|
1979 In Spaceflight
The following is an outline of 1979 in spaceflight. Launches , colspan=8 style="background:white;", January , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", February , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", March , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", April , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", May , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", June , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", July , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", August , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", September , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", October , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", November , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", December , - Deep Space Rendezvous EVAs References Footnotes {{Orbital launches in 1979 Spaceflight by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
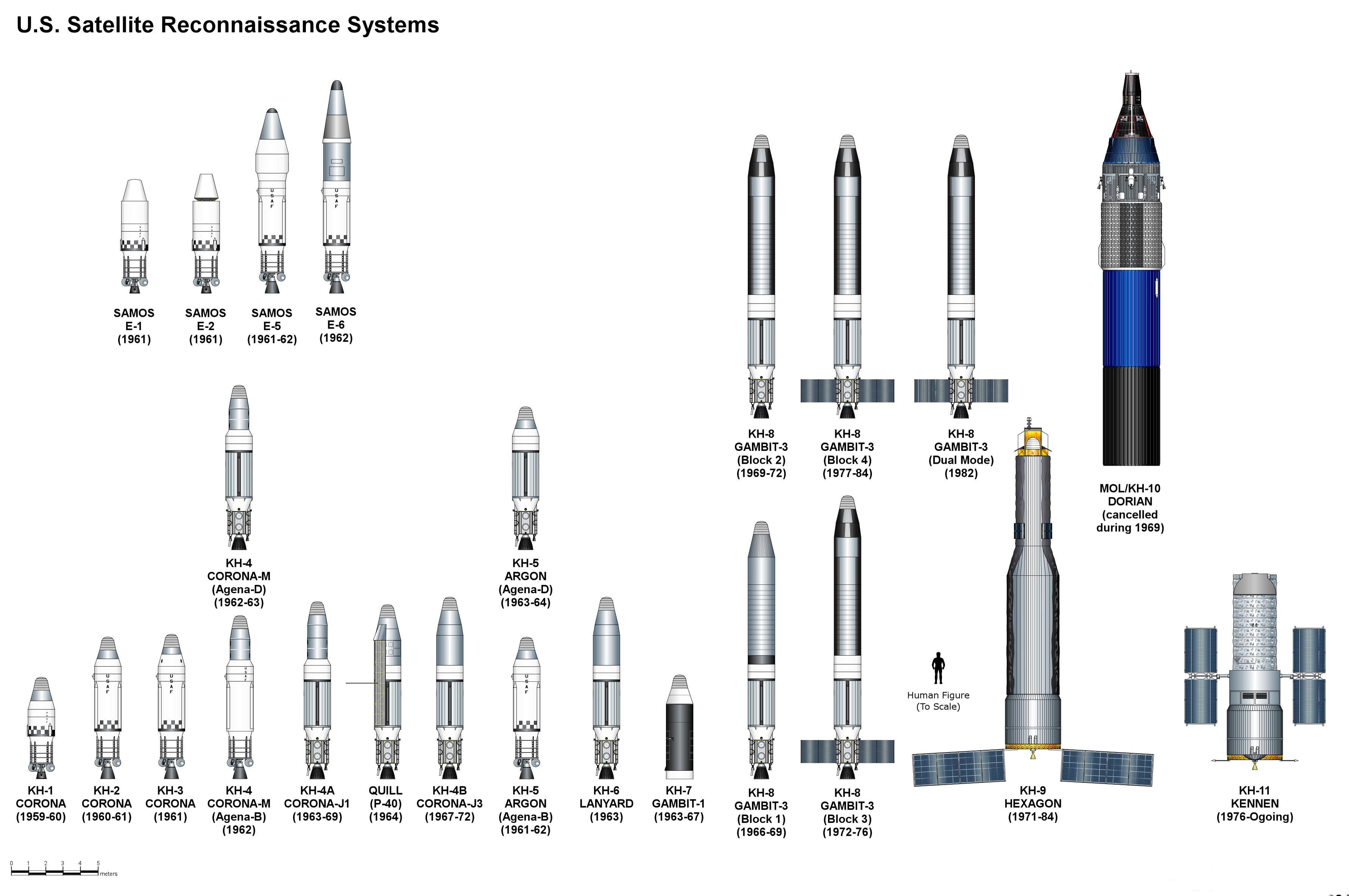
Reconnaissance Satellite
A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications. The first generation type (i.e., Corona and Zenit) took photographs, then ejected canisters of photographic film which would descend back down into Earth's atmosphere. Corona capsules were retrieved in mid-air as they floated down on parachutes. Later, spacecraft had digital imaging systems and downloaded the images via encrypted radio links. In the United States, most information available about reconnaissance satellites is on programs that existed up to 1972, as this information has been declassified due to its age. Some information about programs before that time is still classified information, and a small amount of information is available on subsequent missions. A few up-to-date reconnaissance satellite images have been declassifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteor (satellite)
The Meteor spacecraft are weather observation satellites launched by the Soviet Union and Russia since the Cold War. The Meteor satellite series was initially developed during the 1960s. The Meteor satellites were designed to monitor atmospheric and sea-surface temperatures, humidity, radiation, sea ice conditions, snow-cover, and clouds. Between 1964 and 1969, a total of eleven Soviet Union Meteor satellites were launched. Satellites Unlike the United States, which has separate civilian and military weather satellites, the Soviet Union used a single weather satellite type for both purposes. Meteor Prototype ; Meteor Prototype launches Meteor-1 Meteor-1 was a set of fully operational Russian meteorological satellite launched from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome, Plesetsk site. The satellites were placed in a near-circular, near-polar prograde orbit to provide near-global observations of the earth's weather systems, cloud cover, ice and snow fields, and reflected and emitted radiatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Site 31/6
Baikonur Site 31, also designated as Site 31/6, is a launch complex at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. It serves as a key launch site, supporting Soyuz-2 launches for both crewed and uncrewed missions. The site was first utilized on 14 January 1961 for a test flight of the R-7A, an intercontinental ballistic missile on which the Soyuz rocket family was based. Since 2020, following Roscosmos' transition from the Soyuz-FG to the Soyuz-2 rocket for crewed missions, Site 31 has become the primary launch site for Soyuz flights to the International Space Station (ISS). This shift occurred after Site 1/5, also known as Gagarin's Start, failed to secure funding for upgrades to accommodate the slightly larger Soyuz-2 rocket. Before that, it only saw a handful of crewed flights when Site 1/5 was unavailable. History Construction of Site 31/6 at Baikonur began in late 1958 as a second launch complex for the R-7 intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) at the cosmodrome. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baikonur Cosmodrome
The Baikonur Cosmodrome is a spaceport operated by Russia within Kazakhstan. Located in the Kazakh city of Baikonur, it is the largest operational space launch facility in terms of area. All Russian Human spaceflight, crewed spaceflights are launched from Baikonur. Situated in the Kazakh Steppe, some above sea level, it is to the east of the Aral Sea and north of the Syr Darya. It is close to Töretam, a station on the Trans-Aral Railway. Russia, as the official successor state to the Soviet Union, has retained control over the facility since 1991; it originally assumed this role through the post-Soviet Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), but ratified an agreement with Kazakhstan in 2005 that allowed it to lease the spaceport until 2050. It is jointly managed by Roscosmos and the Russian Aerospace Forces. In 1955, the Ministry of Defense (Soviet Union), Soviet Ministry of Defense issued a decree and founded the Baikonur Cosmodrome. It was originally built as the chief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vostok-2M
The Vostok-2M (), GRAU index: 8A92M was an expendable launch system, expendable launch vehicle, carrier rocket used by the Soviet Union between 1964 and 1991. Ninety-three were launched, of which one failed. Another was destroyed before launch. It was originally built as a specialised version of the earlier Vostok-2 (rocket), Vostok-2, for injecting lighter payloads into higher Sun-synchronous orbits. It was a member of the R-7 (rocket family), R-7 family of rockets, and the last Vostok (rocket), Vostok. The Vostok-2M was similar to the Vostok-2 booster but the adapter portion of the Blok E stage remained attached to the payload and the guidance system was modified specially to assist in putting payloads in sun-synchronous orbits. Vehicles flown in 1967 and later used the 8D74M engines or the 11D511 in 1973 and later. The Vostok-2M made its maiden flight on 28 August 1964 from Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 31, Site 31/6 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome, successfully placing Kosmos 44, a Met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highly Elliptical Orbit
A highly elliptical orbit (HEO) is an elliptic orbit with high eccentricity, usually referring to one around Earth. Examples of inclined HEO orbits include Molniya orbits, named after the Molniya Soviet communication satellites which used them, and Tundra orbits. Many US satellites also have used these orbits, satellites such as the Trumpet electronics intelligence satellites. The acronym HEO normally is expanded to Highly Eccentric Orbit by orbital analysts since all orbits around planets, etc are ellipses - the term "highly elliptical" is not very clear as to what is exaggerated. It would be more proper to call these orbits "elongated" than "highly elliptical". Highly eccentric orbits have two main uses - as transfer orbits and as good orbits for communication with or surveillance of the Polar regions. The transfer orbit was proposed by the German scientist Walter Hohmann in 1925, it connects two circular orbits, a lower one and a higher one, with an eccentric orbit. Ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molniya (satellite)
The Molniya ( rus, Молния, p=ˈmolnʲɪjə, a=Ru-молния.ogg, "Lightning") series satellites were military and communications satellites launched by the Soviet Union from 1965 to 1991, and by the Russian Federation from 1991 to 2004. These satellites used highly eccentric elliptical orbits known as Molniya orbits, which have a long dwell time over high latitudes. They are suited for communications purposes in polar regions, in the same way that geostationary satellites are used for equatorial regions. There were 164 Molniya satellites launched, all in Molniya orbits with the exception of Molniya 1S which was launched into geostationary orbit for testing purposes. History In the early 1960s, when Europe and America were establishing geostationary communication satellites, the Russians found these orbits unsuitable. They were limited in the amount of rocket power available and it is extremely energy intensive to both launch a satellite to 40,000 km, and change it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molniya-M
The Molniya-M (, GRAU index: 8K78M) was a Soviet and Russian launch vehicle derived from the R-7 Semyorka Intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM). The original 8K78 booster had been the product of a rushed development program and its launch record was no better than the 8K72 Luna booster of 1958–1960. As 1962 ended, there had been 12 launches of 8K78s, ten of which failed (five Block L failures, four Block I failures, and one failure caused by the Block A core stage). The two successful launches had had their probes ( Venera 1 and Mars 1) fail en route to their respective planetary targets. As such, work began at the Korolev Bureau to improve the basic 8K78 vehicle. The core and strap-ons received the up-rated 8D74M engines and the Kosberg Bureau completely redesigned the Block I stage. The Block L engine was also slightly enhanced. The first six 8K78Ms built used RD-0108 engines in the Block I stage, which was also used in the two crewed Voskhod boosters, all subseque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navigation Satellite
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geopositioning. A satellite navigation system with global coverage is termed global navigation satellite system (GNSS). , four global systems are operational: the United States's Global Positioning System (GPS), Russia's Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS), China's BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS), and the European Union's Galileo. Two regional systems are operational: India's NavIC and Japan's QZSS. '' Satellite-based augmentation systems'' (SBAS), designed to enhance the accuracy of GNSS, include Japan's Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS), India's GAGAN and the European EGNOS, all of them based on GPS. Previous iterations of the BeiDou navigation system and the present Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), operationally known as NavIC, are examples of stand-alone operating regional navigation satellite systems (RNSS). Satellite navigation dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parus (satellite)
Parus ( meaning ''Sail''), also Tsyklon-B or Tsiklon-B ( meaning ''Cyclone-B'') and Tsikada-M ( meaning ''Cicada-M''), GRAU index 11F627, was a Russian, previously Soviet satellite constellation used for communication and navigation. As of 2010, 99 Parus satellites had been launched, starting with Kosmos 700 in 1974. All launches had been conducted using Kosmos-3M carrier rockets, flying from sites 132 and 133 at the Plesetsk Cosmodrome. The prime function of Parus satellites was to provide location information for the Tsiklon-B navigation system. Parus satellites were produced by JSC Information Satellite Systems (formerly NPO PM), based on the KAUR-1 satellite bus. They had a mass of around , and a design life of 18–24 months. The satellites operated in low Earth orbits, typically with a perigee of about , an apogee of and 82.9° inclination. They were operated by the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces, and were used primarily for navigation, Store and forward commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos 1072
Cosmos generally refers to an orderly or harmonious system. Cosmos or Kosmos may also refer to: Space * ''Cosmos 1'', a privately funded solar sail spacecraft project * Cosmic Evolution Survey (COSMOS), a Hubble Space Telescope Treasury Project * Kosmos (rocket family), a series of Soviet/Russian rockets * Kosmos (satellite), a series of Soviet/Russian satellites * Universe, synonymous with cosmos * COSMOS field, an image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope Places * Cosmos, Minnesota, United States * Cosmos, Rio de Janeiro, a neighborhood of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil * Kosmos, South Africa, a village in North West Province * Kosmos, Washington, an unincorporated community in Washington, United States Books * ''Cosmos'' (serial novel), a 17-chapter serial novel published in ''Science Fiction Digest'' (later ''Fantasy Magazine'') in 1933 - 1934 * ''Cosmos'' (Humboldt book), a scientific treatise by Alexander von Humboldt * ''Cosmos'' (Gombrowicz novel), a 1965 novel by Witold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |