|
2003 Connaught Creek Valley Avalanche
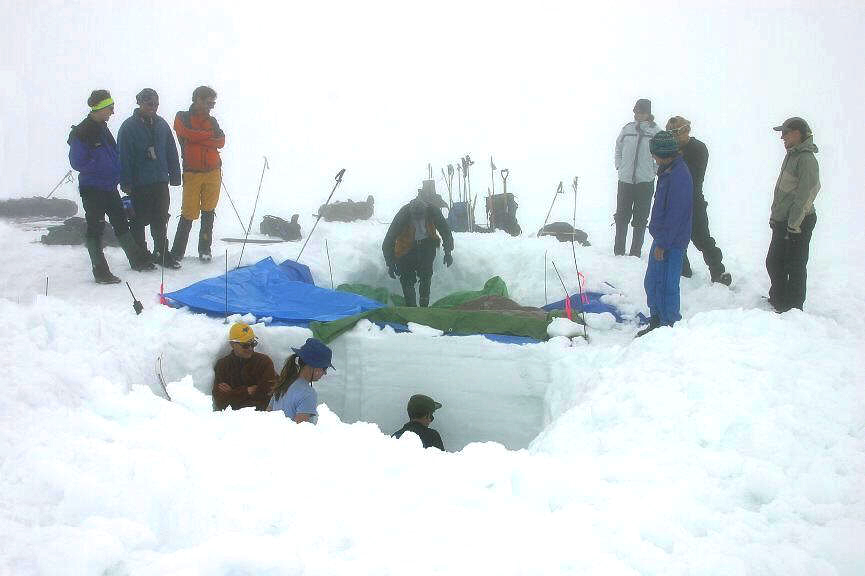
The 2003 Connaught Creek Valley avalanche on Saturday, 1 February 2003 killed seven teenagers in the Columbia Mountains at the foot of Mount Cheops east of Revelstoke, following another avalanche which had killed seven adult skiers on 20 January 2003 on the Durrand Glacier, located in the same area and caused by a rain crust formed at the same time. Background The 14 scholars and their three adult group leaders, two of whom were experienced skiers and trained in avalanche education, were from Strathcona-Tweedsmuir School near Okotoks. They were on the annual 10th grade class backcountry skiing trip, a four-day trip and a 27-year-old tradition of the school's outdoor education program. The group were hiking along the Balu Pass Trail in the Connaught Creek Valley in British Columbia's Glacier National Park, some 5 km west of the Rogers Pass summit, scene of the 1910 avalanche disaster. Those on the trip were educated in avalanche and other potential dangers of the area. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia Mountains
The Columbia Mountains are a group of mountain ranges along the upper Columbia River in British Columbia, Montana, Idaho and Washington. The mountain range covers 135,952 km² (52,491 sq mi). The range is bounded by the Rocky Mountain Trench on the east, and the Kootenai River on the south; their western boundary is the edge of the Interior Plateau. Seventy-five percent of the range is located in Canada and the remaining twenty-five percent in the United States; American geographic classifications place the Columbia Mountains as part of the Rocky Mountains complex, but this designation does not apply in Canada (despite a British Columbia government tourism campaign to rebrand their southern portion as the "Kootenay Rockies"). Mount Sir Sandford is the highest mountain in the range, reaching . Mountain ranges The Columbia Mountains are made up of four large ranges containing many subranges: * Cariboo Mountains ** Lunn Icefield ** Mowdish Range ** Premier Range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
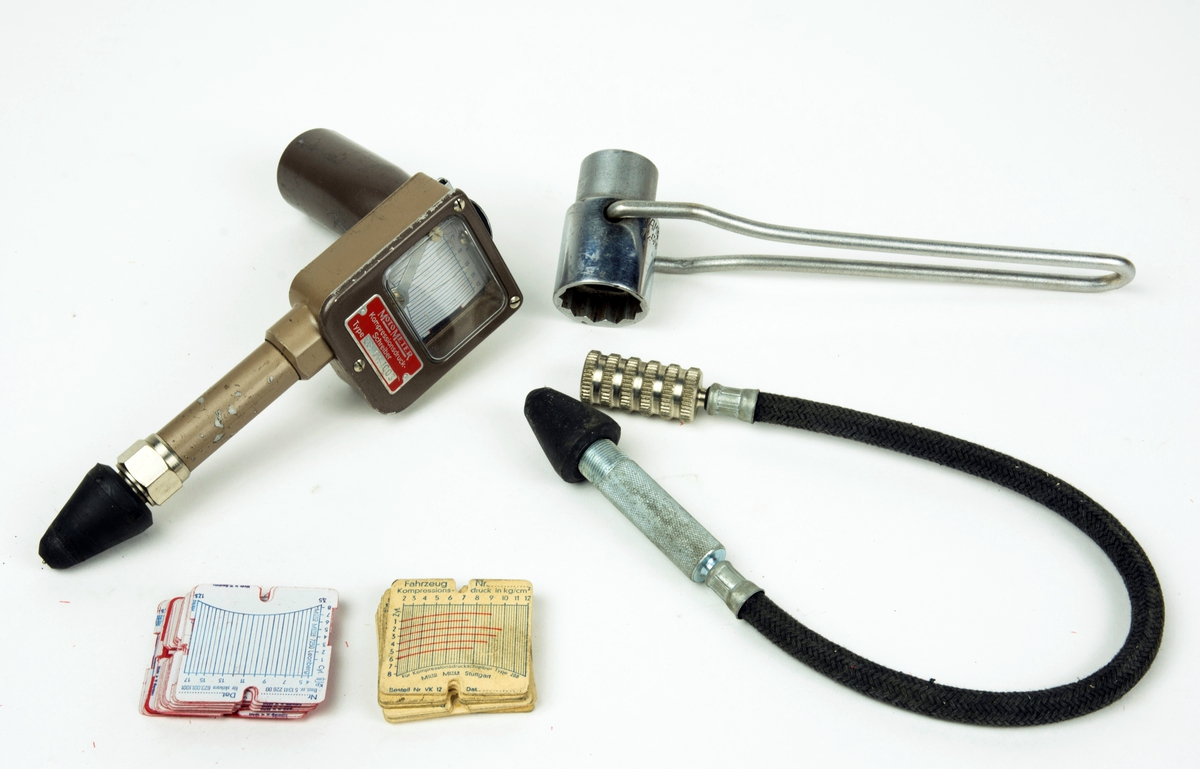
Compression Test
A leak-down tester is a measuring instrument used to determine the condition of internal combustion engines by introducing compressed air into the cylinder and measuring the rate at which it leaks out. Compression testing is a crude form of leak-down testing which also includes effects due to compression ratio, valve timing, cranking speed, and other factors. Compression tests should normally be done with all spark plugs removed to maximize cranking speed. Cranking compression is a dynamic test of the actual low-speed pumping action, where peak cylinder pressure is measured and stored. Leak-down testing is a static test. Leak-down tests cylinder leakage paths. Leak-down primarily tests pistons and rings, seated valve sealing, and the head gasket. Leak-down will not show valve timing and movement problems, or piston movement related sealing problems. Any test should include both compression and leak-down. Testing is done on an engine which is not running, and normally with the tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
February 2003 Events In Canada
February is the second month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The month has 28 days in common years or 29 in leap years, with the 29th day being called the ''leap day''. It is the first of five months not to have 31 days (the other four being April, June, September, and November) and the only one to have fewer than 30 days. February is the third and last month of meteorological winter in the Northern Hemisphere. In the Southern Hemisphere, February is the third and last month of meteorological summer (being the seasonal equivalent of what is August in the Northern Hemisphere). Pronunciation "February" is pronounced in several different ways. The beginning of the word is commonly pronounced either as or ; many people drop the first "r", replacing it with , as if it were spelled "Febuary". This comes about by analogy with "January" (), as well as by a dissimilation effect whereby having two "r"s close to each other causes one to change. The ending of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Disasters In British Columbia
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena. The word ''nature'' is borrowed from the Old French ''nature'' and is derived from the Latin word ''natura'', or "essential qualities, innate disposition", and in ancient times, literally meant "birth". In ancient philosophy, ''natura'' is mostly used as the Latin translation of the Greek word ''physis'' (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics of plants, animals, and other features of the world to develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2000s Avalanches
S, or s, is the nineteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ess'' (pronounced ), plural ''esses''. History Origin Northwest Semitic šîn represented a voiceless postalveolar fricative (as in 'ip'). It originated most likely as a pictogram of a tooth () and represented the phoneme via the acrophonic principle. Ancient Greek did not have a phoneme, so the derived Greek letter sigma () came to represent the voiceless alveolar sibilant . While the letter shape Σ continues Phoenician ''šîn'', its name ''sigma'' is taken from the letter ''samekh'', while the shape and position of ''samekh'' but name of ''šîn'' is continued in the '' xi''. Within Greek, the name of ''sigma'' was influenced by its association with the Greek word (earlier ) "to hiss". The original name of the letter "sigma" may have been ''san'', but due to the complica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2003 In British Columbia
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societies. Evolution of the Arabic digit The use of three lines to denote the number 3 occurred in many writing systems, including some (like Roman and Chinese numerals) that are still in use. That was also the original representation of 3 in the Brahmic (Indian) numerical notation, its earliest forms aligned vertically. However, during the Gupta Empire the sign was modified by the addition of a curve on each line. The Nāgarī script rotated the lines clockwise, so they appeared horizontally, and ended each line with a short downward stroke on the right. In cursive script, the three strokes were eventually connected to form a glyph resembling a with an additional stroke at the bottom: ३. The Indian digits spread to the Caliphate in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disasters In Schools
A disaster is a serious problem occurring over a short or long period of time that causes widespread human, material, economic or environmental loss which exceeds the ability of the affected community or society to cope using its own resources. Disasters are routinely divided into either "natural disasters" caused by natural hazards or "human-instigated disasters" caused from anthropogenic hazards. However, in modern times, the divide between natural, human-made and human-accelerated disasters is difficult to draw. Examples of natural hazards include avalanches, flooding, cold waves and heat waves, droughts, earthquakes, cyclones, landslides, lightning, tsunamis, volcanic activity, wildfires, and winter precipitation. Examples of anthropogenic hazards include criminality, civil disorder, terrorism, war, industrial hazards, engineering hazards, power outages, fire, hazards caused by transportation, and environmental hazards. Developing countries suffer the greates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avalanche Transceiver
An avalanche transceiver or avalanche beacon is a type of emergency locator beacon, a radio transceiver (a transmitter and receiver in one unit) operating at 457 kHz for the purpose of finding people buried under snow. They are widely carried by skiers, particularly back country skiers for use in case a skier is buried by an avalanche. Before setting out on an expedition, all the members of a group activate their transceivers in the transmit mode, causing the device to emit low-power pulsed radio signals during the trip. Following an avalanche, if some members of the ski party are buried, the others may switch their transceivers from transmit into receive mode, allowing use as a radio direction finding device to search for signals coming from the lost skiers. The avalanche beacon is an active device powered by batteries; a ski suit may also contain a passive RECCO transponder sewn into the clothing. Early avalanche transceivers transmitted at 2.275 kHz. In 1986, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snowpack
Snowpack forms from layers of snow that accumulate in geographic regions and high elevations where the climate includes cold weather for extended periods during the year. Snowpacks are an important water resource that feed streams and rivers as they melt. Therefore, snowpacks are both the drinking water source for many communities and a potential source of flooding (in case of sudden melting). Snowpacks also contribute mass to glaciers in their accumulation zone. Assessing the formation and stability of snowpacks is important in the study and prediction of avalanches. Scientists study the physical properties of snow under different conditions and their evolution, and more specifically snow metamorphism, snow hydrology (that is, the contribution of snow melt to catchment hydrology), the evolution of snow cover with climate change and its effect on the ice–albedo feedback and hydrology, both on the ground and by using remote sensing. Snow is also studied in a more global contex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rain Crust
A Melt-Freeze Crust or Rain Crust is a discontinuity between snow layers which can lead to avalanches. The layer can be created in two ways: *A temperature high enough to allow surface snow to melt, creating a layer of melt water which may later re-freeze. *Rain falling and freezing on the surface of existing snow, also creating a frozen layer. This layer is brittle, smooth and slippery, and does not bond with snow layers above it, allowing the overlying slab of snow to move down the mountain under gravity In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the str ... when disturbed or if the accumulated snowfall exceeds a critical mass. The initial slab may be as large as 10,000m² and 10 metres thick. References {{reflist Snow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1910 Rogers Pass Avalanche
The 1910 Rogers Pass Avalanche killed 58 men clearing a railroad line just outside of Revelstoke in Rogers Pass through the Selkirk Mountains in British Columbia on March 4, 1910. It is Canada's worst avalanche disaster. Rogers Pass The Canadian Pacific Railway's line through Rogers Pass completed its transcontinental railroad through to Canada's west coast, and at the time was the only such link. It was therefore of vital importance to keep it open through the winter months. Although completed in November 1885 it was soon abandoned as throughout that winter, up to 12 metres of snow buried the line and avalanches tore away newly-laid sections of track. A costly system of 31 'snow sheds' was constructed to protect the most vulnerable sections of line, covering in all. However, most of the route through the pass was still unprotected, meaning that men and equipment were often called upon to clear the track. March 1910 The winter of 1909–1910 provided conditions particularly cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rogers Pass (British Columbia)
Rogers Pass is a high mountain pass through the Selkirk Mountains of British Columbia, but the term also includes the approaches used by the Canadian Pacific Railway (CP) and the Trans-Canada Highway. In the heart of Glacier National Park, this tourism destination since 1886 is a National Historic Site. Topography Rogers Pass is the lowest route between the Sir Donald and Hermit ranges of the Selkirks, providing a shortcut along the southern perimeter of the Big Bend of the Columbia River from Revelstoke on the west to Donald, near Golden, on the east. The pass is formed by the headwaters of the Illecillewaet River to the west and by the Beaver River to the east. These rivers are tributaries of the Columbia, which arcs to the north. Railway Proposal & planning During the 1870s, when the transcontinental was being planned, the preferred route through the Canadian Rockies was the northerly Yellowhead Pass. After awarding the contract, the government allowed CP to amend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


