|
1812 In Paleontology
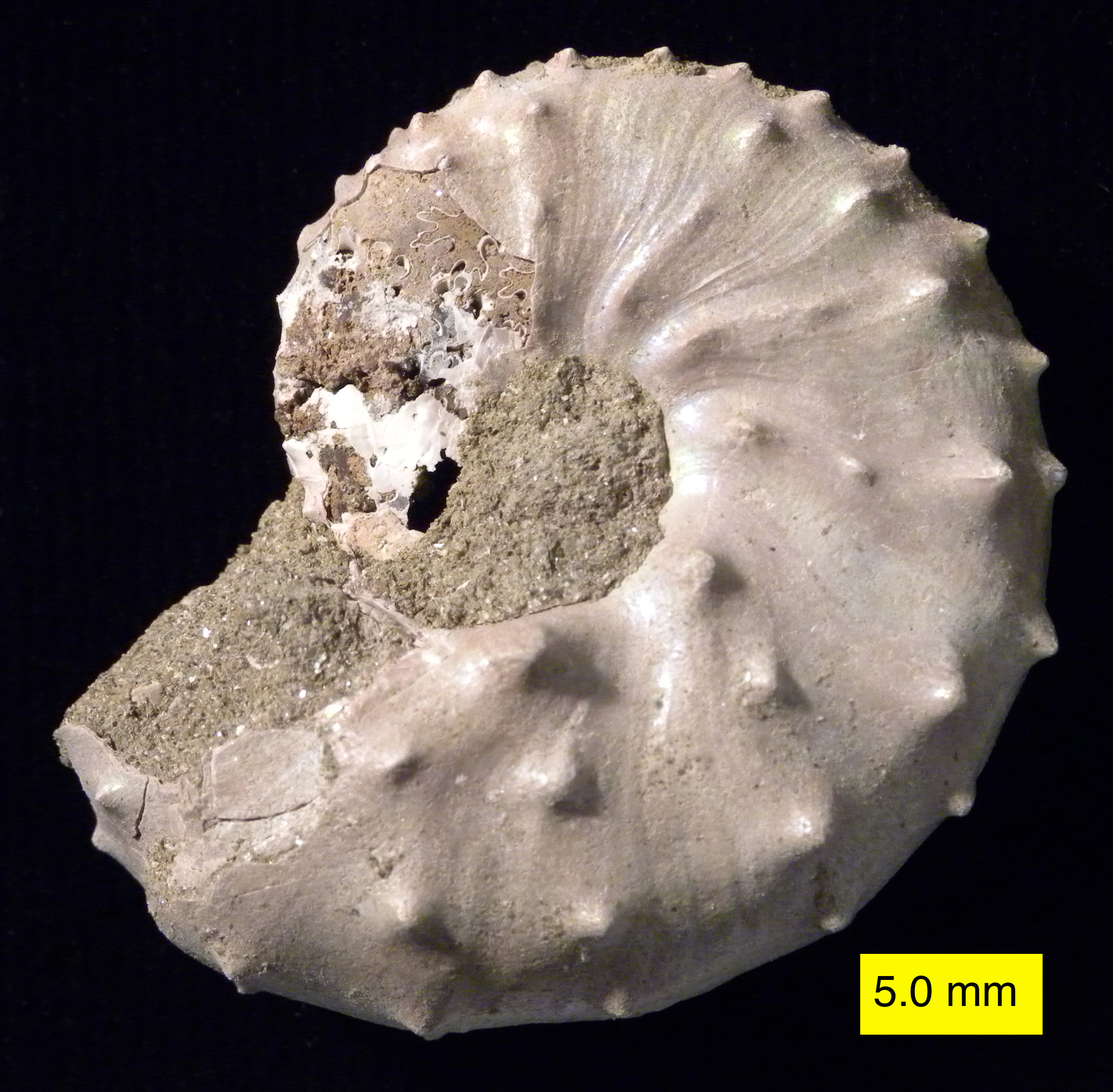
Plesiosaurs Newly named plesiosaurs Refer to article on these Plesiosaur, carnivorous aquatic reptiles. Plesiosaurs (sensu Plesiosauroidea) appeared at the start of the Jurassic Period, and thrived until the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the end of the Cretaceous Period. While they were Mesozoic diapsid reptiles that lived at the same time as dinosaurs, they were not dinosaurs. Pterosaurs New taxa See also * Plesiosaur References {{DEFAULTSORT:1812 In Paleontology 1810s in paleontology 1812 in science, Paleontology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
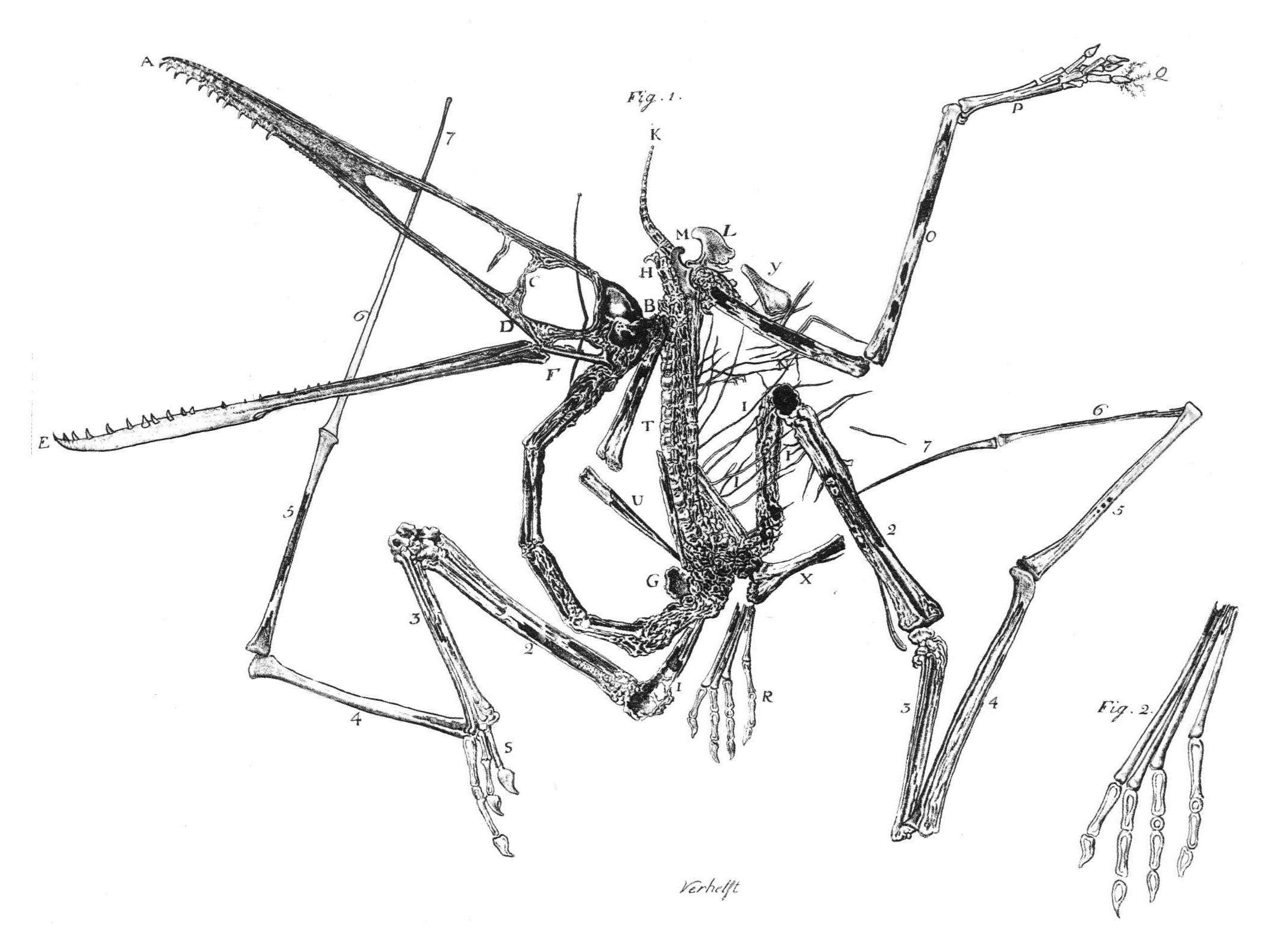
Plesiosaur
The Plesiosauria (; Greek: πλησίος, ''plesios'', meaning "near to" and ''sauros'', meaning "lizard") or plesiosaurs are an order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia. Plesiosaurs first appeared in the latest Triassic Period, possibly in the Rhaetian stage, about 203 million years ago. They became especially common during the Jurassic Period, thriving until their disappearance due to the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous Period, about 66 million years ago. They had a worldwide oceanic distribution, and some species at least partly inhabited freshwater environments. Plesiosaurs were among the first fossil reptiles discovered. In the beginning of the nineteenth century, scientists realised how distinctive their build was and they were named as a separate order in 1835. The first plesiosaurian genus, the eponymous '' Plesiosaurus'', was named in 1821. Since then, more than a hundred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic Period
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and is the only boundary between geological periods to remain formally undefined. By the beginning of the Jurassic, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous–Paleogene Extinction Event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event (also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction) was a sudden extinction event, mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million years ago. With the exception of some ectothermic species such as sea turtles and crocodilians, no tetrapods weighing more than survived. It marked the end of the Cretaceous Period, and with it the Mesozoic era, while heralding the beginning of the Cenozoic era, which continues to this day. In the geologic record, the K–Pg event is marked by a thin layer of sediment called the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, K–Pg boundary, which can be found throughout the world in marine and terrestrial rocks. The boundary clay shows unusually high levels of the metal iridium, which is more common in asteroids than in the Earth's crust. As originally proposed in 1980 by a team of scientists led by Luis Walter Alvarez, Luis Alvarez and his son Walter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous Period
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now- extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian reptiles, like the dinosaurs; an abundance of conifers and ferns; a hot greenhouse climate; and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The Mesozoic is the middle of the three eras since Cambrian explosion, complex life evolved: the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic, and the Cenozoic. The era began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the largest well-documented mass extinction in Earth's history, and ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, another mass extinction whose victims included the non-avian dinosaurs, Pterosaur, pterosaurs, Mosasaur, mosasaurs, and Plesiosaur, plesiosaurs. The Mesozoic was a time of significant tectonic, climatic, and evolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diapsid
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The group first appeared about three hundred million years ago during the late Carboniferous period. All diapsids other than the most primitive ones in the clade Araeoscelidia are sometimes placed into the clade Neodiapsida. The diapsids are extremely diverse, and include birds and all modern reptile groups, including turtles, which were historically thought to lie outside the group. Although some diapsids have lost either one hole (lizards), or both holes (snakes and turtles), or have a heavily restructured skull (modern birds), they are still classified as diapsids based on their ancestry. At least 17,084 species of diapsid animals are extant: 9,159 birds, and 7,925 snakes, lizards, tuatara, turtles, and crocodiles. Characteristics The name Diapsida means "two arches", and diapsids are tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaurs
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya; their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, having evolved from earlier theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomic, morphological and ecological standpoints. Birds, at over 10,700 living species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
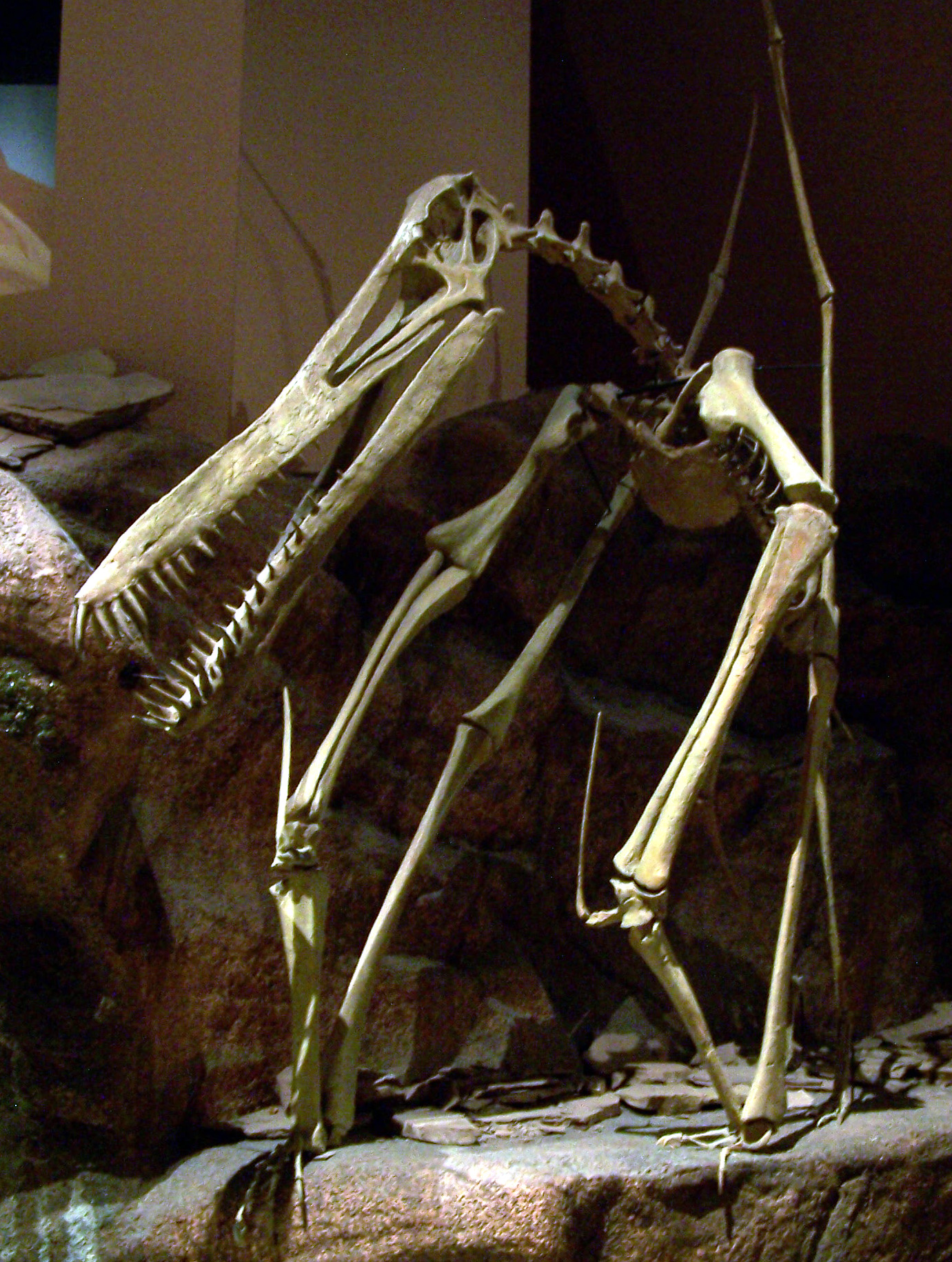
Pterodactylus
''Pterodactylus'' (from Greek () meaning 'winged finger') is an extinct genus of pterosaurs. It is thought to contain only a single species, ''Pterodactylus antiquus'', which was the first pterosaur to be named and identified as a flying reptile. Fossil remains of ''Pterodactylus'' have primarily been found in the Solnhofen limestone of Bavaria, Germany, which dates from the Late Jurassic period (early Tithonian stage), about 150.8 to 148.5 million years ago. More fragmentary remains of ''Pterodactylus'' have tentatively been identified from elsewhere in Europe and in Africa. ''Pterodactylus'' was a generalist carnivore that probably fed on a variety of invertebrates and vertebrates. Like all pterosaurs, ''Pterodactylus'' had wings formed by a skin and muscle membrane stretching from its elongated fourth finger to its hind limbs. It was supported internally by collagen fibres and externally by keratinous ridges. ''Pterodactylus'' was a small pterosaur compared to other fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anhanguera , a television production facility
{{DEFAULTSORT:Anhanguera ...
Anhanguera may refer to: People * Bartolomeu Bueno da Silva (1672–1740), a bandeirante Places in Brazil * Anhanguera, Goiás, a municipality in the state of Goiás * Anhanguera (district of São Paulo), a district in São Paulo * Parque Anhanguera, a municipal park in São Paulo * Rede Anhanguera de Comunicação (RAC), a mass communication company from Campinas * Rodovia Anhanguera, a highway in the state of São Paulo Other meanings * Anhanguera (devil), in Brazilian mythology * ''Anhanguera'' (pterosaur) * Anhanguera Educacional, an educational company * CDT da Anhanguera The Centro de Televisão da Anhanguera, popularly known as CDT da Anhanguera, is the second largest center of television production in Brazil and is the headquarters of the Brazilian TV company SBT. The complex is second only to the Estúdios Gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1810s In Paleontology
Year 181 ( CLXXXI) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aurelius and Burrus (or, less frequently, year 934 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 181 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Imperator Lucius Aurelius Commodus and Lucius Antistius Burrus become Roman Consuls. * The Antonine Wall is overrun by the Picts in Britannia (approximate date). Oceania * The volcano associated with Lake Taupō in New Zealand erupts, one of the largest on Earth in the last 5,000 years. The effects of this eruption are seen as far away as Rome and China. Births * April 2 – Xian of Han, Chinese emperor (d. 234) * Zhuge Liang, Chinese chancellor and regent (d. 234) Deaths * Aelius Aristides, Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |