|
Esperanto Orthography
Esperanto is written in a Latin-script alphabet of twenty-eight letters, with upper and lower case. This is supplemented by punctuation marks and by various logograms, such as the Numerical digit, digits 0–9, currency signs such as $ € ¥ £ ₷, and mathematical symbols. The creator of Esperanto, L. L. Zamenhof, declared a principle of "one letter, one sound", though this is a general rather than strict guideline.Kalocsay & Waringhien, ''Plena analiza gramatiko'', § 17 Twenty-two of the letters are identical in form to letters of the English alphabet (''q, w, x,'' and ''y'' being omitted). The remaining six have diacritical marks: ''C-circumflex, ĉ, G-circumflex, ĝ, H-circumflex, ĥ, J-circumflex, ĵ, S-circumflex, ŝ,'' and ''U-breve, ŭ'' – that is, ''c, g, h, j,'' and ''s circumflex,'' and ''u breve.'' Standard alphabet Standard Esperanto orthography uses the Latin script. Sound values The letters have approximately the sound values of the help:IPA, IPA, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumflex
The circumflex () is a diacritic in the Latin and Greek scripts that is also used in the written forms of many languages and in various romanization and transcription schemes. It received its English name from "bent around"a translation of the (). The circumflex in the Latin script is chevron-shaped (), while the Greek circumflex may be displayed either like a tilde () or like an inverted breve (). For the most commonly encountered uses of the accent in the Latin alphabet, precomposed characters are available. In English, the circumflex, like other diacritics, is sometimes retained on loanwords that used it in the original language (for example '' entrepôt, crème brûlée''). In mathematics and statistics, the circumflex diacritic is sometimes used to denote a function and is called a '' hat operator''. A free-standing version of the circumflex symbol, , is encoded in ASCII and Unicode and has become known as '' caret'' and has acquired special uses, particularly i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H With Stroke
H, or h, is the eighth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, including the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''aitch'' (pronounced , plural ''aitches''), or regionally ''haitch'' (pronounced , plural ''haitches'')''.''"H" ''Oxford English Dictionary,'' 2nd edition (1989); ''Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged'' (1993); "aitch" or "haitch", op. cit. Name English For most English speakers, the name for the letter is pronounced as and spelled "aitch" or occasionally "eitch". The pronunciation and the associated spelling "haitch" are often considered to be h-adding and are considered non-standard in England. It is, however, a feature of Hiberno-English, and occurs sporadically in various other dialects. The perceived name of the letter affects the choice of indefinite article before initialisms beginning with H: for example "an H-bomb" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
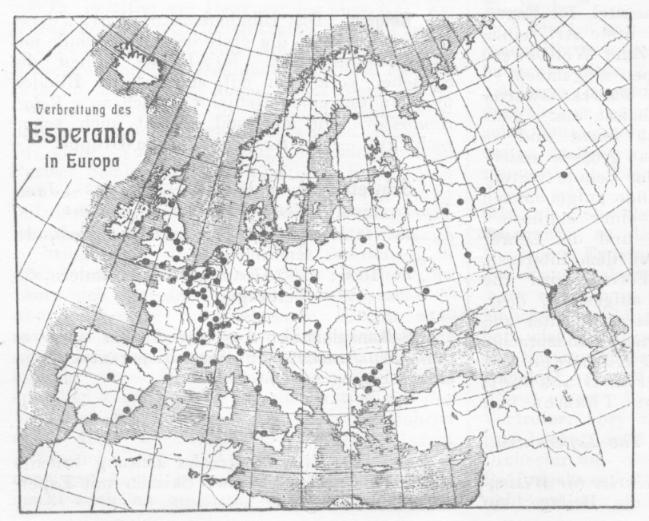
Esperanto
Esperanto (, ) is the world's most widely spoken Constructed language, constructed international auxiliary language. Created by L. L. Zamenhof in 1887 to be 'the International Language' (), it is intended to be a universal second language for international communication. He described the language in ''Dr. Esperanto's International Language'' (), which he published under the pseudonym . Early adopters of the language liked the name and soon used it to describe his language. The word translates into English as 'one who hopes'. Within the range of constructed languages, Esperanto occupies a middle ground between "naturalistic" (imitating existing natural languages) and ''Constructed language#A priori and a posteriori languages, a priori'' (where features are not based on existing languages). Esperanto's vocabulary, syntax and semantics derive predominantly from languages of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European group. A substantial majority of its vocabulary (approximat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esperanto Letters With Diacritics
Esperanto (, ) is the world's most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Created by L. L. Zamenhof in 1887 to be 'the International Language' (), it is intended to be a universal second language for international communication. He described the language in '' Dr. Esperanto's International Language'' (), which he published under the pseudonym . Early adopters of the language liked the name and soon used it to describe his language. The word translates into English as 'one who hopes'. Within the range of constructed languages, Esperanto occupies a middle ground between "naturalistic" (imitating existing natural languages) and '' a priori'' (where features are not based on existing languages). Esperanto's vocabulary, syntax and semantics derive predominantly from languages of the Indo-European group. A substantial majority of its vocabulary (approximately 80%) derives from Romance languages, but it also contains elements derived from Germanic, Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamiltonian (quantum Mechanics)
In quantum mechanics, the Hamiltonian of a system is an operator corresponding to the total energy of that system, including both kinetic energy and potential energy. Its spectrum, the system's ''energy spectrum'' or its set of ''energy eigenvalues'', is the set of possible outcomes obtainable from a measurement of the system's total energy. Due to its close relation to the energy spectrum and time-evolution of a system, it is of fundamental importance in most formulations of quantum theory. The Hamiltonian is named after William Rowan Hamilton, who developed a revolutionary reformulation of Newtonian mechanics, known as Hamiltonian mechanics, which was historically important to the development of quantum physics. Similar to vector notation, it is typically denoted by \hat, where the hat indicates that it is an operator. It can also be written as H or \check. Introduction The Hamiltonian of a system represents the total energy of the system; that is, the sum of the kine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is the foundation of all quantum physics, which includes quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Quantum mechanics can describe many systems that classical physics cannot. Classical physics can describe many aspects of nature at an ordinary (macroscopic and Microscopic scale, (optical) microscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at very small submicroscopic (atomic and subatomic) scales. Classical mechanics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation that is valid at ordinary scales. Quantum systems have Bound state, bound states that are Quantization (physics), quantized to Discrete mathematics, discrete values of energy, momentum, angular momentum, and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italo Disco
Italo disco (variously capitalized, and sometimes hyphenated as Italo-disco) is a music genre which originated in Italy in the late 1970s and was mainly produced in the 1980s. Italo disco evolved from the then-current underground dance, pop, and electronic music, both domestic and foreign (hi-NRG, Euro disco) and developed into a diverse genre. The genre employs electronic drums, drum machines, synthesizers, and occasionally vocoders. It is usually sung in English, and to a lesser extent in Italian and Spanish. The origin of the genre's name is strongly tied to marketing efforts of the ZYX record label, which began licensing and marketing the music outside Italy in 1982.Folklore that ZYX boss Bernhard Mikulski coined the term ''Italo-disco'' in 1983 was long published on Wikipedia, but is unsubstantiated; to date, reliable third-party documentation has not been found to support whether ZYX label boss Mikulski himself named it, or whether ZYX was even the first to publish t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esperanto Vocabulary
The original word base of Esperanto contained around 900 root words and was defined in '' Unua Libro'' ("First Book"), published by L. L. Zamenhof in 1887. In 1894, Zamenhof published the first Esperanto dictionary, '' Universala vortaro'' ("International Dictionary"), which was written in five languages and supplied a larger set of root words, adding 1740 new words. The rules of the Esperanto language allow speakers to borrow words as needed, recommending only that they look for the most international words, and that they borrow one basic word and derive others from it, rather than borrowing many words with related meanings. Since then, many words have been borrowed from other languages, primarily those of Western Europe. In recent decades, most of the new borrowings or coinages have been technical or scientific terms; terms in everyday use are more likely to be derived from existing words (for example computer from o compute, or extending them to cover new mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (, ; ; ), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein ( ), is a Landlocked country#Doubly landlocked, doubly landlocked Swiss Standard German, German-speaking microstate in the Central European Alps, between Austria in the east and north and Switzerland in the west and south. Liechtenstein is a semi-constitutional monarchy headed by the prince of Liechtenstein of the House of Liechtenstein, currently led by Hans-Adam II. It is List of European countries by area, Europe's fourth-smallest country, with an area of just over and a population of 40,023. It is the world's smallest country to border two countries, and is one of the few countries with no debt. Liechtenstein is divided into Municipalities of Liechtenstein, 11 municipalities. Its capital is Vaduz, and its largest municipality is Schaan. It is a member of the United Nations, the European Free Trade Association, and the Council of Europe. It is not a member state of the European Union, but it participates i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jota (music)
The jota () is a genre of music and the associated dance known throughout Spain, most likely originating in Aragon. It varies by region, having a characteristic form in Aragon (where it is the most important), Mallorca, Catalonia, León, Castile, Navarre, Cantabria, Asturias, Galicia, La Rioja, Murcia and Eastern Andalusia. Being a visual representation, the jota is danced and sung accompanied by castanets, and the interpreters tend to wear regional costumes. In Valencia, the jota was once danced during interment ceremonies. The jota tends to have a rhythm, although some authors maintain that the is better adapted to the poetic and choreographic structure. For their interpretation, guitars, bandurrias, lutes, dulzaina, and drums are used in the Castilian style, while the Galicians use bagpipes, drums, and bombos. Theatrical versions are sung and danced with regional costumes and castanets, though such things are not used when dancing the jota in less formal settings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheeler–DeWitt Equation
The Wheeler–DeWitt equation for theoretical physics and applied mathematics, is a field equation attributed to John Archibald Wheeler and Bryce DeWitt. The equation attempts to mathematically combine the ideas of quantum mechanics and general relativity, a step towards a theory of quantum gravity. In this approach, time plays a role different from what it does in non-relativistic quantum mechanics, leading to the so-called " problem of time". More specifically, the equation describes the quantum version of the Hamiltonian constraint using metric variables. Its commutation relations with the diffeomorphism constraints generate the Bergman–Komar "group" (which ''is'' the diffeomorphism group on-shell). Motivation and background In canonical gravity, spacetime is foliated into spacelike submanifolds. The three-metric (i.e., metric on the hypersurface) is \gamma_ and given by g_\,\mathrmx^\,\mathrmx^\nu = (-N^2 + \beta_k\beta^k)\,\mathrmt^2 + 2\beta_k\,\mathrmx^k\,\ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |