|
190 BC
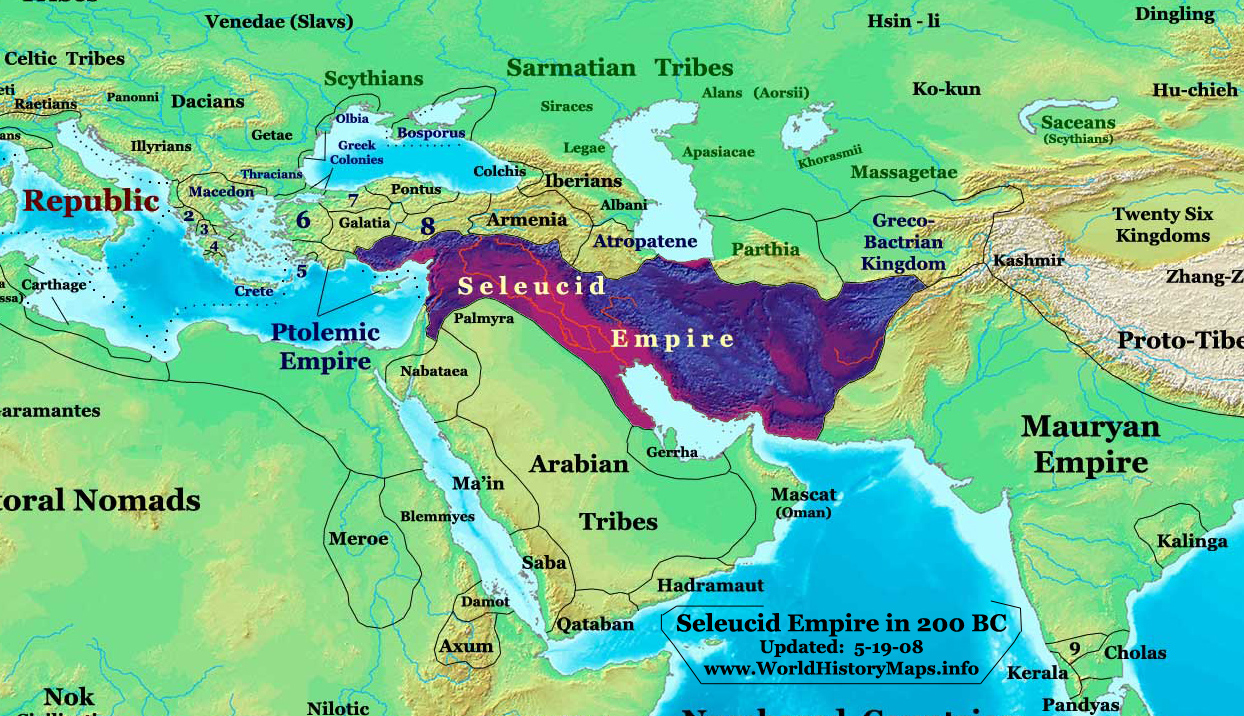
__NOTOC__ Year 190 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Asiaticus and Laelius (or, less frequently, year 564 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 190 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Greece * The Battle of the Eurymedon is fought between a Seleucid fleet and ships from Rhodes and Pergamum, who are allied with the Roman Republic. The Seleucids are led by the famous Carthaginian general Hannibal. The Rhodians and their allies are victorious and Hannibal's fleet is forced to flee. * Subsequently, the naval Battle of Myonessus is fought between a Seleucid fleet and a Roman fleet with the help of Rhodian ships. The Romans and their allies are victorious. * As Philip V of Macedon has aided Rome against her enemies on the Greek peninsula, his tribute to Rome is remitted and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Calendar
The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman Kingdom and Roman Republic. Although the term is primarily used for Rome's pre-Julian calendars, it is often used inclusively of the Julian calendar established by Julius Caesar in 46 BC. According to most Roman accounts, #Romulus, their original calendar was established by their Roman legend, legendary list of kings of Rome, first king Romulus. It consisted of ten months, beginning in spring with March and leaving winter as an unassigned span of days before the next year. These months each had 30 or 31 days and ran for 38 nundinal cycles, each forming a kind of eight-day weeknine days inclusive counting, counted inclusively in the Roman mannerand ending with religious rituals and a Roman commerce, public market. This fixed calendar bore traces of its origin as an observational calendar, observational lunar calendar, lunar one. In particular, the most important days of each monthits kalends, nones (calendar), nones, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellespont
The Dardanelles ( ; ; ), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli (after the Gallipoli peninsula) and in classical antiquity as the Hellespont ( ; ), is a narrow, natural strait and internationally significant waterway in northwestern Turkey that forms part of the continental boundary between Asia and Europe and separates Asian Turkey from European Turkey. Together with the Bosporus, the Dardanelles forms the Turkish Straits. One of the world's narrowest straits used for international navigation, the Dardanelles connects the Sea of Marmara with the Aegean and Mediterranean seas while also allowing passage to the Black Sea by extension via the Bosporus. The Dardanelles is long and wide. It has an average depth of with a maximum depth of at its narrowest point abreast the city of Çanakkale. The first fixed crossing across the Dardanelles opened in 2022 with the completion of the 1915 Çanakkale Bridge. Most of the northern shores of the strait along the Gallipoli peni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophene
Sophene ( or , ; ) was a province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, located in the south-west of the kingdom, and of the Roman Empire. The region lies in what is now southeastern Turkey. History The region that was to become Sophene was part of the kingdom of Ararat (Urartu) in the 8th and 7th centuries BC. After unifying the region with his kingdom in the early 8th century BC, king Argishtis I of Urartu resettled many of its inhabitants in his newly built city of Erebuni (modern day Armenian capital Yerevan). Around 600 BC, Sophene became part of the newly emerged ancient Armenian Kingdom of the Orontids. This dynasty acted as satraps of Persia first under the Median Empire, later under the Achaemenid Empire. After Alexander the Great's campaigns in the 330s BC and the subsequent collapse of the Achaemenid Empire, Sophene remained part of the newly independent kingdom of Greater Armenia. In the early 3rd century BC, at the instigation of the Seleucid Empire, which was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Armenia (Antiquity)
The Kingdom of Greater Armenia or simply Greater Armenia or Armenia Major ( '; ), sometimes referred to as the Armenian Empire under Tigranes the Great, Tigranes II, was an Armenians, Armenian kingdom in the Ancient Near East which existed from 331 BC to 428 AD. Its history is divided into the successive reigns of three Royal family, royal dynasties: Orontid dynasty, Orontid (331–200 BC), Artaxiad dynasty, Artaxiad (189 BC12 AD), and Arsacid dynasty of Armenia, Arsacid (52–428). The root of the kingdom lies in the Satrapy of Armenia of the Achaemenid Empire of Iran, which was formed from the territory of Urartu (860–590 BC) after it was conquered by the Medes in 590 BC. The satrapy became a kingdom in 321 BC during the reign of the Orontid dynasty after the conquest of Persia by Alexander the Great, which was then incorporated as one of the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic kingdoms of the Seleucid Empire. Under the Seleucid Empire ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zariadres
Zariadres was an Orontid ruler of Sophene in the early 2nd century BC. According to Strabo, he was a general of the Seleucid ruler Antiochus III who was made ruler of Sophene, although most scholars believe that he was a member of the Orontid dynasty, which ruled Armenia and Sophene. After the Seleucids were defeated by the Romans in 190 BC, Zariadres and his ally Artaxias I of Greater Armenia (possibly also Zariadres' son) revolted against the Seleucids, became independent kings and expanded their territories. The last information about Zariadres' reign dates to 188 BC. He was succeeded as king by Mithrobouzanes, possibly his son. Name ''Zariadres'' () is the Greek rendering of an Iranian name, attested as ''zrytr''/''zryhr'' in the Aramaic inscriptions of Artaxias I in Sevan and Siwnik, and as in Armenian sources. The name derives from Old Iranian * ('with golden fire'). Biography Strabo writes that Sophene was taken over by a "general 'strategos'' of King Antiochus I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artaxias I
Artaxias I (from ) was the founder of the Artaxiad dynasty of Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Armenia, ruling from 189 BC to 160 BC. Artaxias was a member of a branch of the Orontid dynasty, the earlier ruling dynasty of Armenia. He expanded his kingdom on all sides, consolidating the territory of Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Greater Armenia. He enacted a number of administrative reforms to order his expanded realm. He also founded a new capital in the central valley of the Aras (river), Araxes River called Artaxata (Artashat), which quickly grew into a major urban and commercial center. He was succeeded by his son Artavasdes I of Armenia, Artavasdes I. Modern scholars #Historical assessment, regard him as the founder of independent Armenian statehood. Name The Ancient Greek, Greek form ''Artaxias'' ultimately derives from the Iranian languages, Old Iranian name *, which is also the source of Greek () and Middle Persian Ardeshir (other), Ardashir. The Armenian_lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median kingdom, Median and Achaemenid Empire, Persian (Achaemenid) Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic empires. A satrapy is the territory governed by a satrap. A satrap served as a viceroy to the king, though with considerable autonomy. The word came to suggest tyranny or ostentatious splendour, and its modern usage is a pejorative and refers to any subordinate or local ruler, usually with unfavourable connotations of corruption. Etymology The word is derived via Latin from Ancient Greek, Greek (), itself borrowed from an Old Iranian languages, Old Iranian . In Old Persian, which was the native language of the Achaemenids, it is recorded as (, literally "protector of the province"). The Median language, Median form is reconstructed as . Its Sanskrit cognate is (). The Biblical Hebrew form is , as found in Esther 3:12. In the Parthian l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to the east, and Iran and the Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, Nakhchivan to the south. Yerevan is the Capital city, capital, largest city and Economy of Armenia, financial center. The Armenian Highlands has been home to the Hayasa-Azzi, Shupria and Nairi. By at least 600 BC, an archaic form of Proto-Armenian language, Proto-Armenian, an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, had diffused into the Armenian Highlands.Robert Drews (2017). ''Militarism and the Indo-Europeanizing of Europe''. Routledge. . p. 228: "The vernacular of the Great Kingdom of Biainili was quite certainly Armenian. The Armenian language was obviously the region's vernacular in the fifth century BC, when Persian commanders and Greek writers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and communities. Prior to the Roman period, most of these regions were officially unified only once under the Kingdom of Macedon from 338 to 323 BC. In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Three centuries after the decline of Mycenaean Greece during the Bronze Age collapse, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical Greece, from the Greco-Persian Wars to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC, and which included the Golden Age of Athens and the Peloponnesian War. The u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lydia
Lydia (; ) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom situated in western Anatolia, in modern-day Turkey. Later, it became an important province of the Achaemenid Empire and then the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sardis. At some point before 800 BC, the Lydian people achieved some sort of political cohesion, and existed as an independent kingdom by the 600s BC. At its greatest extent, during the 7th century BC, it covered all of western Anatolia. In 546 BC, it became a Lydia (satrapy), satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire, known as ''Sparda'' in Old Persian. In 133 BC, it became part of the Roman Republic, Roman Asia (Roman province), province of Asia. Lydian coins, made of electrum, are among the oldest in existence, dated to around the 7th century BC. Geography Lydia is generally located east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish provinces of Uşak Province, Uşak, Manisa Province, Manisa and inland İzmir Province, İzmir.Rhodes, P.J. ''A History of the Classical Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesia Ad Sipylum
Magnesia Sipylum ( or ; modern Manisa, Turkey) was a city of Lydia, situated about 65 km northeast of Smyrna (now İzmir) on the river Hermus (now Gediz) at the foot of Mount Sipylus. The city should not be confused with its older neighbor, Magnesia on the Maeander, both founded by colonists from the Greek region of Magnesia. History The first famous mention of the city is in 190 BC, when Antiochus the Great was defeated in the battle of Magnesia by the Roman consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus. It became a city of importance under Roman rule and, though nearly destroyed by an earthquake in the reign of Tiberius, was restored by that emperor and flourished through the Roman Empire. It was an important regional centre through the Byzantine Empire, and during the 13th-century interregnum of the Empire of Nicea. Magnesia housed the Imperial mint, the Imperial treasury, and served as the functional capital of the Empire until the recovery of Constantinople in 1261 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Magnesia
The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the Roman consul, consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of Pergamon under Eumenes II of Pergamum, Eumenes II against a Seleucid Empire, Seleucid army of Antiochus III the Great. The two armies initially camped northeast of Magnesia ad Sipylum in Asia Minor (modern-day Manisa, Turkey), attempting to provoke each other into a battle on favorable terrain for several days. When the battle finally began, Eumenes managed to throw the Seleucid left flank into disarray. While Antiochus' cavalry overpowered his adversaries on the right flank of the battlefield, his army's center collapsed before he could reinforce it. Modern estimates give 10,000 dead for the Seleucids and 5,000 killed for the Romans. The battle resulted in a decisive Roman-Pergamene victory, which led to the Treaty of Apamea t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |