|
1991 CONCACAF Gold Cup Squads
It was the final year of the Cold War, which had begun in 1947. During the year, the Soviet Union collapsed, leaving fifteen sovereign republics and the CIS in its place. In July 1991, India abandoned its policies of dirigism, license raj and autarky and began extensive liberalisation to its economy. This increased GDP but also increased income inequality over the next two decades. A UN-authorized coalition force from 34 nations fought against Iraq, which had invaded and annexed Kuwait in the previous year, 1990. The conflict would be called the Gulf War and would mark the beginning of a since-constant American military presence in the Middle East. The clash between Serbia and the other Yugoslav republics would lead into the beginning of the Yugoslav Wars, which ran through the rest of the decade. In the context of the apartheid, the year after the liberation of political prisoner Nelson Mandela, the Parliament of South Africa repeals the Population Registration Act, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
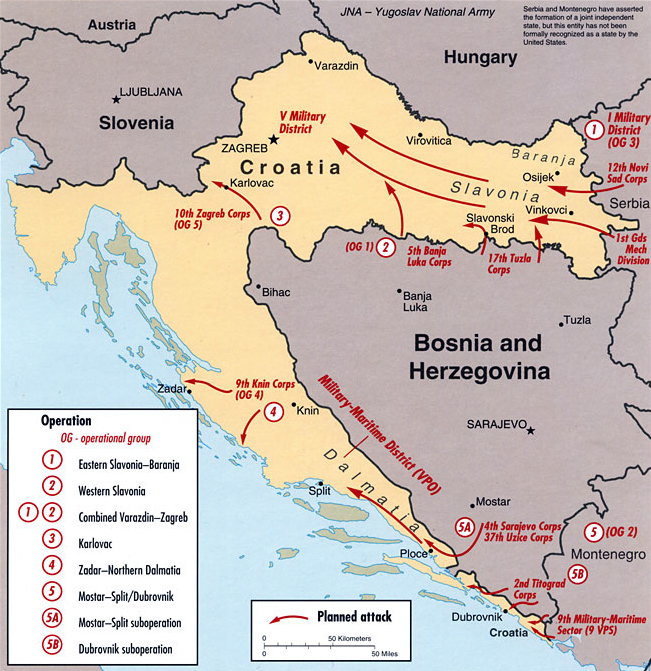
Croatian War Of Independence
The Croatian War of Independence) and (rarely) "War in Krajina" ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, Рат у Крајини, Rat u Krajini) are used. was an armed conflict fought in Croatia from 1991 to 1995 between Croats, Croat forces loyal to the Government of Croatia—which had declared Independence of Croatia, independence from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY)—and the Serbs, Serb-controlled Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) and Serbs of Croatia, local Serb forces, with the JNA ending its combat operations by 1992. A majority of Croats supported Croatia's independence from Yugoslavia, while many ethnic Serbs living in Croatia, supported by Republic of Serbia (1992–2006), Serbia, opposed the secession and advocated Serb-claimed lands to be in a common state with Serbia. Most Serbs sought a new Serb state within a Yugoslav federation, including areas of Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina with ethnic Serb majorities or significant minorities, and attempted to conquer as muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
START I
START I (Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty) was a bilateral treaty between the United States and the Soviet Union on the reduction and the limitation of strategic offensive arms. The treaty was signed on 31 July 1991 and entered into force on 5 December 1994. The treaty barred its signatories from deploying more than 6,000 nuclear warheads and a total of 1,600 intercontinental ballistic missiles ( ICBMs) and bombers. START negotiated the largest and most complex arms control treaty in history, and its final implementation in late 2001 resulted in the removal of about 80% of all strategic nuclear weapons then in existence. Proposed by US President Ronald Reagan, it was renamed START I after negotiations began on START II. The treaty expired on 5 December 2009. On 8 April 2010, the replacement New START Treaty was signed in Prague by US President Barack Obama and Russian President Dmitry Medvedev. Following its ratification by the US Senate and the Federal Assembly of Russ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Income Inequality In India
Income inequality in India refers to the unequal distribution of wealth and income among its citizens. According to the CIA World Factbook, the Gini coefficient of India, which is a measure of income distribution inequality, was 35.2 in 2011, ranking 95th out of 157. Wealth distribution is also uneven, with one report estimating that 54% of the country's wealth is controlled by millionaires, the second highest after Russia, as of November 2016. The richest 1% of Indians own 58% of wealth, while the richest 10% of Indians own 80% of the wealth. This trend has consistently increased, meaning the rich are getting richer much faster than the poor, widening the income gap. Inequality worsened since the establishment of income tax in 1922, overtaking the British Raj's record of the share of the top 1% in national income, which was 20.7% in 1939–40. The latest Oxfam International report titled "Survival of the Richest: The India Story" highlights significant income inequality in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Economy Of India
The economy of India is a Developing country, developing mixed economy with a notable public sector in strategic sectors. * * * * It is the world's fourth-largest economy by gross domestic product, nominal GDP and the third-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP); on a per capita income basis, India ranked List of countries by GDP (nominal) per capita, 136th by GDP (nominal) and List of countries by GDP per capita (PPP), 119th by GDP (PPP). From Independence of India, independence in 1947 until 1991, successive governments followed the Economy of the Soviet Union, Soviet model and promoted Protectionism, protectionist economic policies, with extensive Sovietization, state intervention, demand-side economics, natural resources, bureaucrat-driven enterprises and economic regulation. This is characterised as dirigism, in the form of the Licence Raj. The end of the Cold War and an acute 1991 Indian economic crisis, balance of payments crisis in 1991 led to the adoption of a broa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Economic Liberalisation In India
The economic liberalisation in India refers to the series of policy changes aimed at opening up the country's economy to the world, with the objective of making it more market-oriented and consumption-driven. The goal was to expand the role of private and foreign investment, which was seen as a means of achieving economic growth and development. Although some attempts at liberalisation were made in 1966 and the early 1980s, a more thorough liberalisation was initiated in 1991. The liberalisation process was prompted by a balance of payments crisis that had led to a severe recession, dissolution of the Soviet Union leaving the United States as the sole superpower, and the sharp rise in oil prices caused by the Gulf War of 1990–91. India's foreign exchange reserves fell to dangerously low levels, covering less than three weeks of imports. The country had to airlift gold to secure emergency loans. Trade disruptions with the USSR and a decline in remittances from Gulf countri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Autarky
Autarky is the characteristic of self-sufficiency, usually applied to societies, communities, states, and their economic systems. Autarky as an ideology or economic approach has been attempted by a range of political ideologies and movements, particularly leftist ones like African socialism, mutualism, war communism, communalism, swadeshi, syndicalism (especially anarcho-syndicalism), and left-wing populism, generally in an effort to build alternative economic structures or to control resources against structures a particular movement views as hostile. However, some right-wing ones, like nationalism, conservatism, and anti-globalism, along with even some centrist movements, have also adopted autarky, generally on a more limited scale, to develop a particular industry, to gain independence from other national entities or to preserve part of an existing social order. Proponents of autarky have argued for national self-sufficiency to reduce foreign economic, polit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
License Raj
The Licence Raj or Permit Raj (''rāj'', meaning "rule" in Hindi) is a term coined by Indian independence activist and statesman C. Rajagopalachari for the system of strict government control and regulation of the Indian economy. This economic system, a form of State capitalism, was in place from the 1950s to the early 1990s. Under this system, businesses in India were required to obtain licences from the government in order to operate, and these licences were often difficult to obtain. The Licence Raj was intended to protect Indian industry, promote self-reliance and ensure regional equality. Up to 80 government agencies had to be satisfied before private companies could produce something and, if granted, the government would regulate production. The term "Licence Raj" is a play on the "British Raj" which refers to the period of British rule in India. Chakravarti Rajagopalachari’s criticism of the License Raj stemmed from his opposition to the system of strict governmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dirigism
Dirigisme or dirigism () is an economic doctrine in which the state plays a strong directive (policies) role, contrary to a merely regulatory or non-interventionist role, over a market economy. As an economic doctrine, dirigisme is the opposite of '' laissez-faire'', stressing a positive role for state intervention in curbing productive inefficiencies and market failures. Dirigiste policies often include indicative planning, state-directed investment, and the use of market instruments (taxes and subsidies) to incentivize market entities to fulfill state economic objectives. The term emerged in the post–World War II era to describe the economic policies of France which included substantial state-directed investment, the use of indicative economic planning to supplement the market mechanism and the establishment of state enterprises in strategic domestic sectors. It coincided with both the period of substantial economic and demographic growth, known as the Trente Glorieus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Commonwealth Of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional organization, regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It covers an area of and has an estimated population of 246,200,194. The CIS encourages cooperation in economic, political, and military affairs and has certain powers relating to the coordination of trade, finance, lawmaking, and security, including cross-border crime prevention. As the Soviet Union disintegrated, Byelorussian SSR, Belarus, Russian SFSR, Russia, and Ukrainian SSR, Ukraine signed the Belovezha Accords on 8 December 1991, declaring that the Union had effectively ceased to exist and proclaimed the CIS in its place. On 21 December, the Alma-Ata Protocol was signed, but Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania chose not to participate. Georgia (country), Georgia withdrew its membership in 2008 following Russo-Georgian War, a war with Russia. Ukraine f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Post-soviet States
The post-Soviet states, also referred to as the former Soviet Union or the former Soviet republics, are the independent sovereign states that emerged/re-emerged from the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Prior to their independence, they existed as Republics of the Soviet Union, Union Republics, which were the top-level constituents of the Soviet Union. There are 15 post-Soviet states in total: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Estonia, Georgia (country), Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Moldova, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, and Uzbekistan. Each of these countries succeeded their respective Union Republics: the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic, Armenian SSR, the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic, Azerbaijan SSR, the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Byelorussian SSR, the Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic, Estonian SSR, the Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic, Georgian SSR, the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic, Kazakh SSR, the Kirghiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dissolution Of The Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. Declaration No. 142-Н of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union, formally establishing the dissolution of the Soviet Union as a state and subject of international law. It also brought an end to the Soviet Union's federal government and General Secretary (also President) Mikhail Gorbachev's effort to reform the Soviet political and economic system in an attempt to stop a period of political stalemate and economic backslide. The Soviet Union had experienced internal stagnation and ethnic separatism. Although highly centralized until its final years, the country was made up of 15 top-level republics that served as the homelands for different ethnicities. By late 1991, amid a catastrophic political crisis, with several republics al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |