|
1964 United Kingdom General Election
The 1964 United Kingdom general election was held on Thursday 15 October 1964. It resulted in the Conservatives, led by Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Prime Minister Alec Douglas-Home, narrowly losing to the Labour Party (UK), Labour Party, led by Harold Wilson; Labour secured a parliamentary majority of four seats and ended its thirteen years in opposition since the 1951 United Kingdom general election, 1951 election. At age 47, Wilson became the youngest Prime Minister since Lord Rosebery in 1894. Background Both major parties had changed leadership in 1963. Following the sudden death of Labour leader Hugh Gaitskell early in the year, the party chose Harold Wilson (at the time, thought of as being on the party's centre-left), while Alec Douglas-Home, at the time the Earl of Home, had taken over as Conservative leader and Prime Minister in October after Harold Macmillan announced his resignation in the wake of the Profumo affair. Douglas-Home shortly afterward discla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of United Kingdom Parliament Constituencies (1955–1974)
List of UK Parliamentary constituencies (1950–1955), Constituencies in 1950–1955 , List of MPs elected in the 1955 United Kingdom general election, 1955 MPs , List of MPs elected in the 1959 United Kingdom general election, 1959 MPs , List of MPs elected in the 1964 United Kingdom general election, 1964 MPs , List of MPs elected in the 1966 United Kingdom general election, 1966 MPs , List of MPs elected in the 1970 United Kingdom general election, 1970 MPs , List of UK Parliamentary constituencies (1974–1983), Constituencies in 1974–1983 This is a list of all United Kingdom constituencies, constituencies that were in existence in the 1955 United Kingdom general election, 1955, 1959 United Kingdom general election, 1959, 1964 United Kingdom general election, 1964, 1966 United Kingdom general election, 1966, and 1970 United Kingdom general election, 1970 General Elections. {{DEFAULTSORT:List of United Kingdom Parliament constituencies (1955-1974) Lists of constituen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Of Home
Earl of Home ( ) is a title in the Peerage of Scotland. It was created in 1605 for Alexander Home of that Ilk, 6th Lord Home. The Earl of Home holds, among others, the subsidiary titles of Lord Home (created 1473) and Lord Dunglass (1605) in the Peerage of Scotland, and Baron Douglas, of Douglas in the County of Lanark (1875), in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. Various Earls of Home have also claimed the title of Lord Hume of Berwick. The Earl is also '' Chief of the Name and Arms of Home'' and '' heir general'' to the House of Douglas. The title of Lord Dunglass is used as a courtesy title by the eldest son of the Earl. The most famous recent holder of the title was the 14th Earl, Alexander Frederick Douglas-Home, better known as Sir Alec Douglas-Home. After the unexpected resignation of Harold Macmillan, the 14th Earl was named Prime Minister by the monarch. For the first time in over sixty years, a sitting Prime Minister was a member of the House of Lords rather than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles De Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle (22 November 18909 November 1970) was a French general and statesman who led the Free France, Free French Forces against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government of the French Republic from 1944 to 1946 to restore democracy in France. In 1958, amid the May 1958 crisis in France, Algiers putsch, he came out of retirement when appointed Prime Minister of France, Prime Minister by President René Coty. He rewrote the Constitution of France and founded the French Fifth Republic, Fifth Republic after approval by 1958 French constitutional referendum, referendum. He was elected President of France later that year, a position he held until his resignation in 1969. Born in Lille, he was a decorated officer of World War I, wounded several times and taken prisoner of war (POW) by the Germans. During the interwar period, he advocated mobile armoured divisions. During the German invasion of May 1940, he led an armoured divisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine-launched Ballistic Missiles
A submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) is a ballistic missile capable of being launched from submarines. Modern variants usually deliver multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), each of which carries a nuclear warhead and allows a single launched missile to strike several targets. Submarine-launched ballistic missiles operate in a different way from submarine-launched cruise missiles. Modern submarine-launched ballistic missiles are closely related to intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), with ranges of over , and in many cases SLBMs and ICBMs may be part of the same family of weapons. History Origins The first practical design of a submarine-based launch platform was developed by the Germans near the end of World War II involving a launch tube which contained a V-2 ballistic missile variant and was towed behind a submarine, known by the code-name ''Prüfstand XII''. The war ended before it could be tested, but the engineers who had worked on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polaris Programme
The United Kingdom's Polaris programme, officially named the British Naval Ballistic Missile System, provided its first submarine-based nuclear weapons system. Polaris was in service from 1968 to 1996. Polaris itself was an operational system of four ballistic missile submarines, each armed with 16 Polaris A-3 ballistic missiles. Each missile was able to deliver three ET.317 thermonuclear warheads. This configuration was later upgraded to carry two warheads hardened against the effects of radiation and nuclear electromagnetic pulse, along with a range of decoys. The British Polaris programme was announced in December 1962 following the Nassau Agreement between the US and the UK. The Polaris Sales Agreement provided the formal framework for cooperation. Construction of the submarines began in 1964, and the first patrol took place in June 1968. All four boats were operational in December 1969. They were operated by the Royal Navy, and based at Clyde Naval Base on Scotland' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nassau Agreement
The Nassau Agreement, concluded on 21 December 1962, was an agreement negotiated between President of the United States, John F. Kennedy, and Harold Macmillan, the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, to end the Skybolt Crisis. A series of meetings between the two leaders over three days in the Bahamas followed Kennedy's announcement of his intention to cancel the AGM-48 Skybolt, Skybolt air-launched ballistic missile project. The US agreed to supply the UK with UGM-27 Polaris, Polaris submarine-launched ballistic missiles for the UK Polaris programme. Under an earlier agreement, the US had agreed to supply Skybolt missiles in return for allowing the establishment of a ballistic missile submarine base in the Holy Loch near Glasgow. The British Government had then cancelled the development of its medium-range ballistic missile, known as Blue Streak (missile), Blue Streak, leaving Skybolt as the basis of the UK's independent nuclear deterrent in the 1960s. Without Skybolt, the V-bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Streak (missile)
The de Havilland Propellers Blue Streak was a British Intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM), and later the first stage of the Europa satellite launch vehicle. Blue Streak was cancelled without entering full production. The project was intended to maintain an independent British nuclear deterrent, replacing the V bomber fleet which would become obsolete by 1965. The operational requirement for the missile was issued in 1955 and the design was complete by 1957. During development, it became clear that the missile system was too expensive and too vulnerable to a surprise attack. The missile project was cancelled in 1960, with US-led Skybolt the preferred replacement. Partly to avoid political embarrassment from the cancellation, the UK government proposed that the rocket be used as the first stage of a civilian satellite launcher called Black Prince. As the cost was thought to be too great for the UK alone, international collaboration was sought. This led to the formati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Weapons Delivery
Nuclear weapons delivery is the technology and systems used to place a nuclear weapon at the position of detonation, on or near its target. All nine nuclear states have developed some form of medium- to long-range delivery system for their nuclear weapons. Alongside improvement of weapons, their development and deployment played a key role in the nuclear arms race. Strategic nuclear weapons are intended primarily as part of a doctrine of deterrence by threatening large targets, such as cities or military installations. These are generally delivered by some combination of land-based intercontinental ballistic missiles, sea-based submarine-launched ballistic missiles, and air-based strategic bombers carrying gravity bombs or cruise missiles. The possession of all three is known as a nuclear triad. Tactical nuclear weapons are intended for battlefield usage and/or destroying specific military, communications, or infrastructure targets, and generally have lower yields ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skybolt
The Douglas GAM-87 Skybolt (AGM-48 under the 1963 Tri-service system) was an air-launched ballistic missile (ALBM) developed by the United States during the late 1950s. The basic concept was to allow US strategic bombers to launch their weapons from well outside the range of Soviet defenses, as much as from their targets. To do this in an air-launched form, a lightweight thermonuclear warhead was needed. Initially, the W47 from the Polaris missile was selected, but it was later replaced by the W59 from the Minuteman missile. The UK joined the Skybolt program in 1960, intending to use it on their V bomber force. When the design added a star tracker in addition to its inertial navigation system (INS) this meant that it could only be carried externally where the tracker could see the sky. This requirement along with the required ground clearance on takeoff limited it to the Avro Vulcan bomber. Several design decisions in the W47 led the RAF to question its safety, so they intended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recession Of 1960–1961
The recession of 1960–1961 was a recession in the United States. According to the National Bureau of Economic Research, the recession lasted for 10 months, beginning in April 1960 and ending in February 1961. The recession preceded the third-longest economic expansion in U.S. history, from February 1961 until the beginning of the recession of 1969–1970 in December 1968. The Federal Reserve had started to tighten monetary policy in 1958 and eased off in 1961. During this recession, the Gross domestic product, GDP of the United States fell 1.4 percentage points. Though the recession ended in February 1961, the unemployment rate did not peak for several more months. In May 1961, the rate reached its height for the cycle of 7.1 percent. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Retrieved o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
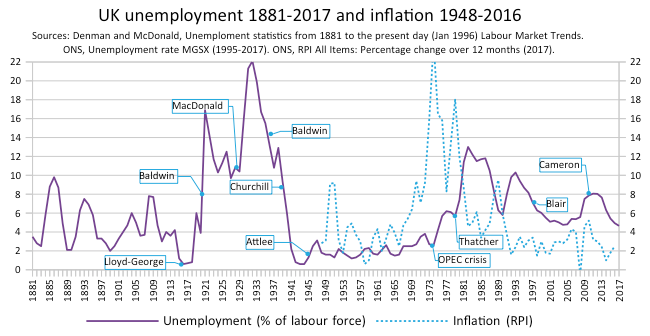
Unemployment In The United Kingdom
Unemployment in the United Kingdom is measured by the Office for National Statistics. As of February 2024, the U.K. unemployment rate is 3.8%, down from 3.9% in January. In the three-month figures (July to September 2022) the unemployment rate was estimated at 3.6%, which is 0.2 percentage points lower than the previous three-month period. The ONS said the employment rate, or percentage of people in work for those aged between 16 and 64, was estimated to be 75.5%. This was largely unchanged compared with the previous three-month period and 1.1 percentage points lower than before the pandemic (December 2019 to February 2020). The economic inactivity rate (is the proportion of people aged between 16 and 64 years who are not in the labour force) is 21.6%, an increase of 0.2 percentage points on the quarter The figures are compiled through the Labour Force Survey, which asks a sample of 53,000 households and is conducted every 3 months. Unemployment levels and rates are published e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1963 Kinross And Western Perthshire By-election
The 1963 Kinross and Western Perthshire by-election of 7 November 1963 was a by-election to the UK House of Commons. It was unique among by-elections since 1918 in that one of the candidates was the sitting prime minister, Alec Douglas-Home; he was nominated for the constituency after disclaiming a peerage, as he felt he needed to be a member of the Commons rather than the House of Lords during his premiership. Douglas-Home won the election. Candidates The by-election was caused when Scottish Office Minister Gilmour Leburn died while on holiday on 15 August 1963. The constituency of Kinross and West Perthshire, a large rural area at the southern end of the Scottish Highlands, was the safest Conservative seat in Scotland (majority 12,248 in 1959) and a plum seat for any Conservative candidate. On 11 September, the Executive of Kinross and West Perthshire Unionist Association selected Hon. George Younger, a 31-year-old heir of the Scottish aristocracy who was looking to make a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |