and its official title in its constitution remains Fine Gael (United Ireland). Fine Gael holds a pro-European stance and is generally considered to be more of a proponent of economic liberalism than its traditional rival, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RTÉ News
RTÉ News and Current Affairs (), also known simply as RTÉ News (''Nuacht RTÉ''), is the national news service provided by Irish public broadcaster (RTÉ). Its services include local, national, European and international news, investigative journalism and current affairs programming for RTÉ television, radio, online, podcasts, on-demand and for independent Irish language public broadcaster TG4. It is the largest and most popular news source in Ireland – with 77% of the Irish public regarding it as their main source of Irish and international news. It broadcasts in English language, English, Irish language, Irish and Irish Sign Language. The organisation is also a source of commentary on current affairs. The division is based at the RTÉ Television Centre in Donnybrook, Dublin, Donnybrook, Dublin; however, the station also operates regional bureaux across Ireland and the world. History Early history On 1 January 1926, 2RN, Ireland's first radio station, began broadcasting. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Stock Exchange
Euronext Dublin (formerly the Irish Stock Exchange, ISE; ) is Ireland's main stock exchange, and has been in existence since 1793. The Euronext Dublin lists debt and fund securities and is used as a European gateway exchange for companies seeking to access investors in Europe and beyond. With over 35,000 securities listed on its markets, the exchange is used by over 4,000 issuers from more than 85 countries to raise funds and access international investors. A study by Indecon (international economic consultants) published in 2014 on the Irish Stock Exchange found that having a local stock market and securities industry directly supports 2,100 jobs in Ireland and is worth €207 million each year to the Irish economy. It also found that having a domestic securities industry centred on the Irish Stock Exchange generates €207 million in estimated direct economic impact (measured in Gross Value Added or GDP) and €230 million in direct tax for the Irish exchequer (including stam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction that occurs when there is a period of broad decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be triggered by various events, such as a financial crisis, an external trade shock, an adverse supply shock, the bursting of an economic bubble, or a large-scale Anthropogenic hazard, anthropogenic or natural disaster (e.g. a pandemic). There is no official definition of a recession, according to the International Monetary Fund, IMF. In the United States, a recession is defined as "a significant decline in economic activity spread across the market, lasting more than a few months, normally visible in real GDP, real income, employment, industrial production, and wholesale-retail sales." The European Union has adopted a similar definition. In the United Kingdom and Canada, a recession is defined as negative economic growth for two consecutive qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2008 Financial Crisis
The 2008 financial crisis, also known as the global financial crisis (GFC), was a major worldwide financial crisis centered in the United States. The causes of the 2008 crisis included excessive speculation on housing values by both homeowners and financial institutions that led to the 2000s United States housing bubble, exacerbated by predatory lending for subprime mortgages and deficiencies in regulation. Cash out refinancings had fueled an increase in consumption that could no longer be sustained when home prices declined. The first phase of the crisis was the subprime mortgage crisis, which began in early 2007, as mortgage-backed securities (MBS) tied to U.S. real estate, and a vast web of Derivative (finance), derivatives linked to those MBS, collapsed in value. A liquidity crisis spread to global institutions by mid-2007 and climaxed with the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers in September 2008, which triggered a stock market crash and bank runs in several countries. The crisis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Property Bubble
The Irish property bubble was the speculative excess element of a long-term price increase of real estate in the Republic of Ireland from the early 2000s to 2007, a period known as the later part of the Celtic Tiger. In 2006, the prices peaked at the top of the bubble, with a combination of increased speculative construction (financed almost entirely by senior debt) and rapidly rising prices; in 2007 the prices first stabilised and then started to fall until 2010 following the shock effect of the Great Recession. By the second quarter of 2010, house prices in Ireland had fallen by 35% compared with the second quarter of 2007, and the number of housing loans approved fell by 73%. The collapse of the property bubble was one of the major contributing factors to the post-2008 Irish banking crisis. House prices in Dublin, the largest city, were briefly down 56% from their peak and apartment prices down over 62%. For a time, house prices returned to twentieth century levels and mort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
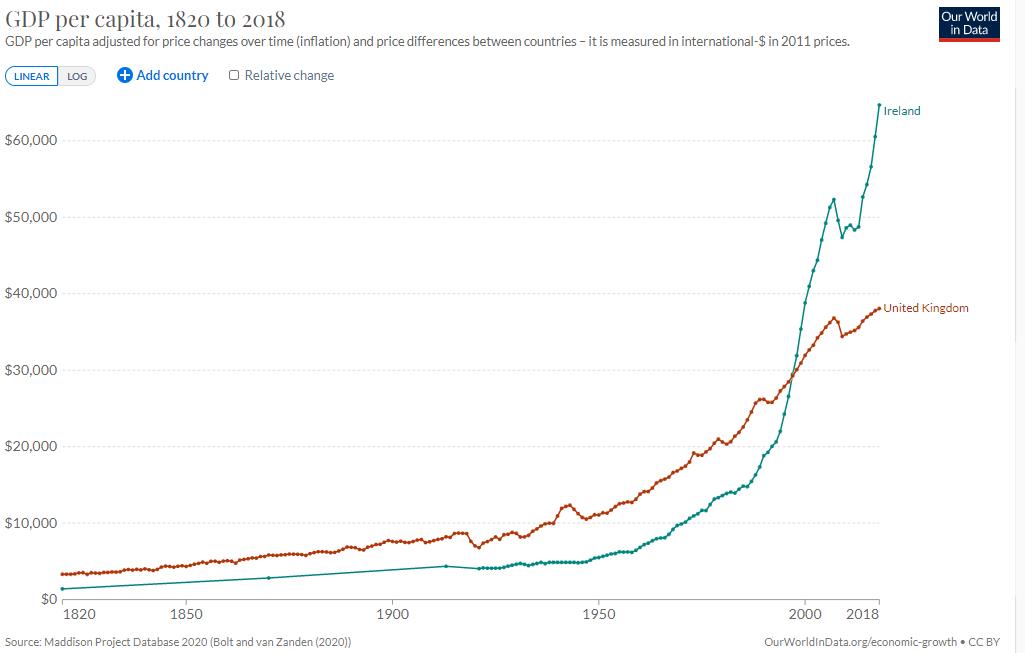
Celtic Tiger
The "Celtic Tiger" () is a term referring to the economy of the Republic of Ireland, economy of Ireland from the mid-1990s to the late 2000s, a period of rapid real economic growth fuelled by foreign direct investment. The boom was dampened by a subsequent property bubble which resulted in a severe economic downturn. At the start of the 1990s, Ireland was a relatively poor country by Western European standards, with high poverty, high unemployment, inflation, and low economic growth. The Irish economy expanded at an average rate of 9.4% between 1995 and 2000, and continued to grow at an average rate of 5.9% during the following decade until 2008, when it Post-2008 Irish economic downturn, fell into recession. Ireland's rapid economic growth has been described as a rare example of a Western country matching the growth of East Asian nations, i.e. the 'Four Asian Tigers'. The economy underwent a dramatic reversal from 2008, affected by the Great Recession and ensuing European deb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University College Dublin
University College Dublin (), commonly referred to as UCD, is a public research university in Dublin, Ireland, and a collegiate university, member institution of the National University of Ireland. With 38,417 students, it is Ireland's largest university. UCD originates in a body founded in 1854, which opened as the Catholic University of Ireland on the feast of Saint Malachy, St. Malachy with John Henry Newman as its first rector; it re-formed in 1880 and chartered in its own right in 1908. The Universities Act, 1997 renamed the constituent university as the "National University of Ireland, Dublin", and a ministerial order of 1998 renamed the institution as "University College Dublin – National University of Ireland, Dublin". Originally located at St Stephen's Green and National Concert Hall, Earlsfort terrace in Dublin's city centre, all faculties later relocated to a campus at Belfield, Dublin, Belfield, six kilometres to the south of the city centre. In 1991, it purchas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinity College Dublin
Trinity College Dublin (), officially titled The College of the Holy and Undivided Trinity of Queen Elizabeth near Dublin, and legally incorporated as Trinity College, the University of Dublin (TCD), is the sole constituent college of the University of Dublin in the Republic of Ireland. Founded by Queen Elizabeth I in 1592 through a royal charter, it is one of the extant seven "ancient university, ancient universities" of Great Britain and Ireland. Trinity contributed to Irish literature during the Georgian era, Georgian and Victorian era, Victorian eras, and areas of the natural sciences and medicine. Trinity was established to consolidate the rule of the Tudor dynasty, Tudor monarchy in Ireland, with Provost (education), Provost Adam Loftus (bishop), Adam Loftus christening it after Trinity College, Cambridge. Built on the site of the former Priory of All Hallows demolished by King Henry VIII, it was the Protestant university of the Protestant Ascendancy, Ascendancy ruling eli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Social Protection
The Department of Social Protection () is a department of the Government of Ireland, tasked with administering Ireland's social welfare system. It oversees the provision of income support and other social services. It is led by the Minister for Social Protection. Departmental team The official headquarters and ministerial offices of the department are in Áras Mhic Dhiarmada, Store Street, Dublin. The departmental team consists of the following: * Minister for Social Protection: Dara Calleary, TD *Secretary General of the Department: John McKeon Overview In carrying out its mandate the department undertakes a variety of functions including: The department formulates appropriate social protection policies and administers and manages the delivery of statutory and non-statutory schemes and services. It is responsible for the delivery of a range of social insurance and social assistance schemes including provision for unemployment, illness, maternity, caring, widowhood, retire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |