|
1753 In Scotland
Events from the year 1753 in Scotland. Incumbents Law officers * Lord Advocate – William Grant of Prestongrange * Solicitor General for Scotland – Patrick Haldane of Gleneagles, jointly with Alexander Hume Judiciary * Lord President of the Court of Session – Lord Arniston the Elder to 26 August; then ''vacant'' * Lord Justice General – Lord Ilay * Lord Justice Clerk – Lord Tinwald Events * 7 June – Archibald Cameron of Lochiel (born 1707) becomes the last Jacobite to be executed for treason when he is hanged and beheaded at Tyburn in London under a bill of attainder. On 26 March he has returned from exile in France in the service of Charles Edward Stuart to retrieve the Loch Arkaig treasure and to participate in a desperate plot to assassinate George II of Great Britain and other members of the British royal family. However, while staying secretly at Brenachyle by Loch Katrine, he has been betrayed by Alastair Ruadh MacDonnell of Glengarry (the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
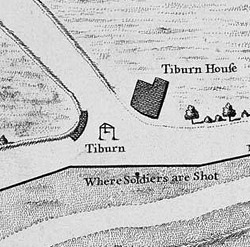
Tyburn
Tyburn was a Manorialism, manor (estate) in London, Middlesex, England, one of two which were served by the parish of Marylebone. Tyburn took its name from the Tyburn Brook, a tributary of the River Westbourne. The name Tyburn, from Teo Bourne (stream), Bourne, means 'boundary stream'.Gover, J. E. B., Allen Mawer and F. M. Stenton ''The Place-Names of Middlesex''. Nottingham: English Place-Name Society, The, 1942: 6. The parish, and probably therefore also the manor, was bounded by Roman roads to the west (modern Edgware Road) and south (modern Oxford Street). The junction of these was the site of the famous Tyburn Gallows (known colloquially as the "Tyburn Tree"), now occupied by Marble Arch. For many centuries the name Tyburn was synonymous with capital punishment: it was the principal place for execution for London and Middlesex criminals and convicted Treason, traitors, including many religious martyrs. In the 18th century it was also known as "God's Tribunal". Hangings at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canmore (database)
Canmore is an online database or index to information on over 320,000 archaeological sites, monuments, and buildings in Scotland. It was launched by the Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland in 1997 as the Computer Application for National MOnuments Record Enquiries. Canmore provided access to the National Monuments Record of Scotland (NMRS), which was founded in 1966 as an amalgam of the important archive of plans and photographs held by the RCAHMS and the Ministry of Public Building and Works. The NMRS was further developed with material from the Scottish National Buildings Record, the National Art Survey, the Ordnance Survey and the Scottish Office Air Photographs Unit. Historic Environment Scotland has maintained Canmore since 2015. The Canmore website now provides access to the National Record of the Historic Environment, formerly the National Monuments Record of Scotland, and contains around 1.3 million catalogue entries. It includes marine m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Dee, Aberdeenshire
The River Dee () is a river in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It rises in the Cairngorms and flows through southern Aberdeenshire to reach the North Sea at Aberdeen. The area it passes through is known as Deeside, or Royal Deeside in the region between Braemar and Banchory because Queen Victoria came for a visit there in 1848 and greatly enjoyed herself. She and her husband, Prince Albert, built Balmoral Castle there which replaced an older castle. Deeside is a popular area for tourists, due to the combination of its scenery and historic royal associations. It is part of the Cairngorms National Park, and the Deeside and Lochnagar National Scenic Area. The Dee is popular with anglers and is one of the most famous salmon fishing rivers in the world. The New Statistical Account of Scotland attributed the name Dee as having been used as early as the second century AD in the work of the Alexandrian geographer Claudius Ptolemy, as ''Δηοῦα'' (=Deva), meaning 'goddess'. This ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marriage In Scotland
Marriage in Scotland is recognised in the form of both civil and religious unions between individuals. Due to Scotland's history as a previously independent country, the laws around marriage developed differently in Scotland compared to other jurisdictions that also became part of the United Kingdom. This was partly a consequence of differences in Scots law and also the role and influence of the national church of Scotland, the Church of Scotland. The tradition of couples from Marriage in England and Wales, England and Wales eloping to Scotland to marry at border towns such as Gretna Green was due to England, at the time, having much higher minimum ages for marriage without parental consent than were required in Scotland, and Scotland recognising irregular marriages by assertion before a witness until 1939 (see below). Today the difference in minimum ages is much closer with the legal minimum age to enter into a marriage in Scotland being sixteen years without requiring parental co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England And Wales
England and Wales () is one of the Law of the United Kingdom#Legal jurisdictions, three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. The substantive law of the jurisdiction is English law. The Welsh devolution, devolved Senedd (Welsh Parliament; ) – previously named the National Assembly for Wales – was created in 1999 under the Government of Wales Act 1998 and provides a degree of Self-governance, self-government in Wales. The powers of the legislature were expanded by the Government of Wales Act 2006, which allows it to pass Welsh law, its own laws, and the Act also formally separated the Welsh Government from the Senedd. There is currently no Devolved English parliament, equivalent body for England, which is directly governed by the parliament and government of the United Kingdom. History of jurisdiction During the Roman occupation of Britain, the area of presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marriage Act 1753
The Clandestine Marriages Act 1753 ( 26 Geo. 2. c. 33), also called the Marriage Act 1753, long title "An Act for the Better Preventing of Clandestine Marriage", popularly known as Lord Hardwicke's Marriage Act, was the first statutory legislation in England and Wales to require a formal ceremony of marriage. It came into force on 25 March 1754. The act contributed to a dispute about the validity of a Scottish marriage, although pressure to address the problem of irregular marriages had been growing for some time. Background Before the act, the legal requirements for a valid marriage in England and Wales had been governed by the canon law of the Church of England. This had stipulated that banns should be called or a marriage licence obtained before a marriage could take place and that the marriage should be celebrated in the parish where at least one of the parties was resident. However, these requirements were directory rather than mandatory and the absence of banns or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliament Of Great Britain
The Parliament of Great Britain was formed in May 1707 following the ratification of the Acts of Union 1707, Acts of Union by both the Parliament of England and the Parliament of Scotland. The Acts ratified the treaty of Union which created a new unified Kingdom of Great Britain and created the parliament of Great Britain located in the former home of the English parliament in the Palace of Westminster, near the City of London. This lasted nearly a century, until the Acts of Union 1800 merged the separate British and Irish Parliaments into a single Parliament of the United Kingdom with effect from 1 January 1801. History Following the Treaty of Union in 1706, Acts of Union 1707, Acts of Union ratifying the Treaty were passed in both the Parliament of England and the Parliament of Scotland, which created a new Kingdom of Great Britain. The Acts paved the way for the enactment of the treaty of Union which created a new parliament, referred to as the 'Parliament of Great Britain' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alastair Ruadh MacDonnell
Alastair Roy MacDonell of Glengarry (ca 1725–1761; Scottish Gaelic: ''Alasdair Ruadh MacDomhnaill'', was the 13th chief of Clan MacDonell of Glengarry. Brought up as a Catholic and largely educated in France, he was arrested in November 1745 on his way to join the 1745 Jacobite Rising. After his release from the Tower of London in 1747, MacDonell became a highly damaging mole (espionage), mole for the Hanoverian government inside the Jacobite movement. In addition to delivering fellow Jacobite leader Dr. Archibald Cameron of Lochiel to the government, resulting in the latter's 1753 execution at Tyburn, Glengarry is also believed to have been used as an agent of influence to divide and rule, sow dissension within the Jacobite movement over the missing Loch Arkaig treasure. Some sources allege that Glengarry simultaneously "helped himself" to the treasure, but even if he did so, he still could never afford to properly rebuild Invergarry Castle, which had been severely damaged by g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loch Katrine
Loch Katrine (; or ) is a freshwater loch in the Trossachs area of the Scottish Highlands, east of Loch Lomond within the Stirling (council area), Stirling council area. It mostly lies within the Shires of Scotland, historic and registration county of Perthshire, with Glengyle Water and the northern part of the loch's mid-line forming part of the boundary with historic Stirlingshire. The loch is about long and wide at its widest point, and runs the length of Strath Gartney (Gaelic: ). It is within the drainage basins of the River Teith and River Forth. It is a popular scenic attraction for tourists and day-visitors from Glasgow and nearby towns; Fly fishing, fly and boat fishing for trout are permitted on the loch from spring to autumn. It also serves as a reservoir for the water supply of the Glasgow conurbation, some south, being connected by two aqueducts constructed in 1859. It is the fictional setting of Sir Walter Scott's poem ''The Lady of the Lake (poem), The Lady o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Royal Family
The British royal family comprises Charles III and other members of his family. There is no strict legal or formal definition of who is or is not a member, although the Royal Household has issued different lists outlining who is considered part of the royal family. Members typically support the monarch in carrying out public engagements and take part in charitable work and ceremonial duties. Senior royals collectively undertake thousands of official engagements across the United Kingdom and abroad each year, including state visits, national events, and patronage activities. The family also represents the UK on the global stage and contributes to soft power through diplomacy and cultural presence. Initiatives associated with the family include charitable foundations such as The King's Trust and The Royal Foundation, which focus on youth development, mental health, conservation, and early childhood. The monarchy operates within a constitutional framework, with succession ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George II Of Great Britain
George II (George Augustus; ; 30 October / 9 November 1683 – 25 October 1760) was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland, Ireland, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg (Electorate of Hanover, Hanover) and a prince-elector of the Holy Roman Empire from 11 June 1727 (Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.) until his death in 1760. Born and brought up in northern Germany, George is the most recent British monarch born outside Great Britain. The Act of Settlement 1701 and the Acts of Union 1707 positioned his grandmother Sophia of Hanover and her Protestant descendants to inherit the British throne. George married Princess Caroline of Ansbach, with whom he had eight children. After the deaths of George's grandmother and Anne, Queen of Great Britain, George's father, the Elector of Hanover, ascended the British throne as George I of Great Britain, George I in 1714. In the first years of his father's reign as king, Prince George was associated with opposition politicians until they rej ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |