|
1983 In Science
The year 1983 in science and technology involved many significant events, as listed below. Anthropology * New Zealand anthropologist Derek Freeman publishes ''Margaret Mead and Samoa: The Making and Unmaking of an Anthropological Myth'', critical of ''Coming of Age in Samoa'' (1928) by Margaret Mead (d. 1978). Astronomy and space science * June 13 – ''Pioneer 10'' passes the orbit of Neptune, becoming the first man-made object to travel beyond the major planets of the Solar System. * September 26 – The ''Soyuz T-10-1'' mission ends in a pad abort at the Baikonur Cosmodrome, when a pad fire occurs at the base of the Soyuz U rocket during the launch countdown. The escape tower system, attached to the top of the capsule containing the crew and Soyuz spacecraft, fires immediately pulling the crew safe from the vehicle, six seconds before the rocket explodes, destroying the launch complex. Biology * April – Kary Mullis discovers polymerase chain reaction. * May 20 – First ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (journal)
''Science'' is the peer review, peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature (journal), Nature'' cover the full range of List of academ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features Peer review, peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2022 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 50.5), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in the autumn of 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander MacMillan (publisher), Alexander MacMillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) is the Biological process, process by which a Cell (biology), cell interacts with itself, other cells, and the environment. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all Cell (biology), cellular life in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Typically, the signaling process involves three components: the signal, the receptor, and the effector. In biology, signals are mostly chemical in nature, but can also be physical cues such as pressure, Membrane potential, voltage, temperature, or light. Chemical signals are molecules with the ability to bind and activate a specific Receptor (biochemistry), receptor. These molecules, also referred to as Ligand (biochemistry), ligands, are chemically diverse, including ions (e.g. Na+, K+, Ca2+, etc.), lipids (e.g. steroid, prostaglandin), peptides (e.g. insulin, ACTH), carbohydrates, glycosylated proteins (proteoglycans), nucleic acids, etc. Peptide and lipid ligands are particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
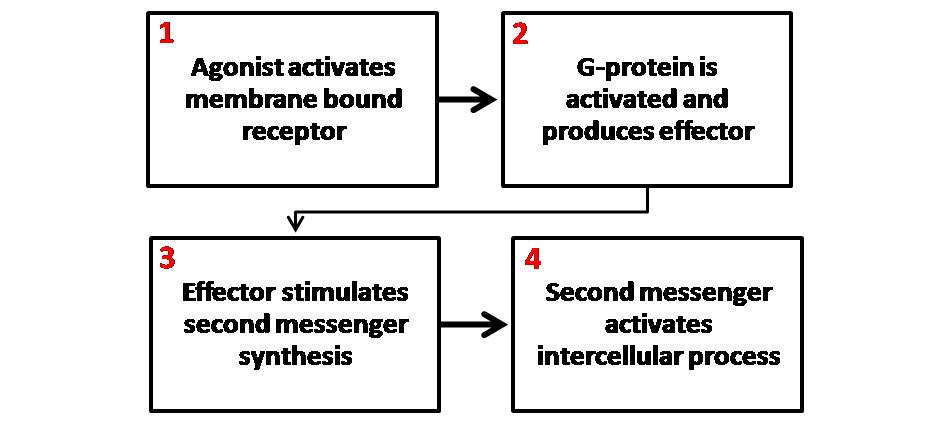
Second Messenger System
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form of cell signaling, encompassing both first messengers and second messengers, are classified as autocrine signaling, autocrine, juxtacrine signalling, juxtacrine, paracrine signaling, paracrine, and endocrine system, endocrine depending on the range of the signal.) Second messengers trigger physiological changes at cellular level such as Cell proliferation, proliferation, cellular differentiation, differentiation, migration, survival, apoptosis and depolarization. They are one of the triggers of intracellular signal transduction cascades. Examples of second messenger molecules include cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cyclic AMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate, cyclic GMP, inositol triphosphate, diacylglycerol, and calcium. First messengers are extracellular factors, often hormones or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inositol Trisphosphate
Inositol trisphosphate or inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate abbreviated InsP3 or Ins3P or IP3 is an inositol phosphate signaling molecule. It is made by hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), a phospholipid that is located in the plasma membrane, by phospholipase C (PLC). Together with diacylglycerol (DAG), IP3 is a second messenger molecule used in signal transduction in biological cells. While DAG stays inside the membrane, IP3 is soluble and diffuses through the cell, where it binds to its receptor, which is a calcium channel located in the endoplasmic reticulum. When IP3 binds its receptor, calcium is released into the cytosol, thereby activating various calcium regulated intracellular signals. Properties Chemical formula and molecular weight IP3 is an organic molecule with a molecular mass of 420.10 g/mol. Its empirical formula is C6H15O15P3. It is composed of an inositol ring with three phosphate groups bound at the 1, 4, and 5 carbon positions, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Berridge
Sir Michael John Berridge (22 October 1938 – 13 February 2020) was a British physiologist and biochemist. He was known for his work on cell signaling, in particular the discovery that inositol trisphosphate acts as a second messenger, linking events at the plasma membrane with the release of calcium ions (Ca2+) within the cell. Early life and education Berridge was born in Gatooma (now Kadoma, Zimbabwe) in Southern Rhodesia (now Zimbabwe). His high school biology teacher convinced him and his parents that he should pursue tertiary education, and he entered the newly founded University of Rhodesia and Nyasaland (now University of Zimbabwe), earning his Bsc in zoology and chemistry in 1960. He became interested in insect physiology after helping with his physiology professor's research on tsetse flies, and went to the United Kingdom to study with Vincent Wigglesworth, regarded as the father of insect physiology, at the Department of Zoology of the University of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate Filament
Intermediate filaments (IFs) are cytoskeleton, cytoskeletal structural components found in the cells of vertebrates, and many invertebrates. Homologues of the IF protein have been noted in an invertebrate, the cephalochordate ''Branchiostoma''. Intermediate filaments are composed of a family of related proteins sharing common structural and sequence features. Initially designated 'intermediate' because their average diameter (10 Nanometre, nm) is between those of narrower microfilaments (actin) and wider myosin filaments found in muscle cells, the diameter of intermediate filaments is now commonly compared to actin microfilaments (7 nm) and microtubules (25 nm). Animal intermediate filaments are subcategorized into six types based on similarities in amino acid sequence and protein structure. Most types are cytoplasmic, but one type, Type V is a nuclear lamin. Unlike microtubules, IF distribution in cells shows no good correlation with the distribution of either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Helix
An alpha helix (or α-helix) is a sequence of amino acids in a protein that are twisted into a coil (a helix). The alpha helix is the most common structural arrangement in the Protein secondary structure, secondary structure of proteins. It is also the most extreme type of local structure, and it is the local structure that is most easily predicted from a sequence of amino acids. The alpha helix has a right-handed helix conformation in which every backbone amino, N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone carbonyl, C=O group of the amino acid that is four residue (biochemistry), residues earlier in the protein sequence. Other names The alpha helix is also commonly called a: * Pauling–Corey–Branson α-helix (from the names of three scientists who described its structure) * 3.613-helix because there are 3.6 amino acids in one ring, with 13 atoms being involved in the ring formed by the hydrogen bond (starting with amidic hydrogen and ending with carbonyl oxygen) Discovery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type II Keratin
Type II keratins (or Type II cytokeratins) constitutes the Type II intermediate filaments (IFs) of the intracytoplasmatic cytoskeleton, which is present in all mammalian epithelial cells. The type 2 cytokeratins consist of basic or neutral, high molecular weight proteins which in vivo are arranged in pairs of heterotypic Type I and Type II keratin chains, coexpressed during differentiation of simple and stratified epithelial tissues. It has been seen that Type II Keratins are developed before Type 1 keratins during human embryonic development. Type II cytokeratins are encoded on chromosome 12q and encompasses: CK1, CK2, CK3, CK4, CK5, CK6, CK7 and CK8. Their molecular weight ranges from 52 kDa (CK8) to 67 kDa (CK18). Overall, keratin type 2 plays a crucial role in maintaining the strength and integrity of the skin, hair, and nails. Mutations in keratin genes can lead to various genetic disorders that affect these tissues, such as epidermolysis bullosa simplex, a rare condit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type I Keratin
Type I keratins (or Type I cytokeratins) are cytokeratins that constitute the Type I intermediate filaments (IFs) of the intracytoplasmatic cytoskeleton, which is present in all mammalian epithelial cells. Most of the type I keratins consist of acidic, low molecular weight proteins which in vivo are arranged in pairs of heterotypic Type I and Type II keratin chains, coexpressed during differentiation of simple and stratified epithelial tissues. Type I keratins are encoded on chromosome 17q and encompasses: K9, K10, K11, K12, K13, K14, K15, K16, K17, K18, K19 and K20. Their molecular weight ranges from 40 kDa (K19) to 64 kDa (K9). See also *Type II keratin Type II keratins (or Type II cytokeratins) constitutes the Type II intermediate filaments (IFs) of the intracytoplasmatic cytoskeleton, which is present in all mammalian epithelial cells. The type 2 cytokeratins consist of basic or neutral, high mo ... External links * Proteopedia page on keratins Keratins {{Fibrous prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |