|
Fula Orthographies
The Fula language (, ''Pulaar'', or ''Pular'') is written primarily in the Latin script, but in some areas is still written in an older Arabic script called the Ajami script or in the recently invented Adlam script. Latin-based alphabets Background The Latin script was introduced to Fula-speaking regions of West and Central Africa by Europeans during, and in some cases immediately before, invasion. Various people — missionaries, colonial administrators, and scholarly researchers — devised various ways of writing . One issue similar to other efforts by Europeans to use their alphabet and home orthographic conventions was how to write African languages with unfamiliar sounds. In the case of Fula, these included how to represent sounds such as the implosive b and d, the ejective y, the velar n (the latter being present in European languages, but never in initial position), prenasalised consonants, and long vowels, all of which can change meaning. Major influences on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Reference Alphabet
The African Reference Alphabet is a largely defunct continent-wide guideline for the creation of Latin alphabets for African languages. Two variants of the initial proposal (one in English and a second in French) were made at a 1978 UNESCO-organized conference held in Niamey, Niger. They were based on the results of several earlier conferences on the harmonization of established Latin alphabets of individual languages. The 1978 conference recommended the use of single letters for speech sounds rather than of Digraph (orthography), letter sequences or of letters with diacritics. A substantial overhaul was proposed in 1982 but was rejected in a follow-up conference held in Niamey in 1984. Since then, continent-wide harmonization has been largely abandoned, because regional needs, practices and thus preferences differ greatly across Africa. Through the individual languages that were its basis, the African Reference Alphabet inherits from the Africa Alphabet, and like the latter uses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fula Language
Fula ( ),Laurie Bauer, 2007, ''The Linguistics Student's Handbook'', Edinburgh also known as Fulani ( ) or Fulah (, , ; Adlam script, Adlam: , , ; Ajami script, Ajami: , , ), is a Senegambian languages, Senegambian language spoken by around 36.8 million people as a set of various dialects in a Dialect continuum, continuum that stretches across some 18 countries in West Africa, West and Central Africa. Along with other related languages such as Serer language, Serer and Wolof language, Wolof, it belongs to the Atlantic languages, Atlantic geographic group within Niger–Congo languages, Niger–Congo, and more specifically to the Senegambian languages, Senegambian branch. Unlike most Niger-Congo languages, Fula does not have Tone (linguistics), tones. It is spoken as a first language by the Fula people ("Fulani", ) from the Senegambia, Senegambia region and Guinea to Cameroon, Nigeria, and Sudan and by related groups such as the Toucouleur people in the Senegal River Valley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noon Language
Noon (''Non, None, Serer-Noon, Serer-Non'') is a Cangin language of Senegal spoken in the Thiès region (). There is an estimated population of 10,000''-'' 50,000 speakers worldwide, rendering this language to be vulnerable. ''Ethnologue'' reports that it is 84% cognate (and 68% intelligible) with Lehar, essentially a divergent dialect, and 68% cognate with the other Cangin languages. The Noon people identify themselves ethnically as Serer. However, their language, often called Serer-Noon on the assumption that it is a Serer dialect, is not closely related to the principal language of the Serer population, Serer-Sine. Status Like many of the local languages in Senegal, the Noon language is officially recognized as one of the national languages of the country. Orthography A Latin alphabet was proposed for Noon in 2001 and adopted by the Senegalese government in 2005. The alphabet consists of 47 letters, as listed below. Consonants The Noon alphabet contains 27 consonant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hausa Language
Hausa (; / ; Hausa Ajami, Ajami: ) is a Chadic language spoken primarily by the Hausa people in the northern parts of Nigeria, Ghana, Cameroon, Benin and Togo, and the southern parts of Niger, and Chad, with significant minorities in Ivory Coast. A small number of speakers also exist in Sudan. Hausa is a member of the Afroasiatic language family and is the most widely spoken language within the Chadic branch of that family. Despite originating from a non-tonal language family, Hausa utilizes differences in pitch to distinguish words and grammar. ''Ethnologue'' estimated that it was spoken as a first language by some 58 million people and as a second language by another 36 million, bringing the total number of Hausa speakers to an estimated 94 million. In Nigeria, the Hausa film industry is known as Kannywood. Classification Hausa belongs to the West Chadic languages subgroup of the Chadic languages group, which in turn is part of the Afroasiatic languages, Afro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hook (diacritic)
In typesetting, the hook or tail is a diacritic mark attached to letters in many alphabets. In shape it looks like a hook and it can be attached below as a descender, on top as an ascender (typography), ascender and sometimes to the side. The orientation of the hook can change its meaning: when it is below and curls to the left it can be interpreted as a palatal hook, and when it curls to the right is called hook tail or tail and can be interpreted as a retroflex consonant, retroflex hook. It should not be mistaken with the hook above, a diacritical mark used in Vietnamese, or the R-colored vowel, rhotic hook, used in the International Phonetic Alphabet. Letter ⟨Z⟩ with tophook - became letter ⟨⟩. Letter ⟨X⟩ with two high hooks - became letter ⟨⟩. Letters with hook It could be argued that the hook was used to derive the letter ⟨J⟩ from the letter ⟨I⟩, or the letter Eng (letter), Eng ⟨ŋ⟩ from the letter ⟨N⟩. However, these letters are usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthography For Languages Of Guinea (pre-1985)
Following independence, the government of Guinea adopted rules of transcription for the languages of Guinea based on the characters and diacritic combinations available on typewriters of that period. This alphabet was used officially until 1989. Guinea language orthography The Guinea alphabet made use of several digraphs (including either "h" or "y" as the second letter), some of which represent consonants not present in European languages, and two diacritics (grave accent and diaeresis) for open vowels. This system was widely used within the country but differed from the orthographies of neighboring countries of West Africa, as developed in the wake of the 1966 Bamako expert meeting on harmonizing orthographies of the cross-border languages of the region. In 1989, following a meeting on reform of the alphabet in 1988, it was decided to adopt an orthography similar to the African reference alphabet The African Reference Alphabet is a largely defunct continent-wide guideli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 6438
ISO 6438:1983, ''Documentation — African coded character set for bibliographic information interchange'', is an ISO standard for an 8-bit character encoding for African languages. Developed separately from the African reference alphabet but apparently based on the same data sets, it has had little use; its forms are retained in Unicode. FreeDOS calls this Code Page 65504. Character set * Prior to Unicode 7.0, mapped to .Prior to Unicode 8.0, mapped to . See also * Africa Alphabet *African Reference Alphabet The African Reference Alphabet is a largely defunct continent-wide guideline for the creation of Latin alphabets for African languages. Two variants of the initial proposal (one in English and a second in French) were made at a 1978 UNESCO-organi ... * Dinka alphabet * Pan-Nigerian alphabet * Lepsius Standard Alphabet References External links"Coded Character Set for African Languages" (June 15, 1979)ISO 6438:1983 "Documentation -- African coded character set for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upsilon
Upsilon (, ; uppercase Υ, lowercase υ; ''ýpsilon'' ) or ypsilon is the twentieth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, has a value of 400. It is derived from the phoenician alphabet, Phoenician Waw (letter), waw . Etymology The name of the letter was originally just (, also called , hence ''hyoid bone, hyoid'', meaning 'shaped like the letter '), but the name changed to (= , 'u-plain' or 'u-simple') to distinguish it from , which had come to have the same pronunciation. Pronunciation In early Attic Greek (6th century BCE), it was pronounced (a close back rounded vowel like the English "long o͞o"). In Ancient Greek language, Classical Greek, it was pronounced (a close front rounded vowel), at least until 1030. In Modern Greek, it is pronounced ; in the digraph (orthography), digraphs and , as or ; and in the digraph as . In ancient Greek, it occurred in both Ancient Greek phonology#Vowels, long and short versions, but Modern Greek does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea to Guinea–Senegal border, the southeast and Guinea-Bissau to Guinea-Bissau–Senegal border, the southwest. Senegal nearly surrounds The Gambia, a country occupying a narrow sliver of land along the banks of the Gambia River, which separates Senegal's southern region of Casamance from the rest of the country. It also shares a maritime border with Cape Verde. Senegal's capital is Dakar. Senegal is the westernmost country in the mainland of the Old World, or Afro-Eurasia. It owes its name to the Senegal River, which borders it to the east and north. The climate is typically Sahelian, though there is a wet season, rainy season. Senegal covers a land area of almost and has a population of around 18 million. The state is a Presidential system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
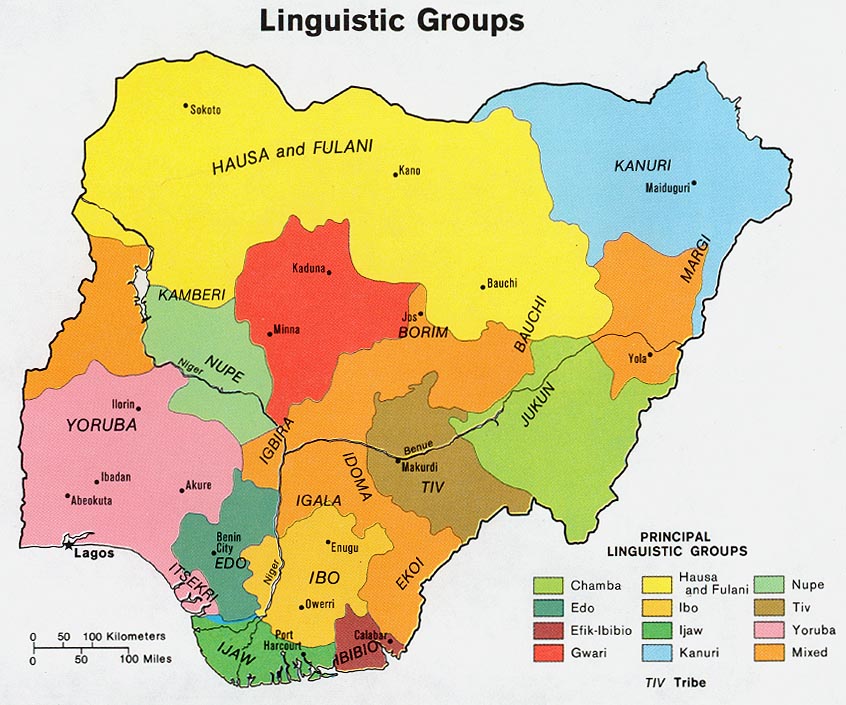
Pan-Nigerian Alphabet
The Pan-Nigerian alphabet is a set of 33 Latin letters standardised by the National Language Centre of Nigeria in the 1980s. It is intended to be sufficient to write all the languages of Nigeria without using digraphs. History Several hundred different languages are spoken in Nigeria. The different Latin alphabets made it impractical to create Nigerian typewriters. In the 1980s the National Language Centre (NLC) undertook to develop a single alphabet suitable for writing all the languages of the country, and replacing use of Arabic script, taking as its starting point a model proposed by linguist Kay Williamson in 1981. A typeface was developed in 1985–1986 by Edward Oguejofor and Victor Manfredi, in co-operation with the NLC, with technical assistance from Hermann Zapf. Characters The acute ( ´ ), grave ( ` ) and circumflex ( ˆ ) accents are also used to mark High, Low, and Falling tone respectively. Mid tone (in languages which contrast High, Mid, and Low) is left ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo, as well as Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom Overseas Territories, United Kingdom Overseas Territory).Paul R. Masson, Catherine Anne Pattillo, "Monetary union in West Africa (ECOWAS): is it desirable and how could it be achieved?" (Introduction). International Monetary Fund, 2001. The population of West Africa is estimated at around million people as of , and at 381,981,000 as of 2017, of which 189,672,000 were female and 192,309,000 male.United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2017). World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision, custom data acquired via webs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |