|
1653 In England
Events from the year 1653 in England. Incumbents * Lord Protector – Oliver Cromwell (starting 16 December) Events * 18–20 February (28 February–2 March New Style) – First Anglo–Dutch War: Battle of Portland off the Isle of Portland. Both sides claim victory but the English retain control of the Channel. * 14 March – First Anglo–Dutch War: Battle of Leghorn: A Dutch fleet defeats the English in the Mediterranean but the Dutch commander, Johan van Galen, later dies of his wounds. * 18 April – London–York stagecoach first recorded. * 20 April – Oliver Cromwell dissolves the Rump Parliament. * 2–3 June (12–13 June New Style) – First Anglo-Dutch War: Battle of the Gabbard off the coast of Suffolk: The English navy defeats the Dutch fleet, which loses 17 ships. * 4 July–12 December – the Barebones Parliament meets in London. * 8 July – John Thurloe becomes Cromwell's head of intelligence. * 8–10 August – Battle of Scheveningen: the final naval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1653
Events January–March * January 3 – By the Coonan Cross Oath, the Eastern Church in India cuts itself off from colonial Portuguese tutelage. * January – The Swiss Peasant War begins after magistrates meeting at Lucerne refuse to hear from a group of peasants who have been financially hurt by the devaluation of the currency issued from Bern. * February 2 – New Amsterdam (now New York City) received municipal rights by a charter from New Netherland Governor Peter Stuyvesant. * February 3 – Cardinal Mazarin returns to Paris from exile. * February 10 – Swiss peasant war of 1653: Peasants from the Entlebuch valley in Switzerland assemble at Heiligkreuz to organize a plan to suspend all tax payments to the authorities in the canton of Lucerne, after having been snubbed at a magisterial meeting in Lucerne. More communities in the canton join in an alliance concluded at Wolhusen on February 26. * February – The Morning Star Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Thurloe
John Thurloe (June 1616 – 21 February 1668) was an English politician who served as secretary to the council of state in The Protectorate, Protectorate England and spymaster for Oliver Cromwell and held the position of Postmaster General between 1655 and 1660. He was from Great Milton in Oxfordshire and of Lincoln's Inn. Origins Thurloe was born in Essex in 1616 and was baptised on 12 June. His father was Rev. Thomas Thurloe, Rector of Abbess Roding. Career He trained as a lawyer in Lincoln's Inn. He was first in the service of Oliver St John, solicitor–general to King Charles I and Lord Chief Justice of the Common Pleas. In January 1645, he became a secretary to the parliamentary commissioners at the Treaty of Uxbridge. In 1647, Thurloe was admitted to Lincoln's Inn as a member. He remained on the sidelines during the English Civil War but after the accession of Oliver Cromwell, became part of his government. In March 1651, Thurloe accompanied Oliver St John as his secreta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staunton Harold
Staunton Harold is a civil parish in North West Leicestershire about north of Ashby-de-la-Zouch. The parish is on the county boundary with Derbyshire and about south of Derby. The 2011 Census (including Lount) recorded the parish's population as 141. A brook flows from the south through the parish, heading for the River Trent which it joins about to the north. In the parish the brook is dammed to form a pair of small lakes. Nikolaus Pevsner (later Sir Nikolaus) described the view westwards across the lakes to Staunton Harold Hall and Holy Trinity parish church as ''"unsurpassed in the country – certainly as far as Englishness is concerned"''. Downstream from Staunton Harold, just over over the boundary in Derbyshire, the brook is dammed again to form Staunton Harold Reservoir. Most of the reservoir is in the Derbyshire parish of Melbourne, but part of the upper reach of one arm of the reservoir is in Staunton Harold parish. History Staunton Harold is mentioned as ''Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Fens
The Fens or Fenlands in eastern England are a naturally marshy region supporting a rich ecology and numerous species. Most of the fens were drained centuries ago, resulting in a flat, dry, low-lying agricultural region supported by a system of drainage channels and man-made rivers (Ditch, dykes and drains) and automated pumping stations. There have been unintended consequences to this reclamation, as the land level has continued to sink and the dykes have been built higher to protect it from flooding. ''Fen'' is the local term for an individual area of marshland or former marshland. It also designates the type of marsh typical of the area, which has pH, neutral or alkaline water and relatively large quantities of dissolved minerals, but few other plant nutrition, plant nutrients. The Fens are a National Character Area, based on their landscape, biodiversity, geodiversity and economic activity. The Fens lie inland of the Wash, and are an area of nearly in the south east of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forty Foot Drain
The Forty Foot or Forty Foot Drain is a name given to several of the principal channels in the drainage schemes of the Fens of Eastern England, the name being qualified when there is a need to distinguish between them. They are Vermuyden's Drain, South Forty Foot and North Forty Foot. The Forty Foot Drain in Cambridgeshire The Forty Foot Drain, also known as Vermuyden's Drain, is an artificial drainage river in Cambridgeshire, which is one of the key elements in draining the Middle Level of the Bedford Level, in the Cambridgeshire part of the Fens. It was instrumental in Sir Cornelius Vermuyden's great drainage scheme of 1649–1653. Located near Chatteris and Ramsey, the river runs , from Wells Bridge, where it joins the old River Nene, to Welches Dam Sluice, where it joins the Counter Wash Drain, which then changes identity, becoming the Old Bedford River. These junctions are at grid references and respectively. When the drain was newly made, its western end was in Hun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornelius Vermuyden
Sir Cornelius Vermuyden (, ; also spelled ''Vermuijden''; 1595 – 11 October 1677) was a Dutch engineer who introduced Dutch land reclamation methods to England. Vermuyden was commissioned by the Crown to drain Hatfield Chase in the Isle of Axholme, Lincolnshire. In the 1650s, he directed major projects to drain The Fens of East Anglia, introducing the innovation of constructing washes, to allow periodic flooding of the area by excess waters. Early life and education Cornelius was the son of Gillis Vermuyden and Sarah Werkendet. He was born in 1595 in Haestinge on the Isle of Tholen in the Zeeland province of the Dutch Republic. He trained in the Netherlands as an engineer, learning Dutch techniques for controlling water and draining marshland. Career in England By the period of 1621 to 1623, Vermuyden was working in England, where his first projects were on the River Thames, repairing a sea wall at Dagenham and working to reclaim Canvey Island, Essex. The latter project w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Of England
The Commonwealth of England was the political structure during the period from 1649 to 1660 when Kingdom of England, England and Wales, later along with Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, were governed as a republic after the end of the Second English Civil War and the High Court of Justice for the trial of Charles I, trial and execution of Charles I. The republic's existence was declared through "An Act declaring England to be a Commonwealth", adopted by the Rump Parliament on 19 May 1649. Power in the early Commonwealth was vested primarily in the Parliament and a English Council of State, Council of State. During the period, fighting continued, particularly in Ireland and Scotland, between the parliamentary forces and those opposed to them, in the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland and the Anglo-Scottish war of 1650–1652. In 1653, after dissolution of the Rump Parliament, the Army Council (1647), Army Council adopted the Instrument of Gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Council Of State
The English Council of State, later also known as the Protector's Privy Council, was first appointed by the Rump Parliament on 14 February 1649 after the execution of King Charles I. Charles's execution on 30 January was delayed for several hours so that the House of Commons could pass an emergency bill to declare the representatives of the people, the House of Commons, as the source of all just power and to make it an offence to proclaim a new King. This in effect abolished the monarchy and the House of Lords. History The Council of State was appointed by Parliament on 14 and 15 February 1649, with further annual elections. The Council's duties were to act as the executive of the country's government in place of the King and the Privy Council. It was to direct domestic and foreign policy and to ensure the security of the English Commonwealth. Due to the disagreements between the New Model Army and the weakened Parliament, it was dominated by the Army. The Council held its f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelanda sovereign state covering five-sixths of the island) and Northern Ireland (part of the United Kingdomcovering the remaining sixth). It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the List of islands of the British Isles, second-largest island of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, third-largest in Europe, and the List of islands by area, twentieth-largest in the world. As of 2022, the Irish population analysis, population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the List of European islands by population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjacent Islands of Scotland, islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. To the south-east, Scotland has its Anglo-Scottish border, only land border, which is long and shared with England; the country is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the north-east and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. The population in 2022 was 5,439,842. Edinburgh is the capital and Glasgow is the most populous of the cities of Scotland. The Kingdom of Scotland emerged as an independent sovereign state in the 9th century. In 1603, James VI succeeded to the thrones of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, forming a personal union of the Union of the Crowns, three kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instrument Of Government
The Instrument of Government was the first constitution of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland and was also the first codified and written constitution in England. It was drafted by Major-General John Lambert in 1653. Antecedence The ''Instrument of Government'' included elements incorporated from an earlier document, " Heads of Proposals", a set of propositions that had been agreed to by the Army Council in 1647, intended to be a basis for a constitutional settlement after King Charles I was defeated in the First English Civil War. Charles had rejected the propositions, but before the start of the Second Civil War the "Grandees" (senior officers opposing the Leveller faction) of the New Model Army had presented the ''Heads of Proposals'' as their alternative to the more radical Agreement of the People presented by the Agitators and their civilian supporters at the Putney Debates. On 4 January 1649, the Rump Parliament declared "that the people are, un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
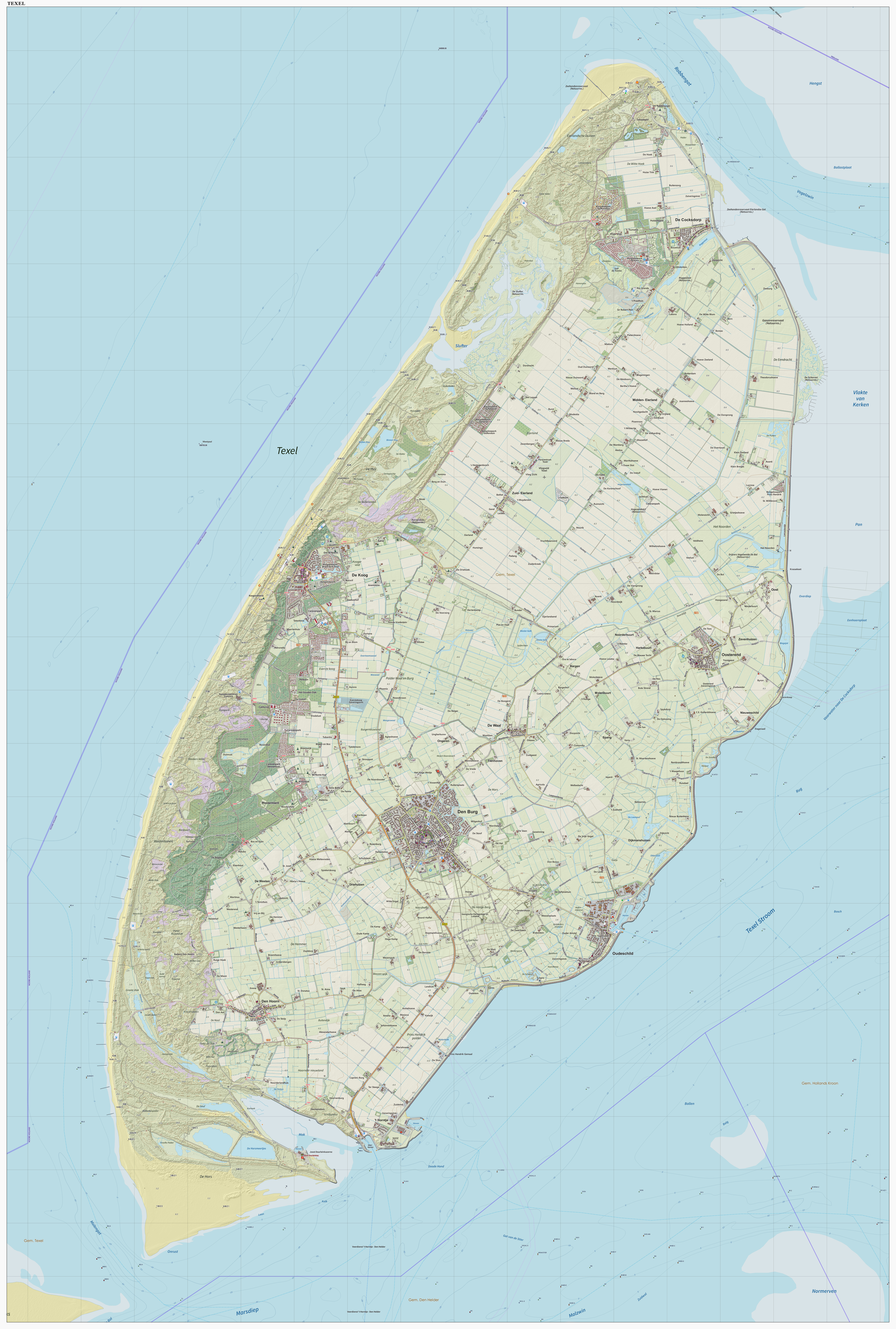
Texel
Texel (; Texels dialect: ) is a municipality and an island with a population of 13,643 in North Holland, Netherlands. It is the largest and most populated island of the West Frisian Islands in the Wadden Sea. The island is situated north of Den Helder, northeast of Noorderhaaks, and southwest of Vlieland. Name The name ''Texel'' is Frisian, but because of historical sound-changes in Dutch, where all -x- sounds have been replaced with -s- sounds (compare for instance English ''fox'', Frisian ''fokse'', German ''Fuchs'' with Dutch ''vos''), the name is typically pronounced ''Tessel'' in Dutch. History The All Saints' Flood of 1170 created the islands of Texel and Wieringen from North Holland. In the 13th century Ada, Countess of Holland was held prisoner on Texel by her uncle, William I, Count of Holland. Texel received city rights in 1415. The first Dutch expedition to the Northwest Passage departed from the island on 5 June 1594. Texel was involved in the Battle o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |