|
1991 In Science
The year 1991 in science and technology involved many significant events, some listed below. Astronomy and space exploration * May 18 – Helen Sharman becomes the first British person in space, flying with the Soyuz TM-12 mission. * October 29 – The ''Galileo'' probe becomes the first spacecraft to visit an asteroid ( 951 Gaspra). * Steven Balbus and John F. Hawley publish their insights on magnetorotational instability. * Asteroid 6859 Datemasamune is discovered by Masahiro Koishikawa. * Asteroid 11514 Tsunenaga is discovered by Masahiro Koishikawa. * There are four lunar eclipses: three penumbral on January 30, July 26, and June 27, and one minor partial lunar eclipse on December 21. * There are two solar eclipses: one annular eclipse on January 15, and a very long total eclipse on July 11 (lasting 6 minutes and 53 seconds). Chemistry * Carbon nanotubes discovered in the insoluble material of arc-burned graphite rods by Sumio Iijima of NEC. Computer scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
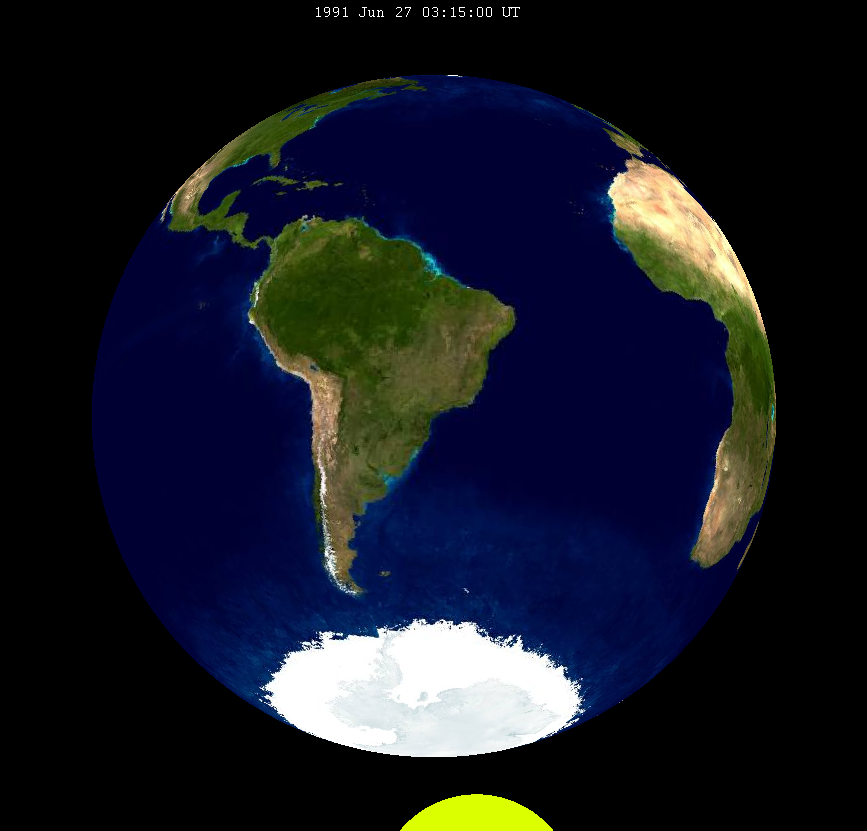
June 1991 Lunar Eclipse
A penumbral lunar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s Lunar node, ascending node of orbit on Thursday, June 27, 1991, with an umbral Magnitude of eclipse, magnitude of −0.7571. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. A penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when part or all of the Moon's near side passes into the Earth's penumbra. Unlike a solar eclipse, which can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world, a lunar eclipse may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth. Occurring only about 5 hours before Apsis, apogee (on June 27, 1991, at 8:20 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller. This eclipse was the second of four lunar eclipses in 1991, with the others occurring on January 1991 lunar eclipse, January 30 (penumbral), July 1991 lunar eclipse, July 26 (penumbral), and December 1991 lunar eclipse, December 21 (partial). Visibility The eclipse was completely visible over eastern North America, So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicola Pellow
Nicola Pellow is an English mathematician and information scientist who was one of the nineteen members of the ''WWW Project'' at CERN working with Tim Berners-Lee. She joined the project in November 1990, while an undergraduate maths student enrolled on a sandwich course at Leicester Polytechnic (now De Montfort University). Pellow recalled having little experience with programming languages, "... apart from using a bit of Pascal (programming language), Pascal and Fortran, FORTRAN as part of my degree course." Almost immediately after Berners-Lee completed the WorldWideWeb web browser for the NeXT platform Pellow was tasked with creating a browser using her recently acquired skills in the C (programming language), C programming language. The outcome was that she wrote the first generic Line Mode Browser that could run on non-NeXT systems. The WWW team began to improve on her work, creating several experimental versions. Pellow was involved in porting the browser to different ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTML Editor
An HTML editor is a program used for editing HTML, the markup of a web page. Although the HTML markup in a web page can be controlled with any text editor, specialized HTML editors can offer convenience, added functionality, and organisation. For example, many HTML editors handle not only HTML, but also related technologies such as CSS, XML and JavaScript , or ECMAScript. In some cases, they also manage communication with remote web servers via FTP and WebDAV, and version control systems such as Subversion or Git. Many word processing, graphic design, and page layout programs that are not dedicated to web design, such as Microsoft Word or Quark XPress, also have the ability to function as HTML editors. Text editors Text editors intended for use with HTML usually provide at least syntax highlighting. Some editors additionally feature templates, toolbars , and keyboard shortcuts to quickly insert common HTML elements and structures. Wizards, tooltip prompts, and autocompl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WYSIWYG
In computing, WYSIWYG ( ), an acronym for what you see is what you get, refers to software that allows content to be edited in a form that resembles its appearance when printed or displayed as a finished product, such as a printed document, web page, or slide presentation. WYSIWYG implies a user interface that allows the user to view something very similar to the result while the document is being created. In general, WYSIWYG implies the ability to directly manipulate the layout of a document without having to type or remember names of layout commands. History Before the adoption of WYSIWYG techniques, text appeared in editors using the system standard typeface and style with little indication of layout (margins, spacing, etc.). Users were required to enter special non-printing ''control codes'' (now referred to as markup ''code tags'') to indicate that some text should be in boldface, italics, or a different typeface or size. In this environment there was very little distincti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Browser
A web browser, often shortened to browser, is an application for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers can also display content stored locally on the user's device. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, smartwatches and consoles. As of 2024, the most used browsers worldwide are Google Chrome (~66% market share), Safari (~16%), Edge (~6%), Firefox (~3%), Samsung Internet (~2%), and Opera (~2%). As of 2023, an estimated 5.4 billion people had used a browser. Function The purpose of a web browser is to fetch content and display it on the user's device. This process begins when the user inputs a Uniform Resource Locator (URL), such as ''https://en.wikipedia.org/'', into the browser's address bar. Virtually all URLs on the Web start with either ''http:'' or ''h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WorldWideWeb
WorldWideWeb (later renamed Nexus to avoid confusion between the software and the World Wide Web) is the first web browser and web page editor. It was discontinued in 1994. It was the first WYSIWYG HTML editor. The source code was released into the public domain on 30 April 1993. History Tim Berners-Lee wrote what would become known as WorldWideWeb on a NeXT Computer during the second half of 1990, while working for CERN, a European nuclear research agency. The first edition was completed "some time before" 25 December 1990, according to Berners-Lee, after two months of development. The browser was announced on the newsgroups and became available to the general public in August 1991. By this time, several others, including Bernd Pollermann, Robert Cailliau, Jean-François Groff, and visiting undergraduate student Nicola Pellow – who later wrote the Line Mode Browser – were involved in the project. Berners-Lee considered different names for his new application, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
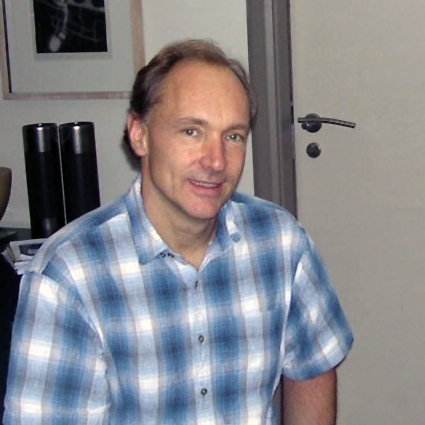
Tim Berners-Lee
Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee (born 8 June 1955), also known as TimBL, is an English computer scientist best known as the inventor of the World Wide Web, the HTML markup language, the URL system, and HTTP. He is a professorial research fellow at the University of Oxford and a professor emeritus at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Berners-Lee proposed an information management system on 12 March 1989 and implemented the first successful communication between a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) client and Server (computing), server via the Internet in mid-November. He devised and implemented the first Web browser and Web server and helped foster the Web's subsequent development. He is the founder and emeritus director of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), which oversees the continued development of the Web. He co-founded (with Rosemary Leith) the World Wide Web Foundation. In April 2009, he was elected as Foreign Associate of the National Academy of Sciences. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features Peer review, peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2022 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 50.5), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in the autumn of 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander MacMillan (publisher), Alexander MacMillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumio Iijima
is a Japanese physicist and inventor, often cited for his discovery of carbon nanotubes. Although carbon nanotubes had been observed prior to his "invention", Iijima's 1991 paper generated unprecedented interest in the carbon nanostructures and has since fueled intense research in the area of nanotechnology. Born in Saitama Prefecture in 1939, Iijima graduated with a Bachelor of Engineering degree in 1963 from the University of Electro-Communications, Tokyo. He received a Master's degree in 1965 and completed his Ph.D. in solid-state physics in 1968, both at Tohoku University in Sendai. Between 1970 and 1982 he performed research with crystalline materials and high-resolution electron microscopy at Arizona State University. He visited the University of Cambridge during 1979 to perform studies on carbon materials. He worked for the Research Development Corporation of Japan from 1982 to 1987, studying ultra-fine particles, after which he joined NEC Corporation where he is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Nanotube
A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with a diameter in the nanometre range ( nanoscale). They are one of the allotropes of carbon. Two broad classes of carbon nanotubes are recognized: * ''Single-walled carbon nanotubes'' (''SWCNTs'') have diameters around 0.5–2.0 nanometres, about 100,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair. They can be idealised as cutouts from a two-dimensional graphene sheet rolled up to form a hollow cylinder. * ''Multi-walled carbon nanotubes'' (''MWCNTs'') consist of nested single-wall carbon nanotubes in a nested, tube-in-tube structure. Double- and triple-walled carbon nanotubes are special cases of MWCNT. Carbon nanotubes can exhibit remarkable properties, such as exceptional tensile strength and thermal conductivity because of their nanostructure and strength of the bonds between carbon atoms. Some SWCNT structures exhibit high electrical conductivity while others are semiconductors. In addition, carbon nanotubes can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of July 11, 1991
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Thursday, July 11, 1991, with a magnitude of 1.08. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 8 hours after perigee (on July 11, 1991, at 11:00 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. The eclipse lasted for 6 minutes and 53.08 seconds at the point of maximum eclipse. There will not be a longer total eclipse until June 13, 2132. This was the largest total solar eclipse of Solar Saros series 136. This eclipse was the most central total eclipse in 800 years, with a gamma of −0.00412. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |