|
1975 In Israel
Events in the year 1975 in Israel. Incumbents * President of Israel – Ephraim Katzir * Prime Minister of Israel – Yitzhak Rabin (Alignment (political party), Alignment) * Supreme Court of Israel, President of the Supreme Court – Shimon Agranat * Chief of General Staff (Israel), Chief of General Staff – Mordechai Gur * Government of Israel – Seventeenth government of Israel, 17th Government of Israel Events * 8 January – Yehoshua Ben-Zion convicted of embezzling £20 million from the Israeli-British Bank which collapsed in July 1974 owing British investors £46.6 million. He was sentenced to 12 years in prison. Later, Ben-Zion was pardoned by the Israeli president after intervention of Menachem Begin and was released after serving 3 years. * 22 March – Shlomo Artzi represents Israel in the Eurovision Song Contest 1975, Israel at the Eurovision Song Contest with the song “At Va'Ani” ("You and Me"). * 25 April – Leading Israeli pop star Mike Brant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of Israel
The president of the State of Israel (, or ) is the head of state of Israel. The president is mostly, though not entirely, ceremonial; actual executive power is vested in the Cabinet of Israel, cabinet led by the Prime Minister of Israel, prime minister. The incumbent president is Isaac Herzog, who took office on 7 July 2021. Presidents are elected by the Knesset for a single seven-year term. Election The President of Israel is elected by an Majority, absolute majority in the Knesset, by secret ballot. If no candidate receives an absolute majority of votes in the first or second round of voting, the candidate with the fewest votes is eliminated in each subsequent round, if needed until only two remain. From 1949 to 2000, the president was elected for a five-year term, and was allowed to serve up to two terms in office. Since 2000, the president serves a single seven-year term. Any Israeli resident citizen is eligible to run for president; as there is no minimum age of candid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinai Interim Agreement
The Sinai Interim Agreement, also known as the Sinai II Agreement, was a diplomatic agreement signed by Egypt and Israel on September 4, 1975, with the intention of peacefully resolving territorial disputes. The signing ceremony took place in Geneva. The agreement stated that the conflicts between the countries "shall not be resolved by military force but by peaceful means." It also called "for a further withdrawal in the Sinai and a new UN buffer zone." Thus, the agreement strengthened Israel's and Egypt's commitment to abiding by U.N. Resolution 338 and strengthened diplomatic relations between Egypt, Israel, and the United States.Meital, pp. 149–151 The purpose of this agreement, in the eyes of the Egyptians, was to gain back as much of the Sinai Peninsula (which had been occupied by Israel since 1967) as they could through diplomacy. Although the agreement strengthened Egypt's relationship with the Western world, it diminished its relationships with other members of the Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestinian Political Violence
Palestinian political violence refers to acts of violence or terrorism committed by Palestinians with the intent to accomplish political goals in the context of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict. Common objectives of political violence by Palestinian groups include self-determination in and sovereignty over all of the region of Palestine (including seeking to replace Israel),de Waart, 1994p. 223. or the recognition of a Palestinian state inside the 1967 borders. This includes the objective of ending the Israeli occupation. More limited goals include the release of Palestinian prisoners held by Israel and recognition of the Palestinian right of return. Palestinian groups that have been involved in politically motivated violence include the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), Fatah, the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP), the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine – General Command (PFLP-GC), the Democratic Front for the Liberation of Pal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai ( ; ; ; ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Africa. Sinai has a land area of about (6 percent of Egypt's total area) and a population of approximately 600,000 people. Administratively, the vast majority of the area of the Sinai Peninsula is divided into two Governorates of Egypt, governorates: the South Sinai Governorate and the North Sinai Governorate. Three other governorates span the Suez Canal, crossing into African Egypt: Suez Governorate on the southern end of the Suez Canal, Ismailia Governorate in the center, and Port Said Governorate in the north. In the classical era, the region was known as Arabia Petraea. The peninsula acquired the name ''Sinai'' in modern times due to the assumption that a mountain near Saint Catherine's Monastery is the Biblical Mount Sinai. Mount Sinai i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arish
ʻArish or el-ʻArīsh ( ' ) is the capital and largest city of the North Sinai Governorate of Egypt, as well as the largest city on the Sinai Peninsula, lying on the Mediterranean coast northeast of Cairo and west of the Egypt–Gaza border. The population was 204,391 in 2023. In antiquity and the Early Middle Ages, the city was known as Rinokoroura (, ). ʻArīsh is located at the mouth of Wadi al-Arish, a long ephemeral watercourse. The Azzaraniq Protectorate is on the eastern side of ʻArīsh. Etymology There are several hypothetical possibilities for the origin of the modern name of the city, which is first mentioned under it in the 9th century. One possibility is that the name might be an Arab phonetic transcription of a pre-existing toponym. However, there is no name that fully qualifies as such, apart from the Ariza () of Hierokles, which is difficult to interpret. Another possibility is that the name el-Arish was given to a city that already existed in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jebel Halal
Jabal, Jabel, Jebel or Jibal may refer to: People * Jabal (name), a male Arabic given name * Jabal (Bible), mentioned in the Hebrew Bible Places In Arabic, ''jabal'' or ''jebel'' (spelling variants of the same word) means 'mountain'. * Dzhebel, a town in Bulgaria * Jabal Amman, part of Amman, Jordan * Jabel, a German municipality * Jabal, Amreli, a village in Gujarat, India * Jabal Pur, city in Madhya Pradesh, India * Jabal Rural District, in Iran * Jebel, Timiș, a commune in Timiș County, Romania * Jebel, Turkmenistan, a town * Jebel Airport is international airport in Turkmenistan * Jibal Jibāl (), also al-Jabal (), was the name given by the Arabs to a region and province located in western Iran, under the Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphates. Its name means "the Mountains", being the plural of ''jabal'' ("mountain, hill"), highlight ... or al-Jabal, a late 1st-millennium-CE West-Asian realm Other uses * Djebel (1937–1958), a racehorse See also * * * * * * Jubal ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli Air Force
The Israeli Air Force (IAF; , commonly known as , ''Kheil HaAvir'', "Air Corps") operates as the aerial and space warfare branch of the Israel Defense Forces (IDF). It was founded on May 28, 1948, shortly after the Israeli Declaration of Independence. , Aluf Tomer Bar has been serving as the Air Force commander. The Israeli Air Force was established using commandeered or donated civilian aircraft and obsolete and surplus World War II combat aircraft. Eventually, more aircraft were procured, including Boeing B-17s, Bristol Beaufighters, de Havilland Mosquitoes and P-51D Mustangs. The Israeli Air Force played an important part in Operation Kadesh, Israel's part in the 1956 Suez Crisis, dropping paratroopers at the Mitla Pass. On June 5, 1967, the first day of the Six-Day War, the Israeli Air Force performed Operation Focus, debilitating the opposing Arab air forces and attaining air supremacy for the remainder of the war. Shortly after the end of the Six-Day War, Egypt i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The UN
The history of the United Nations has its origins in World War II, beginning with the Declaration of St James's Palace. Taking up the Wilsonian mantle in 1944–1945, US President Franklin D. Roosevelt pushed as his highest postwar priority the establishment of the United Nations to replace the defunct League of Nations. Roosevelt planned that it would be controlled by the United States, Soviet Union, United Kingdom and China. He expected this Big Four would resolve all major world problems at the powerful Security Council. However the UN was largely paralyzed by the veto of the Soviet Union when dealing with Cold War issues from 1947 to 1989. Since then its aims and activities have expanded to make it the archetypal body in the early 21st century. Background The first international organizations were created to enable countries to cooperate on specific matters. The International Telegraph Union was founded in 1865 and the Universal Postal Union was established in 1874. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
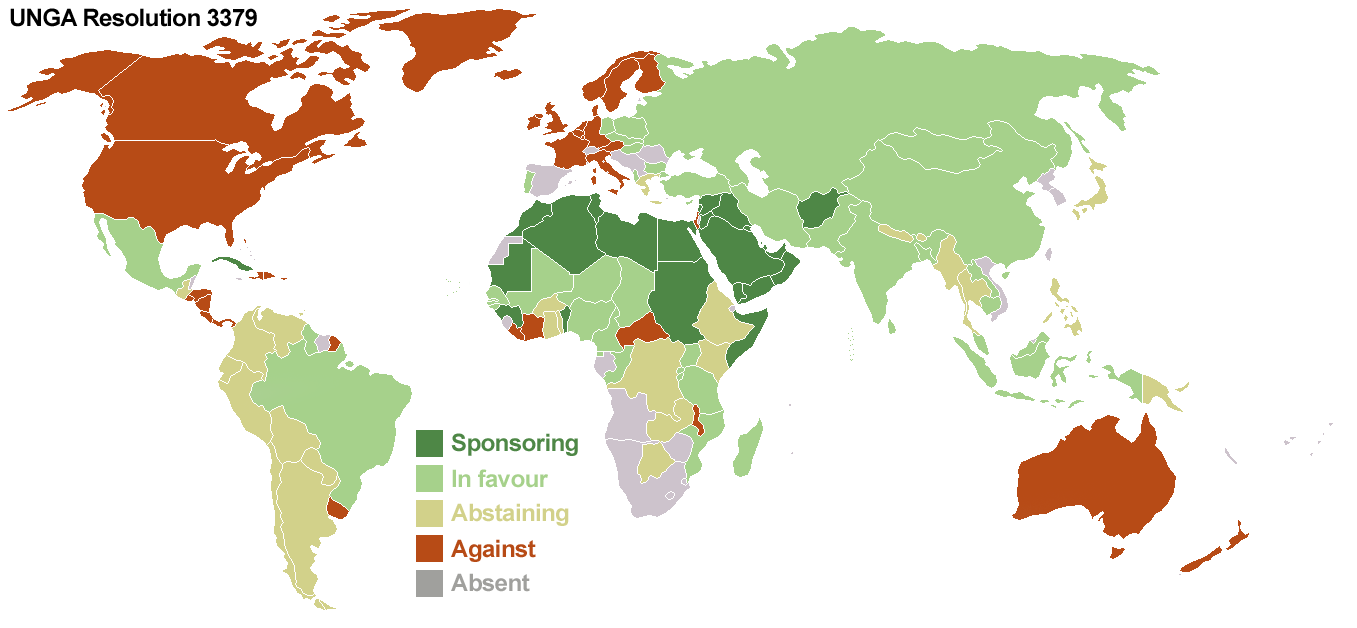
UN General Assembly Resolution 46/86
United Nations General Assembly Resolution 3379, adopted on 10 November 1975, "''Determines'' that Zionism is a form of racism and racial discrimination" with 72 votes in favour, 35 votes against, and 32 abstentions. It was revoked by Resolution 46/86, adopted on 16 December 1991 with 111 votes in favour, 25 votes against, and 13 abstentions. The vote for Resolution 3379 was held nearly one year after the adoption of Resolution 3236 anResolution 3237 the former recognized the " Question of Palestine" and invited the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) to participate in international diplomacy; and the latter designated the PLO as a non-member Assembly observer following the " Olive Branch Speech" by Palestinian political leader Yasser Arafat. In the context of the Declaration on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination, adopted on 10 November 1963, Resolution 3379 officially condemned the national ideology of the State of Israel. It was sponsored by the Arab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racism
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one Race (human categorization), race or ethnicity over another. It may also mean prejudice, discrimination, or antagonism directed against other people because they are of a different ethnic background. Modern variants of racism are often based in social perceptions of biological differences between peoples. These views can take the form of social actions, practices or beliefs, or political systems in which different races are ranked as inherently superior or inferior to each other, based on presumed shared inheritable traits, abilities, or qualities. There have been attempts to legitimize racist beliefs through scientific means, such as scientific racism, which have been overwhelmingly shown to be unfounded. In terms of political systems (e.g. apartheid) that support the expression of prejudice or aversion in discri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zionism
Zionism is an Ethnic nationalism, ethnocultural nationalist movement that emerged in History of Europe#From revolution to imperialism (1789–1914), Europe in the late 19th century that aimed to establish and maintain a national home for the Jews, Jewish people, pursued through the colonization of Palestine (region), Palestine, a region roughly corresponding to the Land of Israel in Judaism, with central importance in Jewish history. Zionists wanted to create a Jewish state in Palestine with as much land, as many Jews, and as few Palestinian people, Palestinian Arabs as possible. Zionism initially emerged in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe as a secular nationalist movement in the late 19th century, in reaction to newer waves of antisemitism and in response to the Haskalah, or Jewish Enlightenment. The arrival of Zionist settlers to Palestine during this period is widely seen as the start of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict. The Zionist claim to Palestine was base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |