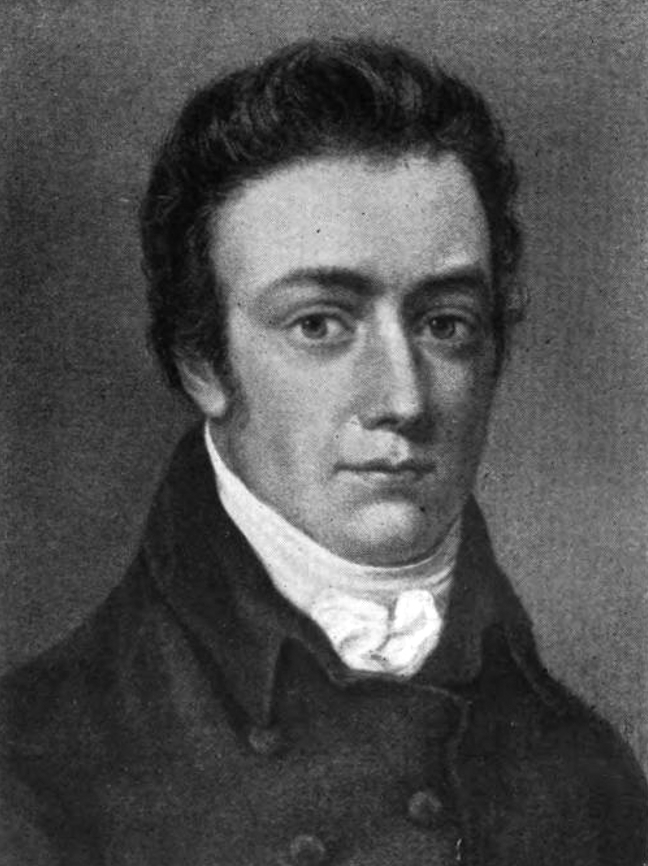|
1817 In Poetry
Nationality words link to articles with information on the nation's poetry or literature (for instance, Irish or France). Events * February 28 – Lord Byron writes a letter to Thomas Moore and includes in it his poem, "So, we'll go no more a roving". Moore will publish the poem in 1830 as part of ''Letters and Journals of Lord Byron''. * March – Percy and Mary Shelley with Claire Clairmont and the latter's new daughter by Byron, Allegra (at this time called Alba), having moved from Bath, begin a year's residence in Marlow, Buckinghamshire, England, where Mary completes ''Frankenstein'' and gives birth to her third child, and Percy writes ''The Revolt of Islam''. * September 19 – The body of Scottish poet Robert Burns (died 1796) is moved to a new mausoleum in Dumfries. * December 28 – English painter Benjamin Haydon introduces John Keats to William Wordsworth and Charles Lamb at a dinner in London to celebrate progress on his painting ''Christ's Entry in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Poetry
Poetry of Scotland includes all forms of verse written in Brythonic, Latin, Scottish Gaelic, Scots, French, English and Esperanto and any language in which poetry has been written within the boundaries of modern Scotland, or by Scottish people. Much of the earliest Welsh literature was composed in or near Scotland, but only written down in Wales much later. These include ''The Gododdin'', considered the earliest surviving verse from Scotland. Very few works of Gaelic poetry survive from this period and most of these in Irish manuscripts. ''The Dream of the Rood'', from which lines are found on the Ruthwell Cross, is the only surviving fragment of Northumbrian Old English from early Medieval Scotland. In Latin early works include a "Prayer for Protection" attributed to St Mugint, and '' Altus Prosator'' ("The High Creator") attributed to St Columba. There were probably filidh who acted as poets, musicians and historians. After the "de-gallicisation" of the Scottish court from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Combe
William Combe (25 March 174219 June 1823) was a British miscellaneous writer. His early life was that of an adventurer, his later was passed chiefly within the "rules" of the King's Bench Prison. He is most notable as the author of ''The Three Tours of Doctor Syntax'', a comic poem, illustrated by artist Thomas Rowlandson's colour plates, that satirised William Gilpin. Combe also wrote a series of imaginary letters, supposed to have been written by the second, or "wicked" Lord Lyttelton. Of a similar kind were his letters between Swift and " Stella". He also wrote the letterpress for various illustrated books, and was a general hack. Early life Combe's father, Robert Combes, was a rich Bristol ironmonger who died in 1756; his mother, Susannah Hill (died 1748), was from a Quaker background. He was educated at Eton College, but was withdrawn from the school by William Alexander, his guardian, on his father's death; Alexander died in 1762. He inherited from both his father an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frost At Midnight
''Frost at Midnight'' is a poem by Samuel Taylor Coleridge, written in February 1798. Part of the conversation poems, the poem discusses Coleridge's childhood experience in a negative manner and emphasizes the need to be raised in the countryside. The poem expresses hope that Coleridge's son, Hartley, would be able to experience a childhood that his father could not and become a true "child of nature". The view of nature within the poem has a strong Christian element in that Coleridge believed that nature represents a physical presence of God's word and that the poem is steeped in Coleridge's understanding of Neoplatonism. ''Frost at Midnight'' has been well received by critics, and is seen as the best of the conversation poems. Background ''Frost at Midnight'' was written in February 1798 when he described to Thomas Poole aspects of his childhood at Christ's Hospital school that are similar to the content of the poem. The rest comes from Coleridge's experience with his frie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manfred
''Manfred: A dramatic poem'' is a closet drama written in 1816–1817 by Lord Byron. It contains supernatural elements, in keeping with the popularity of the ghost story in England at the time. It is a typical example of Gothic fiction. Byron commenced this work in late 1816, a few months after the famous ghost-story sessions with Percy Bysshe Shelley and Mary Shelley that provided the initial impetus for '' Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus''. The supernatural references are made clear throughout the poem. ''Manfred'' was adapted musically by Robert Schumann in 1848–1849, in a composition entitled '' Manfred: Dramatic Poem with Music in Three Parts'', and in 1885 by Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky in his '' Manfred Symphony''. Friedrich Nietzsche was inspired by the poem's depiction of a super-human being to compose a piano score in 1872 based on it, "Manfred Meditation". Background Byron wrote this "metaphysical drama", as he called it, after his marriage to Annabella M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Lamb
Charles Lamb (10 February 1775 – 27 December 1834) was an English essayist, poet, and antiquarian, best known for his '' Essays of Elia'' and for the children's book '' Tales from Shakespeare'', co-authored with his sister, Mary Lamb (1764–1847). Friends with such literary luminaries as Samuel Taylor Coleridge, Robert Southey, William Wordsworth, Dorothy Wordsworth and William Hazlitt, Lamb was at the centre of a major literary circle in England. He has been referred to by E. V. Lucas, his principal biographer, as "the most lovable figure in English literature". Youth and schooling Lamb (née Field) was born in London, the son of John Lamb (–1799) and Elizabeth (died 1796), . Lamb had an elder brother, also John, and sister, Mary; four other siblings did not survive infancy. John Lamb (Lamb's father) was a lawyer's clerk and spent most of his professional life as the assistant to barrister Samuel Salt, who lived in the Inner Temple in the legal district of London; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth (7 April 177023 April 1850) was an English Romantic poetry, Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romanticism, Romantic Age in English literature with their joint publication ''Lyrical Ballads'' (1798). Wordsworth's ''masterpiece, magnum opus'' is generally considered to be ''The Prelude'', a semi-autobiographical poem of his early years that he revised and expanded a number of times. It was posthumously titled and published by his wife in the year of his death, before which it was generally known as "The Poem to Coleridge". Wordsworth was Poet Laureate of the United Kingdom, Poet Laureate from 1843 until his death from pleurisy on 23 April 1850. He remains one of the most recognizable names in English poetry and was a key figure of the Romantic poets. Early life Family and education The second of five children born to John Wordsworth and Ann Cookson, William Wordsworth was born on 7 April 1770 in what is now named Word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Keats
John Keats (31 October 1795 – 23 February 1821) was an English poet of the second generation of Romantic poets, along with Lord Byron and Percy Bysshe Shelley. His poems had been in publication for less than four years when he died of tuberculosis at the age of 25. They were indifferently received in his lifetime, but his fame grew rapidly after his death. By the end of the century, he was placed in the canon of English literature, strongly influencing many writers of the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood; the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' of 1888 described his "Ode to a Nightingale" as "one of the final masterpieces". Keats had a style "heavily loaded with sensualities", notably in the series of odes. Typically of the Romantics, he accentuated extreme emotion through natural imagery. Today his poems and letters remain among the most popular and analysed in English literature – in particular "Ode to a Nightingale", " Ode on a Grecian Urn", " Sleep and Poetry" and the sonnet " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Haydon
Benjamin Robert Haydon (; 26 January 178622 June 1846) was a British painter who specialised in grand historical pictures, although he also painted a few contemporary subjects and portraits. His commercial success was damaged by his often tactless dealings with patrons, and by the enormous scale on which he preferred to work. He was troubled by financial problems throughout his life, which led to several periods of imprisonment for debt. Early years Childhood Haydon was born in Plymouth, the only son of another Benjamin Robert Haydon, a prosperous printer, stationer and publisher, and his wife Mary, the daughter of the Rev. Benjamin Cobley, rector of Dodbrooke, near Kingsbridge, Devon. At an early age he showed an aptitude for study, which was carefully fostered by his mother. At the age of six he was placed in Plymouth Grammar School, and at twelve in Plympton Grammar School, where Sir Joshua Reynolds had received most of his education. Reading Albinus inspired him with a lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Poetry
This article focuses on poetry from the United Kingdom written in the English language. The article does not cover poetry from other countries where the English language is spoken, including the Republic of Ireland after December 1922. The earliest surviving English poetry, written in Old English language, Anglo-Saxon, the direct predecessor of modern English, may have been composed as early as the 7th century. The earliest English poetry The earliest known English poem is a hymn on the creation; Bede attributes this to Cædmon (floruit, fl. 658–680), who was, according to legend, an illiterate herdsman who produced extemporaneous poetry at a monastery at Whitby. This is generally taken as marking the beginning of Old English poetry, Anglo-Saxon poetry. Much of the poetry of the period is difficult to date, or even to arrange chronologically; for example, estimates for the date of the great epic ''Beowulf'' range from A.D. 608 right through to A.D. 1000, and there has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumfries
Dumfries ( ; ; from ) is a market town and former royal burgh in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland, near the mouth of the River Nith on the Solway Firth, from the Anglo-Scottish border. Dumfries is the county town of the Counties of Scotland, historic county of Dumfriesshire. Before becoming King of Scots, Robert the Bruce killed his rival John Comyn III of Badenoch at Greyfriars Kirk in the town in 1306. The Young Pretender had his headquarters here towards the end of 1745. In World War II, the Norwegian armed forces in exile in Britain largely consisted of a brigade in Dumfries. Dumfries is nicknamed ''Queen of the South''. This is also the name of the town's Queen of the South F.C., football club. People from Dumfries are known colloquially in Scots language as ''Doonhamers''. Toponymy There are a number of theories on the etymology of the name, with an ultimately Common Celtic, Celtic derivation (either from Common Brittonic, Brythonic, Old Irish, Gaelic or a mixture of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |