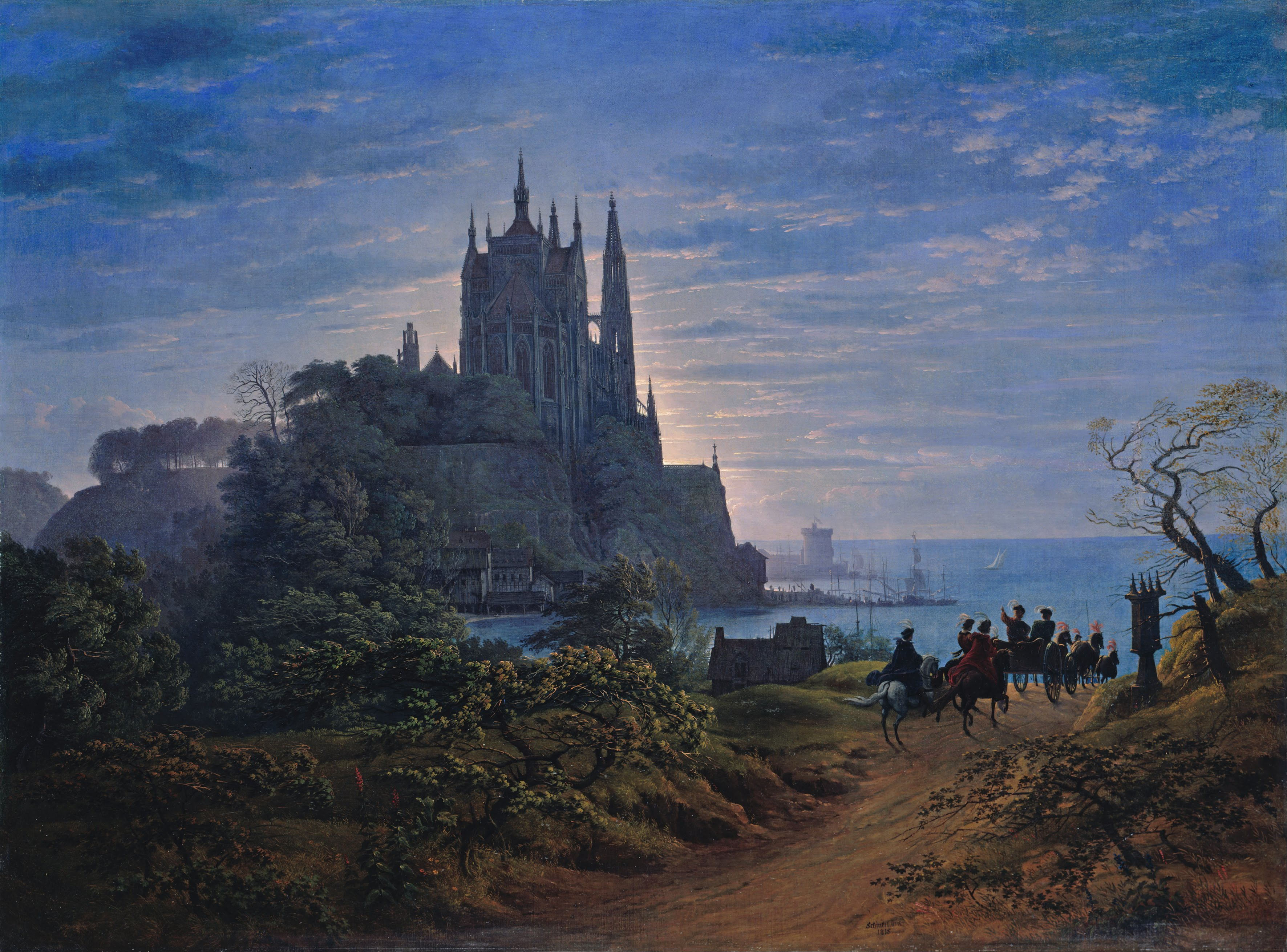|
–ü–Ķ—ā–Ķ—Ä–≥–ĺ—Ą - —Ā–į–ī
Petergof (), known as Petrodvorets () from 1944 to 1997, is a municipal town in Petrodvortsovy District of the federal city of St. Petersburg, located on the southern shore of the Gulf of Finland. The town hosts one of two campuses of Saint Petersburg State University and the Petrodvorets Watch Factory, one of the leading Russian watch manufactures. A series of palaces and gardens, laid out on the orders of Peter the Great and sometimes called the "Russian Versailles", is also situated there. The palace-ensemble along with the city center is recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Palaces, fountains, and gardens Petergof is named after the Peterhof Grand Palace, a sixteen-meter-high bluff lying less than a hundred meters from the shore. The so-called Lower Gardens (''Nizhny Sad''), at comprising the better part of the palace complex land area, are confined between this bluff and the shore, stretching east and west for roughly . The majority of Peterhof's fountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrodvortsovy District
Petrodvortsovy District () is a district of the federal city of St. Petersburg, Russia. As of the 2010 Census, its population: was 128,156; up from 77,542 recorded in the 2002 Census. Municipal divisions Petrodvortsovy District comprises two municipal towns ( Lomonosov and Petergof) and one municipal settlement (Strelna Strelna ( rus, –°—ā—Ä–ĶŐĀ–Ľ—Ć–Ĺ–į, p=ňąstr ≤el ≤n…ô) is a municipal settlement in Petrodvortsovy District of the federal city of Saint Petersburg, Russia, about halfway between Saint Petersburg proper and Petergof, and overlooking the shore ...).Law #411-68 References Notes Sources * {{Use mdy dates, date=June 2015 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from the early 17th century until the 1750s. It followed Renaissance art and Mannerism and preceded the Rococo (in the past often referred to as "late Baroque") and Neoclassicism, Neoclassical styles. It was encouraged by the Catholic Church as a means to counter the simplicity and austerity of Protestant architecture, art, and music, though Lutheran art#Baroque period, Lutheran Baroque art developed in parts of Europe as well. The Baroque style used contrast, movement, exuberant detail, deep color, grandeur, and surprise to achieve a sense of awe. The style began at the start of the 17th century in Rome, then spread rapidly to the rest of Italy, France, Spain, and Portugal, then to Austria, southern Germany, Poland and Russia. By the 1730s, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2129
In contemporary history, the third millennium is the current millennium in the ''Anno Domini'' or Common Era, under the Gregorian calendar. It began on 1 January 2001 ( MMI) and will end on 31 December 3000 ( MMM), spanning the 21st to 30th centuries. Ongoing futures studies seek to understand what will likely continue and what could plausibly change in this period and beyond. Predictions and forecasts not included on this timeline * Climate change * Extinction * List of dates predicted for apocalyptic events * List of future astronomical events ** List of lunar eclipses in the 21st century ** List of solar eclipses in the 21st century * List of time capsules * Near future centennial (bi, tri, etc.) events. * Near future in fiction * Predictions and claims for the Second Coming * Projections of population growth ** Representative Concentration Pathway ** Shared Socioeconomic Pathways 21st century 2000s * See: 2000 * 2001 * 2002 * 2003 * 2004 * 2005 * 2006 * 2007 * 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raketa
Raketa ( rus, –†–į–ļ–Ķ—ā–į, p=r…źňąk ≤…õt…ô, "Rocket") is a brand of wristwatches that have been manufactured since 1961 by the Petrodvorets Watch Factory in Saint Petersburg. The Petrodvorets Watch Factory is Russia's oldest factory, founded by Peter the Great in 1721. Raketa watches have been produced for the Red Army, the Soviet Navy, and for North Pole expeditions, as well as for civilians. Today, Raketa is one of a handful of global watch brands that produces its own movements from start to finish. History On 13 April 1961, Yuri Gagarin made the first manned flight in outer space on the rocket Vostok 1. In honor of this achievement, the Petrodvorets Watch Factory named its watches "Rocket"; ''Raketa'' in Russian language, Russian. However, at the height of the Cold War the name "Raketa" was perceived negatively in Western world, the West, as the word was associated with the latest generation of Soviet intercontinental ballistic missiles, the R-16 (missile), R-16. During Sov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 ‚Äď 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lapidary
Lapidary () is the practice of shaping rock (geology), stone, minerals, or gemstones into decorative items such as cabochons, engraved gems (including cameo (carving), cameos), and faceted designs. A person who practices lapidary techniques of cutting, grinding, and polishing is known as a lapidary or lapidarist. Hardstone carving requires specialized carving techniques. In modern contexts, a gemcutter is a person who specializes in cutting diamonds, but in older contexts the term refers to artists who produced hardstone carvings; engraved gems such as jade carvings, a branch of miniature sculpture or ornament in gemstone. By extension, the term ''lapidary'' has sometimes been applied to collectors of and dealers in gems, or to anyone who is knowledgeable in precious stones. Etymology The etymological root of the word ''lapidary'' is the Latin word , meaning "stone".Douglas Harper (2014)Lapidary Online Etymology Dictionary In the 14th century, the term evolved from , meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naukograd
Naukograd ( rus, –Ĺ–į—É–ļ–ĺ–≥—Ä–įŐĀ–ī, p=n…ô äk…źňągrat, also technopole), meaning "science city", is a formal term for towns with high concentrations of research and development facilities in Russia and the Soviet Union, some specifically built by the Soviet Union for these purposes. Some of the towns were secret and were part of a larger system of closed cities in the USSR, many built by forced labour from the Soviet Gulag. In the Russian Federation in post-Soviet times, the term is used generally for about seventy towns that have concentrations of scientific research and production, and specifically, refers to a small number of towns that have been recognised for their scientific capabilities and hence get special privileges. Of the more general naukograds, about thirty are located in Moscow Oblast and the rest mainly in the Volga, Urals, and Siberian regions. Few are now "closed" — there are only ten closed nuclear towns where Russia's nuclear military work is still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Petersburg State University Department Of Chemistry
The Faculty of Chemistry (since 2014 The Institute of Chemistry) at Saint Petersburg State University is one of the leading chemistry faculties in Russia. History Formally, the Department of Chemistry has been created as a separate entity of Saint Petersburg State University (then Leningrad State University) in 1929. However, the history of chemistry at Saint Petersburg State University began much earlier. First chemistry laboratory and lectures in chemistry were introduced at the university in 1833. Many Russian chemists began their career and/or worked there. Among them are Nikolay Zinin, Alexey Favorsky, Lev Aleksandrovich Chugaev, Sergei Vasiljevich Lebedev, Vyacheslav Tishchenko, Vladimir Ipatieff, Nikolay Semyonov, Boris Nikolsky, Mikhail Shultz. In the Soviet era, the Department of Chemistry continued to grow with new divisions: colloid chemistry (1939), electrochemistry (1940), chemistry of macromolecular compounds (1944), radiochemistry (1945), physical organic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximilian De Beauharnais, 3rd Duke Of Leuchtenberg
Maximilian Joseph Eugene Auguste Napoleon de Beauharnais, 3rd Duke of Leuchtenberg, Prince Romanowsky (2 October 1817 ‚Äď 1 November 1852) was the husband of Grand Duchess Maria Nikolayevna of Russia and first cousin of Emperors Napoleon III of the French and Francis Joseph I of Austria. He was a grandson of Napoleon I's first wife, the Empress Josephine, by her prior marriage to Alexandre de Beauharnais. A student of Moritz von Jacobi, he is known as one of pioneers in galvanoplasty and an expert in copper and bronze metalworks generally, as well as an art collector. He was the proprietor of the first locomotive works in Russia. Childhood He was born as the second son of Eug√®ne de Beauharnais, Duke of Leuchtenberg and Prince of Eichst√§tt and Princess Augusta Amalia Ludovika Georgia of Bavaria. His maternal grandparents were Maximilian I, King of Bavaria and his first wife Marie Wilhelmine Auguste, Landgravine of Hesse-Darmstadt. His maternal grandmother Marie Wilhelmin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graduate School Of Management (St
Graduate School of Management may refer to: * Graduate School of Management, University of California, Davis * Graduate School of Management, University of Dallas, USA * Graduate School of Management, St. Petersburg State University, Russia {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Friedrich Schinkel
Karl Friedrich Schinkel (13 March 1781 ‚Äď 9 October 1841) was a Prussian architect, urban planning, city planner and painter who also designed furniture and stage sets. Schinkel was one of the most prominent architects of Germany and designed both Neoclassical architecture, Neoclassical and Gothic revival architecture, neo-Gothic buildings. His most famous buildings are found in and around Berlin. Schinkel's Bauakademie is considered one of the forerunners of modern architecture. Biography Schinkel was born in Neuruppin, Margraviate of Brandenburg. When he was six, his father died in the disastrous Neuruppin fire of 1787. He became a student of architect Friedrich Gilly (1772‚Äď1800) (the two became close friends) and his father, David Gilly, in Berlin. At that time, the architectural taste in Prussia was shaped in Neoclassical style, mainly by Carl Gotthard Langhans, the architect of the Brandenburg Gate in Berlin. After returning to Berlin from his first trip to Italy in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |