|
18th-century Literature
Literature of the 18th century refers to world literature produced during the years 1700–1799. European literature in the 18th century European literature of the 18th century refers to literature (poetry, drama, satire, essays, and novels) produced in Europe during this period. The 18th century saw the development of the modern novel as literary genre, in fact many candidates for the first novel in English date from this period, of which Daniel Defoe's 1719 ''Robinson Crusoe'' is probably the best known. Subgenres of the novel during the 18th century were the epistolary novel, the sentimental novel, histories, the gothic novel and the libertine novel. 18th century Europe started in the Age of Enlightenment and gradually moved towards Romanticism. In the visual arts, it was the period of Neoclassicism. The Enlightenment The 18th century in Europe was the Age of Enlightenment, and literature explored themes of social upheaval, reversals of personal status, political satire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially novels, Play (theatre), plays, and poetry, poems. It includes both print and Electronic literature, digital writing. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include oral literature, much of which has been transcribed.; see also Homer. Literature is a method of recording, preserving, and transmitting knowledge and entertainment. It can also have a social, psychological, spiritual, or political role. Literary criticism is one of the oldest academic disciplines, and is concerned with the literary merit or intellectual significance of specific texts. The study of books and other texts as artifacts or traditions is instead encompassed by textual criticism or the history of the book. "Literature", as an art form, is sometimes used synonymously with literary fiction, fiction written with the goal of artistic merit, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Ockley
Simon Ockley (16789 August 1720) was a British Orientalist. Biography Ockley was born at Exeter. He was educated at Queens' College, Cambridge, and graduated B.A. in 1697, MA. in 1701, and B.D. in 1710. He became a fellow of Jesus College and vicar of Swavesey, and in 1711, was chosen Adams Professor of Arabic in the university. He had a large family, and his latter days were embittered by pecuniary embarrassments, which form the subject of a chapter in Isaac D'Israeli's ''Calamities of Authors''. The preface to the second volume of his '' History of the Saracens'' is dated from Cambridge Castle, where he lay a prisoner for debt. Ockley maintained that a knowledge of Oriental literature was essential to the proper study of theology, and in the preface to his first book, the '' Introductio ad linguas orientales'' (1706), he urges the importance of the study. He died at Swavesey. Works *'' The History of the Saracens'', is his main work. It was published in two volumes, 1708� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massinger
Massinger is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Philip Massinger Philip Massinger (1583 – 17 March 1640) was an English dramatist. His plays, including '' A New Way to Pay Old Debts'', '' The City Madam'', and '' The Roman Actor'', are noted for their satire and realism, and their political and soci ... (1583–1640), English dramatist * William Massinger (1514/15–1593/94), English politician {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Rowe (dramatist)
Nicholas Rowe (; 20 June 1674 – 6 December 1718) was an English dramatist, poet and miscellaneous writer who was appointed Poet Laureate in 1715. His plays and poems were well-received during his lifetime, with one of his translations described as one of the greatest productions in English poetry. He was also considered the first editor of the works of William Shakespeare. Life Nicholas Rowe was born in Little Barford, Bedfordshire, England, son of John Rowe (d. 1692), barrister and sergeant-at-law, and Elizabeth, daughter of Jasper Edwards, on 20 June 1674. His family possessed a considerable estate at Lamerton in Devonshire. His father practised law and published Benlow's and Dallison's Reports during the reign of King James II. The future Poet Laureate was educated first at Highgate School, and then at Westminster School under the guidance of Richard Busby. In 1688, Rowe became a King's Scholar, which was followed by his entrance into Middle Temple in 1691. His entr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereotype
In social psychology, a stereotype is a generalization, generalized belief about a particular category of people. It is an expectation that people might have about every person of a particular group. The type of expectation can vary; it can be, for example, an expectation about the group's personality, preferences, appearance or ability. Stereotypes make information processing easier by allowing the perceiver to rely on previously stored knowledge in place of incoming information. Stereotypes are often faulty generalization, faulty, inaccurate, and Belief perseverance, resistant to new information. Although stereotypes generally have negative implications, they aren't necessarily negative. They may be positive, neutral, or negative. They can be broken down into two categories: explicit stereotypes, which are conscious, and implicit stereotypes, which are subconscious. Explicit stereotypes An explicit stereotype is a belief about a group that a person is consciously aware of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subplot
In fiction, a subplot or side story is a strand of the plot that is a supporting side story for any story or for the main plot. Subplots may connect to main plots, in either time and place or thematic significance. Subplots often involve supporting characters, those besides the protagonist or antagonist. Subplots may also intertwine with the main plot at some point in a story. An example of a subplot interacting with a main plot can be found in the TV series '' Mr. Robot'' (season 1). One of the main plots followed the hacker ring known as F-society, led by Elliot Alderson, where they intended to perform a massive hack against the conglomerate Evil Corp; they were executing this hack through a partnership with another hack-ring known as The Dark Army. A subplot emerged around the character development of Elliot's childhood friend and love interest Angela Moss where she evolved from a brow-beaten assistant at cybersecurity firm Allsafe into a powerbroker at Evil Corp through first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Way Of The World
''The Way of the World'' is a play written by the English playwright William Congreve. It premiered in early March 1700 in the theatre in Lincoln's Inn Fields in London. It is widely regarded as one of the best works of Restoration comedy ever written, and a centerpiece of the genre. It is still occasionally performed in operas, concerts, and theatres. Initially, however, the play struck many audience members as continuing the "immorality" of the previous decades, and was not well received. Characters The play is based on the two lovers Mirabell and Millamant (originally played by John Verbruggen and Anne Bracegirdle). In order for them to marry and receive Millamant's full dowry, Mirabell must receive the blessing of Millamant's aunt, Lady Wishfort. Unfortunately, Lady Wishfort is a very bitter lady who despises Mirabell and wants her own nephew, Sir Wilfull, to wed Millamant. Meanwhile, Lady Wishfort, a widow, wants to marry again and has her eyes on an uncle of Mirabell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Congreve (playwright)
William Congreve (24 January 1670 – 19 January 1729) was an English playwright, satirist, poet, and Whigs (British political party), Whig politician. He spent most of his career between London and Dublin, and was noted for his highly polished style of writing, being regarded by critics as one of the most important dramatists of the early Georgian era. He wrote some of the most popular poems of the 17th century, and is credited with developing the satirical comedy of manners genre. His plays and poems, which formed a major part of Restoration literature, were favorably viewed for their use of satire and comedy. Congreve is remembered for his play ''The Way of the World'' (1700), which is considered by literary commentators to be one of the centerpieces of Restoration comedy literature. Congreve also wrote several other notable plays, including ''The Old Bachelor'' (1693), ''The Double Dealer'' (1693), ''Love for Love'' (1695), and ''The Mourning Bride'' (1697), all of which he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaitai Shinsho
is a medical text translated into Japanese during the Edo period. It was written by Sugita Genpaku, and was published by Suharaya Ichibee () in 1774, the third year of An'ei. The body comprises four volumes, the illustrations, one. The contents are written kanbun-style. It is based on a translation of the Dutch , often known in Japan as , of Johann Adam Kulmus’ Latin , published before 1722 (exact year is unknown) in Gdańsk, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. As a full-blown translation from a Western language, it was the first of its kind in Japan. Background On 4 March 1771, the eighth year of Meiwa, the students of Rangaku medicine Sugita Genpaku, Maeno Ryōtaku, Nakagawa Jun'an, ''et al.'', by studying performing autopsies on criminals executed at the Kozukappara execution grounds (now, there is a possibility that Katsuragawa Hoshū was at this facility as well, but from the description in , it seems more likely that he was not). Both Sugita and Maeno had the book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugita Genpaku
was a Japanese physician and scholar known for his translation of '' Kaitai Shinsho'' (New Book of Anatomy) and a founder of ''Rangaku'' (Western learning) and ''Ranpō'' (Dutch style medicine) in Japan. He was one of the first Japanese scholars in Edo (modern day Tokyo) to study the Dutch language and is credited with being one of the first Japanese physicians to study Western medical teachings in Japan. In 1771 Genpaku and Maeno Ryōtaku, a Japanese scholar studying the Dutch language, translated a Dutch book of anatomy ''Ontleedkundige Tafelen'', originally published in German by physician and professor Johann Adam Kulmus in 1734. Genpaku was inspired to translate the Dutch text after witnessing the dissection of a female criminal while viewing ''Ontleekundige Tafelen'' as an anatomical reference throughout the dissection. He was inspired by the German drawings of human organs, which accurately depicted the organs and vasculature he saw during the dissection. The German dra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Lockman (author)
John Lockman (1698–1771) was an English author. Life Born in humble circumstances, he was a self-taught scholar who learnt to speak French by frequenting Slaughter's Coffee House. He had enough acquaintance with Alexander Pope that he could dedicate to him in 1734 his translation of Charles Porée's ''Oration''. His inoffensive character procured for him the name of the ‘Lamb.’ but when ‘Hesiod’ Cooke abused his poetry, Lockman retorted, ‘It may be so; but, thank God! my name is not at full length in the “ Dunciad.”’ His poems were chiefly occasional verse intended to be set to music for Vauxhall. In 1762 he tried, fruitlessly, to get them printed by subscription. He frequently went to court to present his verses to the royal family, and after he became secretary to the British Herring Fishery, he tendered gifts of pickled herrings. Both poems and herrings, he declared, were ‘most graciously accepted.’ He died in Brownlow Street, Long Acre, on 2 February ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
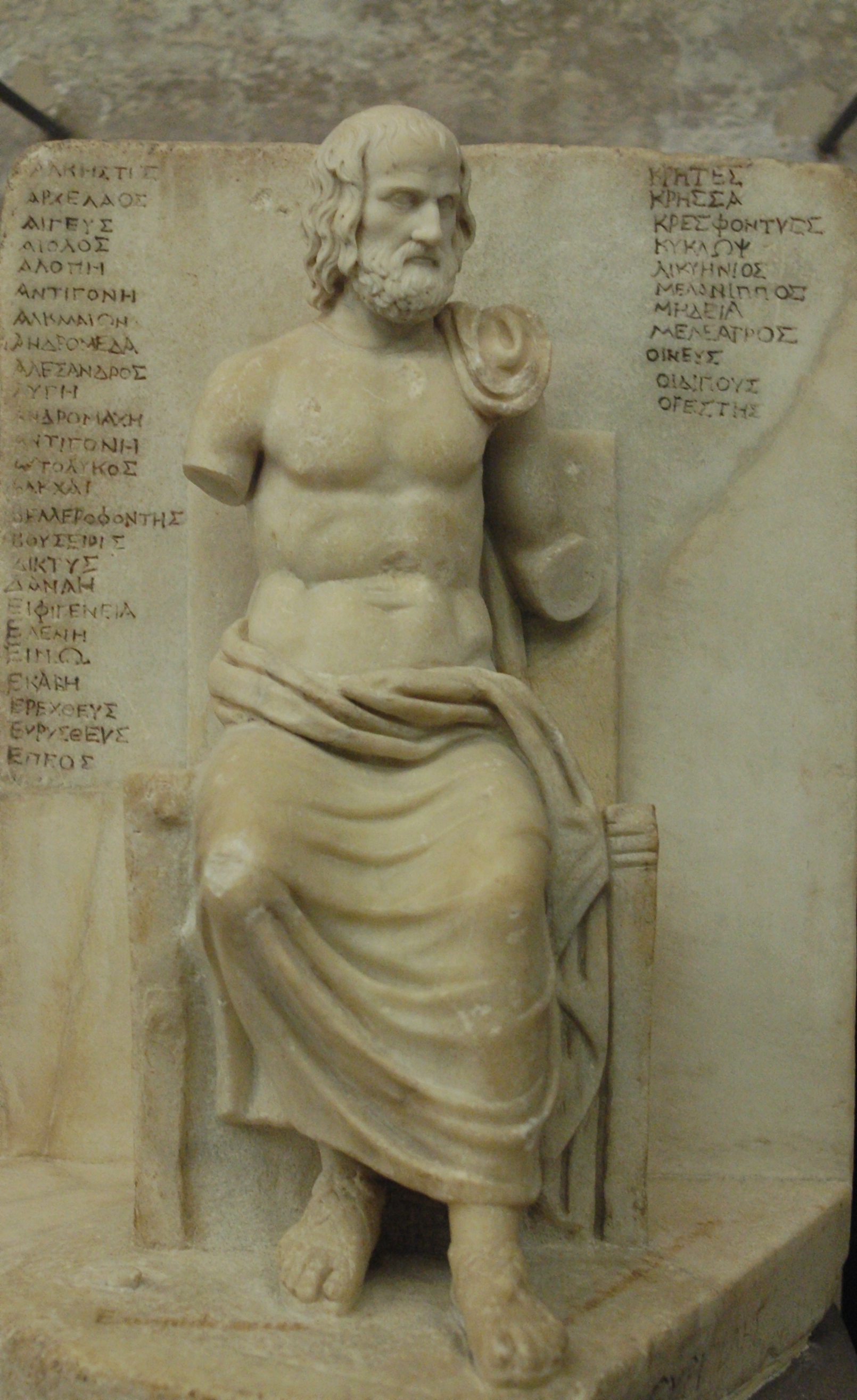
Euripides
Euripides () was a Greek tragedy, tragedian of classical Athens. Along with Aeschylus and Sophocles, he is one of the three ancient Greek tragedians for whom any plays have survived in full. Some ancient scholars attributed ninety-five plays to him, but the ''Suda'' says it was ninety-two at most. Of these, eighteen or nineteen have survived more or less complete (''Rhesus (play), Rhesus'' is suspect). There are many fragments (some substantial) of most of his other plays. More of his plays have survived intact than those of Aeschylus and Sophocles together, partly because his popularity grew as theirs declinedMoses Hadas, ''Ten Plays by Euripides'', Bantam Classic (2006), Introduction, p. ixhe became, in the Hellenistic Age, a cornerstone of ancient literary education, along with Homer, Demosthenes, and Menander.L.P.E.Parker, ''Euripides: Alcestis'', Oxford University Press (2007), Introduction p. lx Euripides is identified with theatrical innovations that have profoundly influ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |