|
1979 In Northern Ireland
Events during the year 1979 in Northern Ireland. Incumbents * Secretary of State – Roy Mason (until 5 May), Humphrey Atkins (from 5 May) Events January to March *5 January – Two members of the Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA) are killed in Ardoyne, Belfast, when the car bomb they are transporting explodes prematurely. *4 February – A former prison officer and his wife are shot dead at their home in Oldpark Road, Belfast, by the IRA. *20 February – Eleven Loyalists, known as the Shankill Butchers, are sentenced to life imprisonment for 112 offences, including nineteen sectarian murders.Larkspirit Irish History *24 February – Two Catholic teenagers, mistaken in the dark for a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label=Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Northern Ireland shares an open border to the south and west with the Republic of Ireland. In 2021, its population was 1,903,100, making up about 27% of Ireland's population and about 3% of the UK's population. The Northern Ireland Assembly (colloquially referred to as Stormont after its location), established by the Northern Ireland Act 1998, holds responsibility for a range of devolved policy matters, while other areas are reserved for the UK Government. Northern Ireland cooperates with the Republic of Ireland in several areas. Northern Ireland was created in May 1921, when Ireland was partitioned by the Government of Ireland Act 1920, creating a devolved government for the six northeastern counties. As was intended, Northern Irela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Ulster Constabulary
The Royal Ulster Constabulary (RUC) was the police force in Northern Ireland from 1922 to 2001. It was founded on 1 June 1922 as a successor to the Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC) Richard Doherty, ''The Thin Green Line – The History of the Royal Ulster Constabulary GC'', pp. 5, 17, 27, 93, 134, 271; Pen & Sword Books; following the partition of Ireland. At its peak the force had around 8,500 officers, with a further 4,500 who were members of the RUC Reserve. The RUC policed Northern Ireland from the aftermath of the Irish War of Independence until after the turn of the 21st century, and played a major role in the Troubles between the 1960s and the 1990s. Due to the threat from the Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA), who saw the RUC as enforcing British rule, the force was heavily armed and militarised. Officers routinely carried submachine guns and assault rifles, travelled in armoured vehicles, and were based in heavily-fortified police stations.Weitzer, Ronald. ''Pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaelic Athletic Association
The Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA; ga, Cumann Lúthchleas Gael ; CLG) is an Irish international amateur sporting and cultural organisation, focused primarily on promoting indigenous Gaelic games and pastimes, which include the traditional Irish sports of hurling, camogie, Gaelic football, Gaelic handball and rounders. The association also promotes Irish music and dance, as well as the Irish language. As of 2014, the organisation had over 500,000 members worldwide, and declared total revenues of €65.6 million in 2017. The Games Administration Committee (GAC) of the Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA) governing bodies organise the fixture list of Gaelic games within a GAA county or provincial councils. Gaelic football and hurling are the most popular activities promoted by the organisation, and the most popular sports in the Republic of Ireland in terms of attendances. Gaelic football is also the second most popular participation sport in Northern Ireland. The women's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossmaglen
Crossmaglen (, ) is a village and townland in County Armagh, Northern Ireland. It had a population of 1,610 in the 2011 Census and is the largest village in South Armagh. The village centre is the site of a large Police Service of Northern Ireland base and formerly of an observation tower (known locally as the "look-out post"). The square's name commemorates Cardinal Tomás Ó Fiaich, a local man who became Primate of All Ireland (head of the Catholic Church in Ireland), and who died in 1990. However, the Cardinal originated from Crossmaglen's close neighbour, Cullyhanna. Crossmaglen has its own GAA team, Crossmaglen Rangers GAC. Travelling by road, Crossmaglen is to the north of Dublin, to the west of Newry, and to the south of Belfast. History On 13 January 1921, during the Irish War of Independence, the Irish Republican Army (IRA) shot dead an Ulster Special Constabulary (USC) constable in Crossmaglen. He was the first member of the USC to be killed whilst on dut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Member Of The European Parliament
A Member of the European Parliament (MEP) is a person who has been elected to serve as a popular representative in the European Parliament. When the European Parliament (then known as the Common Assembly of the European Coal and Steel Community, ECSC) first met in 1952, its members were directly appointed by the governments of member states from among those already sitting in their own national parliaments. Since 1979, however, MEPs have been elected by direct universal suffrage. Earlier European organizations that were a precursor to the European Union did not have MEPs. Each Member state of the European Union, member state establishes its own method for electing MEPs – and in some states this has changed over time – but the system chosen must be a form of proportional representation. Some member states elect their MEPs to represent a single national constituency; other states apportion seats to sub-national regions for election. They are sometimes referred to as delega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulster Unionist Party
The Ulster Unionist Party (UUP) is a unionist political party in Northern Ireland. The party was founded in 1905, emerging from the Irish Unionist Alliance in Ulster. Under Edward Carson, it led unionist opposition to the Irish Home Rule movement. Following the partition of Ireland, it was the governing party of Northern Ireland between 1921 and 1972. It was supported by most unionist voters throughout the conflict known as the Troubles, during which time it was often referred to as the Official Unionist Party (OUP). Under David Trimble, the party helped negotiate the Good Friday Agreement of 1998, which ended the conflict. Trimble served as the first First Minister of Northern Ireland from 1998 to 2002. However, it was overtaken as the largest unionist party in 2003 by the Democratic Unionist Party (DUP). As of 2022 it is the fourth-largest party in the Northern Ireland Assembly, after the DUP, Sinn Féin, and the Alliance Party. The party has been unrepresented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Democratic And Labour Party
The Social Democratic and Labour Party (SDLP) ( ga, Páirtí Sóisialta Daonlathach an Lucht Oibre) is a social-democratic and Irish nationalist political party in Northern Ireland. The SDLP currently has eight members in the Northern Ireland Assembly ( MLAs) and two Members of Parliament (MPs) in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom. The SDLP party platform advocates Irish reunification and further devolution of powers while Northern Ireland remains part of the United Kingdom. During the Troubles, the SDLP was the most popular Irish nationalist party in Northern Ireland, but since the Provisional IRA ceasefire in 1994, it has lost ground to the republican party Sinn Féin, which in 2001 became the more popular of the two parties for the first time. Established during the Troubles, a significant difference between the two parties was the SDLP's rejection of violence, in contrast to Sinn Féin's then-support for (and organisational ties to) the Provisional IRA and phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Unionist Party
The Democratic Unionist Party (DUP) is a unionist, loyalist, and national conservative political party in Northern Ireland. It was founded in 1971 during the Troubles by Ian Paisley, who led the party for the next 37 years. Currently led by Jeffrey Donaldson, it is the second largest party in the Northern Ireland Assembly, and is the fifth-largest party in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom. The party has been described as right-wing and socially conservative, being anti-abortion and opposing same-sex marriage. The DUP sees itself as defending Britishness and Ulster Protestant culture against Irish nationalism and Irish republicanism; the party is Eurosceptic and supported Brexit. It supports Northern Ireland remaining in the United Kingdom and opposes the unification of Ireland. The DUP evolved from the Protestant Unionist Party and has historically strong links to the Free Presbyterian Church of Ulster, the church Paisley founded. During the Troubles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it adopts European legislation, following a proposal by the European Commission. The Parliament is composed of 705 members (MEPs). It represents the second-largest democratic electorate in the world (after the Parliament of India), with an electorate of 375 million eligible voters in 2009. Since 1979, the Parliament has been directly elected every five years by the citizens of the European Union through universal suffrage. Voter turnout in parliamentary elections decreased each time after 1979 until 2019, when voter turnout increased by eight percentage points, and rose above 50% for the first time since 1994. The voting age is 18 in all EU member states except for Malta and Austria, where it is 16, and Greece, where it is 17. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979 European Parliament Election In The United Kingdom
The 1979 European Parliament election, was the first European election to be held in the United Kingdom after the European Communities (EC) decided to directly elect representatives to the European Parliament. It was held on 7 June. Elections were also held in eight other EC states. European elections were incorporated into UK law by the European Assembly Elections Act 1978. Out of the 410 members of the European Parliament, 81 were elected from the UK. The electoral system was First Past the Post in England, Scotland and Wales (electing 78 MEPs in total) and Single Transferable Vote in Northern Ireland (electing 3 MEPs). The result was a landslide victory for the Conservative Party, which won 60 of the 78 seats available in England, Wales and Scotland. Their decisive victory in the general election of the previous month and divisions within the Labour party on whether to stay in the EC probably helped the Conservatives to such a comprehensive victory. There was a very low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HM Prison Armagh
Armagh Prison in Armagh, Northern Ireland, is a former prison. The construction of the prison began in the 1780 and it was extended in the style of Pentonville Prison in the 1840 and 1850s. For most of its working life Armagh Gaol was the primary women's prison in Ulster. Although the prison is often described as Armagh Women's Gaol, at various points in its history, various wings in the prison were used to hold male prisoners. During the period of the internment, 33 republican women were interned in the prison from 1973 to 1975. On 19 April 1979, Agnes Wallace (40), a prison officer, was shot dead and three colleagues were injured in an Irish National Liberation Army (INLA) gun and grenade attack outside the prison. The prison was the scene of a protest by female Irish republican prisoners demanding the reinstatement of political status, although the numbers involved were much smaller than in the Maze (also known as Long Kesh) men's prison. As all women prisoners in North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
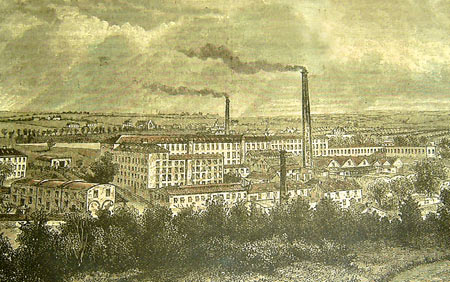
Bessbrook
Bessbrook is a village in County Armagh, Northern Ireland. It lies about three miles (5 km) northwest of Newry and near the Newry bypass on the main A1 Belfast- Dublin road and Belfast-Dublin railway line. Today the village of Bessbrook straddles the three townlands of Maghernahely, Clogharevan and Maytown. Bessbrook is near Newry railway station. It had a population of 2,750 at the 2011 Census. This article contains quotations from this source, which is available under th Open Government Licence v3.0 © Crown copyright. The model village of Bessbrook, Co. Armagh is a visible memorial to the commercial endeavours of the Richardson family over a number of generations. During the late 20th century some of the worst violence of " the Troubles" took place near the village and it became a military zone with a large garrison. The small village became the busiest (military) heliport in Europe. History Bessbrook is named from Elizabeth or Bess Nicholson, wife of Joseph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)