|
1 E-9 S
A nanosecond (ns) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one billionth of a second, that is, of a second, or seconds. The term combines the SI prefix ''nano-'' indicating a 1 billionth submultiple of an SI unit (e.g. nanogram, nanometre, etc.) and ''second'', the primary unit of time in the SI. A nanosecond is to one second, as one second is to approximately 31.69 years. A nanosecond is equal to 1000 picoseconds or microsecond. Time units ranging between 10 and 10 seconds are typically expressed as tens or hundreds of nanoseconds. Time units of this granularity are commonly found in telecommunications, pulsed lasers, and related aspects of electronics. Common measurements * 0.001 nanoseconds – one picosecond * 0.96 nanoseconds – 100 Gigabit Ethernet Interpacket gap * 96 nanoseconds – Gigabit Ethernet Interpacket gap * 1.0 nanosecond – cycle time of an electromagnetic wave with a frequency of 1 GHz (). * 1.0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time
Time is the continuous progression of existence that occurs in an apparently irreversible process, irreversible succession from the past, through the present, and into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, to compare the duration of events (or the intervals between them), and to quantify rates of change of quantities in material reality or in the qualia, conscious experience. Time is often referred to as a fourth dimension, along with Three-dimensional space, three spatial dimensions. Time is one of the seven fundamental physical quantities in both the International System of Units (SI) and International System of Quantities. The SI base unit of time is the second, which is defined by measuring the electronic transition frequency of caesium atoms. General relativity is the primary framework for understanding how spacetime works. Through advances in both theoretical and experimental investigations of spacetime, it has been shown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves), phase'' on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings. Wavelength is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The multiplicative inverse, inverse of the wavelength is called the ''spatial frequency''. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter lambda (''λ''). For a modulated wave, ''wavelength'' may refer to the carrier wavelength of the signal. The term ''wavelength'' may also apply to the repeating envelope (mathematics), envelope of modulated waves or waves formed by Interference (wave propagation), interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed phase velocity, wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shake (time)
A shake is an informal metric unit of time equal to 10 nanoseconds, or 10−8 seconds. It was originally coined for use in nuclear physics, helping to conveniently express the timing of various events in a nuclear reaction. Etymology Like many informal units having to do with nuclear physics, it arose from top secret operations of the Manhattan Project during World War II. The word "shake" was taken from the idiomatic expression "in two shakes of a lamb's tail", which indicates a very short time interval. The phrase "a couple of shakes", in reference to the measurement of time, may have been popularized by Richard Barham's '' Ingoldsby Legends'' (1840); however, the phrase was already part of vernacular language long before that. Nuclear physics For nuclear-bomb designers, the term was a convenient name for the short interval, rounded to 10 nanoseconds, which was frequently seen in their measurements and calculations: The typical time required for one step in a chain rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
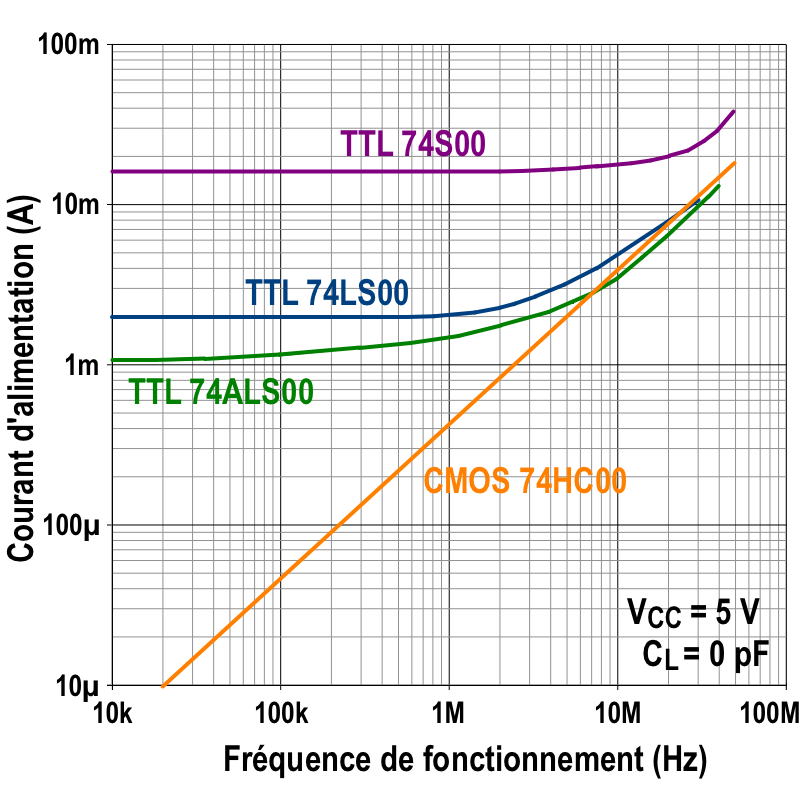
HCMOS
HCMOS ("high-speed CMOS") is the set of specifications for electrical ratings and characteristics, forming the 74HC00 family, a part of the 7400 series of integrated circuits.HCMOS family characteristics , Philips Semiconductors, March 1988 The 74HC00 family followed, and improved upon, the 74C00 series (which provided an alternative CMOS logic family to the 4000 series but retained the part number scheme and pinouts of the standard 7400 series
The 7400 series is a popular logic family of transistor–transistor logic (TTL) integrated circuits ( ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7400-series Integrated Circuits
The 7400 series is a popular logic family of transistor–transistor logic (TTL) integrated circuits (ICs). In 1964, Texas Instruments introduced the SN5400 series of logic chips, in a ceramic semiconductor package. A low-cost plastic package SN7400 series was introduced in 1966 which quickly gained over 50% of the logic chip market, and eventually becoming ''de facto'' standardized electronic components. Since the introduction of the original bipolar-transistor TTL parts, pin-compatible parts were introduced with such features as low power CMOS technology and lower supply voltages. Surface mount packages exist for several popular logic family functions. Overview The 7400 series contains hundreds of devices that provide everything from basic logic gates, flip-flops, and counters, to special purpose bus transceivers and arithmetic logic units (ALU). Specific functions are described in a list of 7400 series integrated circuits. Some TTL parts were made with an ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propagation Delay
Propagation delay is the time duration taken for a signal to reach its destination, for example in the electromagnetic field, a wire, speed of sound, gas, fluid or seismic wave, solid body. Physics * An electromagnetic wave travelling through a medium has a propagation delay determined by the speed of light in that particular medium, or ca. 1 nanosecond per in a vacuum. * An electric signal travelling through a wire has an propagation delay of ca. 1 nanosecond per . See also radio propagation, velocity factor, signal velocity and mechanical wave. Electronics Logic gates can have a gate delay ranging from picoseconds to more than 10 nanoseconds, depending on the technology being used. It is the time between the gate input becoming stable and the gate output becoming stable. Manufacturers often refer to the time from the input changing to 50% of its final input level, to the output reaching 50% of its final output level; this may depend on the direction of the level cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metre
The metre (or meter in US spelling; symbol: m) is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). Since 2019, the metre has been defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of of a second, where the second is defined by a hyperfine transition frequency of caesium. The metre was originally defined in 1791 by the French National Assembly as one ten-millionth of the distance from the equator to the North Pole along a great circle, so the Earth's polar circumference is approximately . In 1799, the metre was redefined in terms of a prototype metre bar. The bar used was changed in 1889, and in 1960 the metre was redefined in terms of a certain number of wavelengths of a certain emission line of krypton-86. The current definition was adopted in 1983 and modified slightly in 2002 to clarify that the metre is a measure of proper length. From 1983 until 2019, the metre was formally defined as the length of the pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequency, frequencies of 750–420 terahertz (unit), terahertz. The visible band sits adjacent to the infrared (with longer wavelengths and lower frequencies) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies), called collectively ''optical radiation''. In physics, the term "light" may refer more broadly to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. The primary properties of light are intensity (physics), intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarization (waves), polarization. Its speed of light, speed in vacuum, , is one of the fundamental physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metre
The metre (or meter in US spelling; symbol: m) is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). Since 2019, the metre has been defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of of a second, where the second is defined by a hyperfine transition frequency of caesium. The metre was originally defined in 1791 by the French National Assembly as one ten-millionth of the distance from the equator to the North Pole along a great circle, so the Earth's polar circumference is approximately . In 1799, the metre was redefined in terms of a prototype metre bar. The bar used was changed in 1889, and in 1960 the metre was redefined in terms of a certain number of wavelengths of a certain emission line of krypton-86. The current definition was adopted in 1983 and modified slightly in 2002 to clarify that the metre is a measure of proper length. From 1983 until 2019, the metre was formally defined as the length of the pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Bureau Of Weights And Measures
The International Bureau of Weights and Measures (, BIPM) is an List of intergovernmental organizations, intergovernmental organisation, through which its 64 member-states act on measurement standards in areas including chemistry, ionising radiation, physical metrology, as well as the International System of Units (SI) and Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). It is headquartered in the Pavillon de Breteuil in Saint-Cloud, near Paris, France. The organisation has been referred to as IBWM (from its name in English) in older literature. Function The BIPM has the mandate to provide the basis for a single, coherent system of measurements throughout the world, traceable to the International System of Units, International System of Units (SI). This task takes many forms, from direct dissemination of units to coordination through international comparisons of national measurement standards (as in electricity and ionising radiation). Following consultation, a draft version of the BIPM Work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Yard
The international yard and pound are two units of measurement that were the subject of an agreement among representatives of six nations signed on 1 July 1959: Australia, Canada, New Zealand, South Africa, the United Kingdom and the United States. The agreement defined the yard as exactly and the avoirdupois pound as exactly . History In October 1834, the British Houses of Parliament were destroyed in a fire. Among the items lost were the objects that defined the imperial standards of length and mass. New prototypes were subsequently created to replace the items lost in the fire, among them a new "yardstick" ruler in 1855, and with it a new formal definition of the yard. Two copies of the ruler were subsequently presented to the United States, which in turn adopted the measure for the United States national standard yard. In 1866, the U.S. Congress passed a law that allowed, but did not require, the use of the metric system in trade and commerce. Included in the law was a tab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |