|
1929 24 Hours Of Le Mans
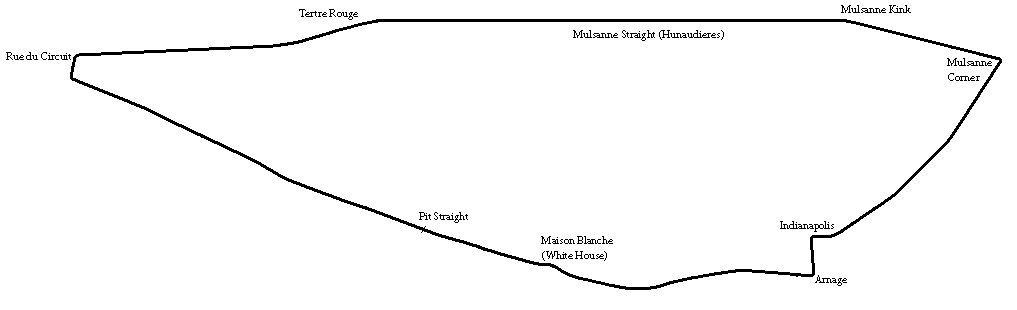
The 1929 24 Hours of Le Mans was the 7th Grand Prix of Endurance that took place at the Circuit de la Sarthe on 15 and 16 June 1929. In the most dominant display in the race to date, Bentley achieved a comprehensive victory taking the first four places on distance. Bentley director Woolf Barnato repeated his victory of the previous year, co-driven this time by fellow Bentley Boy ''Sir'' Henry “Tim” Birkin. They had led from start to finish, setting a new distance record and lap record. The race was relatively quiet,Clarke 1998, p.59-61: Motor Jun18 1929Laban 2001, p.58 without serious incident, aside from a fuel fire burning Stutz driver Édouard Brisson. Half of the reduced field had retired by dawn on the Sunday and the Bentley team was able to stage a formation finish for its four finishers. Regulations The international regulations remained unchanged. However, for its part, the Automobile Club de l'Ouest (ACO) decreed that 2-seater cars could now be no bigger tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circuit De La Sarthe Le Mans 1929-1931
Circuit may refer to: Science and technology Electrical engineering * Electrical circuit, a complete electrical network with a closed-loop giving a return path for current ** Analog circuit, uses continuous signal levels ** Balanced circuit, paths are impedance-matched ** Circuit analysis, the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in an electrical circuit ** Circuit diagram, a graphical representation of an electrical circuit ** Digital circuit, uses discrete signal levels ** Electronic circuit, contains "active" (nonlinear) electronic components capable of performing amplification, computation, and data transfer *** Asynchronous circuit, or self-timed circuit, a sequential digital logic circuit that is not governed by a clock circuit or global clock signal *** Integrated circuit, a set of electronic circuits on a small "chip" of semiconductor material **** Mixed-signal integrated circuit, contains both analog and digital signals * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Chassagne
Julien Jean Chassagne (26 July 1881 – 13 April 1947) was a pioneer submariner, aviator, and French racing driver active 1906–1930. Chassagne finished third in the 1913 French Grand Prix; won the Grand Prix Sunbeams 1921, 1922 TT, 1922 Tourist Trophy and finished second in the 1925 24 Hours of Le Mans, 1925 Le Mans Grand Prix d'Endurance - all in Sunbeam Motor Car Company, Sunbeam motorcars. He was second in the 1921 Italian Grand Prix with a Ballot (automobile), Ballot, and set speed records and won races at Brooklands and hill climbs internationally. Chassagne was also associated with the Bentley Boys, who are described as having captured the spirit of the times, partying as hard as they worked. Larger than life, their restless and often reckless love of speed and adventure complemented the big green Bentleys from Cricklewood perfectly. As a result of his association with Bentley Motors, Chassagne Square in Crewe was named in his honour. Chassagne applied to serve as a pilo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Motors Company
Continental Motors Company was an American manufacturer of internal combustion engines. The company produced engines as a supplier to many independent manufacturers of automobiles, tractors, trucks, and stationary equipment (such as pumps, generators, and industrial machinery drives) from the 1900s through the 1960s. Continental Motors also produced automobiles in 1932–1933 under the name Continental Automobile Company. The Continental Aircraft Engine Company was formed in 1929 to develop and produce its aircraft engines, and would become the core business of Continental Motors, Inc. History In 1905, Continental Motors was founded with the introduction of a four-cylinder, four-stroke L-head engine utilizing a single camshaft. In August 1929, the Continental Motors Company formed the Continental Aircraft Engine Company as a subsidiary to develop and produce its aircraft engines. Continental Motors entered into the production of automobiles rather indirectly. Continental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Du Pont Motors
Du Pont Motors was founded by E. Paul du Pont to produce marine engines for the Allied nations during World War I. After the war, Du Pont Motors produced extremely high-end automobiles. The cars were manufactured in Wilmington, Delaware. E. Paul du Pont's resources allowed him to hire top-quality automotive and management talent. The company's first product, the Model A, was introduced at the 1919 International Salon at the Commodore Hotel in New York City (an event for the wealthy by invitation only, along with the finest manufacturers and coach builders). The Model G was introduced in 1928, with a 5.3 liter side-valve straight eight engine of . Between 1919 and 1931, the company produced approximately 625 automobiles. They were compared to such luxury cars as Packard, Cadillac and even Stutz, and Duesenberg, and were known for their quality and style. Customers included Mary Pickford and Douglas Fairbanks, Will Rogers, and Jack Dempsey. The company went bankrupt in 193 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roots Blower Company
The Roots Blower Company was an American engineering company based in Connersville, Indiana. It was founded in 1854 by the inventors Philander Higley Roots and Francis Marion Roots. It is notable for the Roots-type supercharger, Roots blower, a type of pump.INDIANA ONE HUNDRED AND FIFTY YEARS OF AMERICAN DEVELOPMENT Vol. 3, By Charles Roll, The Lewis Publishing Company, 1931 Retrieved 1 April 2012. Today, Roots blowers are mainly used as air pumps in superchargers for internal combustion engines; they were first used in blast furnaces to blow combustion air to melt iron. History Legend of origin The Roots brothers located their business in Connersville, Indiana, as the Whitewater ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Chiron
Louis Alexandre Chiron (; 3 August 1899 – 22 June 1979) was a Monégasque racing driver who competed in rallies, sports car races, and Grands Prix. Among the greatest drivers between the two World Wars, his career embraced over thirty years, starting in 1923, and ending at the end of the 1950s. He is still the oldest driver ever to have started a race in the Formula One World Championship, having taken 6th place in the 1955 Monaco Grand Prix when he was 55. Three years later he became the oldest driver to enter a Formula One race, at 58. The Bugatti Chiron takes its name from him. Until 2024, when Charles Leclerc matched his achievement, he was the only Monegasque driver to have won the Monaco Grand Prix. Early life and career Coming from a family of wine-growers, Louis Chiron's father gained employment as a butler in the Hôtel de Paris at Monaco. As a teenager, Louis was employed as a bellboy at the hotel, and his interest in cars and racing started at that time. Durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Terres Weymann
Charles Terres Weymann (2 August 1889 – 1976) was a Haitian-born early aeroplane racing pilot and businessman. During World War I he flew for Nieuport as a test pilot and was awarded the rank of Chevalier of the Legion of Honour. Early years Weymann was born in Port-au-Prince, Haiti, on 2 August 1889 to an American father of Alsatian descent and a Haitian mother. It is said that Weymann's mother was Cornelie Miot, herself Haitian and daughter of Charles Miot and Lesinska Cecile Rivière, both Haitians. Lesinska Cecile Rivière (1829–1908), Charles's maternal grandmother, was the sister of Bienaimé "Mémé" Rivière, the richest person in Haiti at the time, who owned shipping lines among other things. Inventor Fabric bodies After the war Charles Weymann used his knowledge of airframe manufacture to develop a system of making fabric bodies for road vehicles. He opened factories in Paris in 1921, London in 1923 and Indianapolis in 1928. The market for these grew and Weyman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippe De Rothschild
Philippe, Baron de Rothschild (13 April 1902 – 20 January 1988) was a member of the Rothschild banking family who became a Grand Prix motor racing driver, a screenwriter and playwright, a theatrical producer, a film producer, a poet, and one of the most successful wine growers in the world. Early life Born in Paris, Georges Philippe de Rothschild was the younger son of Baron Henri de Rothschild (who was a noted playwright under the name André Pascal) and Mathilde Sophie Henriette von Weissweiller. At the outbreak of World War I, 12-year-old Philippe was sent to the safety of the family's vineyard in the village of Pauillac in the Médoc. There, he developed a love of the country and the wine business, an enterprise in his family since 1853, but one his father and grandfather had shown little interest in. As a young man, in sharp contrast to the Rothschild family's staid aristocratic traditions, Philippe de Rothschild became a larger-than-life figure. Car racing Durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Eyston
Captain George Edward Thomas Eyston MC OBE (28 June 1897 – 11 June 1979) was a British engineer, inventor, and racing driver best known for breaking the land speed record three times between 1937 and 1939. Early life George Eyston was educated at Stonyhurst College and Trinity College, Cambridge. His study of engineering at Cambridge was interrupted by World War I when he was commissioned in the Dorset Regiment and later served in the Royal Field Artillery. After the war he returned to Trinity College and was captain of the First Trinity Boat Club. Career Motor racing Eyston's racing career began before World War One, when he was still a schoolboy, and raced motorcycles under an assumed name. After the war (in which he was awarded the Military Cross) he reverted to his own name, moved on to car racing and entered European road races, particularly in Bugattis, with success in races such as the 1921 and 1926 French Grand Prix Later he became well known for racing superc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mrs Victor Bruce
Mildred Mary Petre (10 November 1895 – 21 May 1990) was a British record-breaking racing motorist, speedboat racer and aviator in the 1920s and 1930s, and later, successful businesswoman. Commonly referred to as Mrs Victor Bruce, she was also known in contemporary references as Mary Petre Bruce, Mildred Bruce, Mildred Mary Bruce and Mary Victor Bruce. Early life Mildred Mary Petre was born at Coptfold Hall, Margaretting, Ingatestone, Chelmsford, Essex, England, on 10 November 1895, the daughter of Jennie Maginness (née Williams), a Shakespearean actress from Indiana and Lawrence Petre, a descendant of Sir William Petre. She had five brothers and was educated at the Convent of Notre Dame de Sion, in Bayswater, London. Her childhood involved sailing, riding, and learning to ride a motorcycle, and drive a car. In 1911, aged 15, she began her passion for motor vehicles by riding her brother's Matchless motorcycle, travelling around Osterley, west London, with her collie dog Lad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autodrome De Linas-Montlhéry
A race track (racetrack, racing track or racing circuit) is a facility built for racing of vehicles, athletes, or animals (e.g. horse racing or greyhound racing). A race track also may feature grandstands or concourses. Race tracks are also used in the study of animal locomotion. A ''racetrack'' is a permanent facility or building. ''Racecourse'' is an alternate term for a horse racing track, found in countries such as the United Kingdom, India, Australia, Hong Kong, and the United Arab Emirates. Race tracks built for bicycles are known as ''velodromes''. ''Circuit'' is a common alternate term for race track, given the circuit configuration of most race tracks, allowing races to occur over several laps. Some race tracks may also be known as ''speedways'', or ''raceways''. A ''race course'', as opposed to a ''racecourse'', is a nonpermanent track for sports, particularly road running, water sports, road racing, or rallying. Many sports usually held on race tracks also can occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard Rubin
Bernard Rubin (6 December 1896 – 27 June 1936) was an Australian racing driver and pilot who was a member of the " Bentley Boys" team at the Bentley Motor Company and winner of the 1928 24 Hours of Le Mans. Personal life The son of Australian pearl salesman Mark Rubin (1867 – 1919), Bernard was born in the Melbourne suburb of Carlton, before he eventually moved to London with his family in 1908. His mother was the former Rebecca de Vahl Davis, who came from a notable Jewish Melbourne family. He had a brother, well-known grazier, art collector and philanthropist Harold de Vahl Rubin (1899–1964). His uncle, wealthy entrepreneur Abraham de Vahl Davis (1864 – 1912), went down with the steamship '' SS Koombana'' after having purchased the legendary – and presumably cursed – Roseate Pearl on behalf of Bernard's father, the Broome Pearler Mark Rubin. On 29 March 1935, in Paris, Rubin married Audrey Mary Simpson, daughter of Charles Ringham Simpso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |