|
Caron
A caron or háček ( ), is a diacritic mark () placed over certain letters in the orthography of some languages, to indicate a change of the related letter's pronunciation. Typographers tend to use the term ''caron'', while linguists prefer the Czech word '. The symbol is common in the Baltic, Slavic, Finnic, Samic and Berber language families. Its use differs according to the orthographic rules of a language. In most Slavic and other European languages it indicates present or historical palatalization (e → ě; [] → []), iotation, or postalveolar consonant, postalveolar articulation (c → č; → ). In Salishan languages, it often represents a uvular consonant (x → x̌; [] → ). When placed over vowel symbols, the caron can indicate a contour tone, for instance the falling and then rising tone in the Pinyin romanization of Standard Chinese, Mandarin Chinese. It is also used to decorate symbols in mathematics, where it is often pronounced ("check"). The caro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Language
Czech ( ; ), historically known as Bohemian ( ; ), is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. Spoken by over 12 million people including second language speakers, it serves as the official language of the Czech Republic. Czech is closely related to Slovak, to the point of high mutual intelligibility, as well as to Polish to a lesser degree. Czech is a fusional language with a rich system of morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German. The Czech–Slovak group developed within West Slavic in the high medieval period, and the standardization of Czech and Slovak within the Czech–Slovak dialect continuum emerged in the early modern period. In the later 18th to mid-19th century, the modern written standard became codified in the context of the Czech National Revival. The most widely spoken non-standard variety, known as Common Czech, is based on the vernacular of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbo-Croatian Language
Serbo-Croatian ( / ), also known as Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS), is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro. It is a pluricentric language with four mutually intelligible standard varieties, namely Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin. South Slavic languages historically formed a dialect continuum. The region's turbulent history, particularly due to the expansion of the Ottoman Empire, led to a complex dialectal and religious mosaic. Due to population migrations, Shtokavian became the most widespread supradialect in the western Balkans, encroaching westward into the area previously dominated by Chakavian and Kajkavian. Bosniaks, Croats, and Serbs differ in religion and were historically often part of different cultural spheres, although large portions of these populations lived side by side under foreign rule. During that period, the language was referred to by various names, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian ( / ), also known as Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS), is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro. It is a pluricentric language with four mutually intelligible Standard language, standard varieties, namely Serbian language, Serbian, Croatian language, Croatian, Bosnian language, Bosnian, and Montenegrin language, Montenegrin. South Slavic languages historically formed a dialect continuum. The region's turbulent history, particularly due to the expansion of the Ottoman Empire, led to a complex dialectal and religious mosaic. Due to population migrations, Shtokavian became the most widespread supradialect in the western Balkans, encroaching westward into the area previously dominated by Chakavian and Kajkavian. Bosniaks, Croats, and Serbs differ in religion and were historically often part of different cultural spheres, although large portions of these populations lived side by side und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovak Language
Slovak ( ; endonym: or ), is a West Slavic language of the Czech-Slovak languages, Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script and formerly in Cyrillic script. It is part of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken by approximately 5 million people as a native language, primarily ethnic Slovaks, it serves as the official language of Slovakia and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Slovak is closely related to Czech language, Czech, to the point of very high mutual intelligibility, as well as to Polish language, Polish. Like other Slavic languages, Slovak is a fusional language with a complex system of morphology (linguistics), morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German language, German, as well as other Slavic languages. History The Czech–Slovak gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Che (Cyrillic)
Che (Ч ч; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It commonly represents the voiceless postalveolar affricate , like the in "switch" or in "choice". In English, it is romanized typically as but sometimes as , like in French. In German, it can be transcribed as . In Slavic languages using the Latin Alphabet, it is transcribed as so "Tchaikovsky" (Чайковский in Russian) may be transcribed as ''Chaykovskiy'' or ''Čajkovskij''. Form The letter Che (Ч ч) resembles an upside-down lowercase Latin h, as well as resembling the digit 4, especially in digital or open-ended form. Cursive forms look like lowercase cursive forms of the letter R. History The name of Che in the Early Cyrillic alphabet was Чрьвь (''črĭvĭ''), meaning "worm". In the Cyrillic numeral system, Che originally did not have a value, however, by the 1300s it started to be used with the numeric value 90 as a replacement for Koppa, some varieties that preserved Koppa around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rade Language
Rade (Rhade; Rade: ; or ) is an Austronesian language of southern Vietnam. There may be some speakers in Cambodia. It is a member of the Chamic subgroup, and is closely related to the Cham language of central Vietnam. Dialects Đoàn Văn Phúc (1998:24) lists nine dialects of Rade. They are spoken mostly in Đắk Lắk Province in the Central Highlands region of Vietnam. *Kpă: spoken throughout Buôn Ma Thuột *Krung: spoken in Ea H'leo and Krông Năng; some Krung also live among the Jarai in Gia Lai Province *Adham: spoken in Krông Buk, Krông Năng, and Ea H'leo *Ktul: spoken in Krông Bông and the southern part of Krông Pắk *Drao (Kơdrao): spoken in M'Đrăk (in the townships of Krông Jing, Cư M'Ta, and Ea Trang) *Blô: spoken in M'Đrăk (small population) *Êpan: spoken in M'Đrăk (small population) *Mdhur: spoken in Ea Kar and M'Đrăk; also in Gia Lai Province and Phu Yen Province *Bih: spoken in Krông Ana and in the southern part of Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
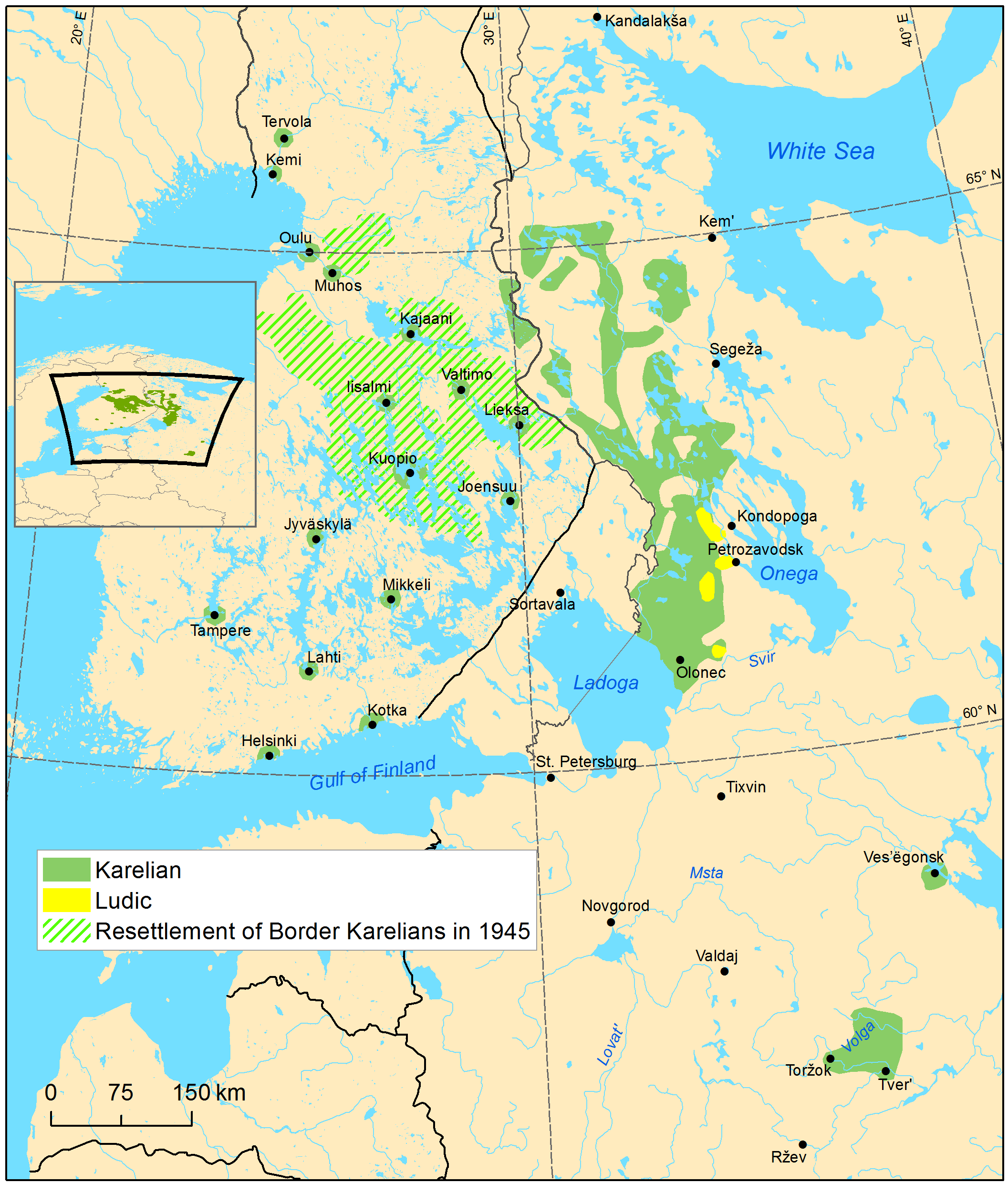
Karelian Language
Karelian (; ; ; ) is a Finnic language spoken mainly by the Karelians, Karelian people in the Russian Republic of Karelia. Linguistically, Karelian is closely related to the Finnish language, Finnish dialects spoken in eastern Finland, and some Finnish linguists have even classified Karelian as a dialect of Finnish, but nowadays it is widely considered a separate language. Karelian is not to be confused with the South Karelian dialects, Southeastern dialects of Finnish, sometimes referred to as ("Karelian dialects") in Finland. In the Russian 2020–2021 census, around 9,000 people spoke Karelian natively, but around 14,000 said they were able to speak the language. There are around 11,000 speakers of Karelian in Finland, and around 30,000 people in Finland have at least some knowledge of Karelian. The Karelian language is a group of two supradialects. The two supradialects are Karelian Proper language, Karelian Proper (which comprises Northern Karelian dialect, Northern Kareli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakota Language
Lakota ( ), also referred to as Lakhota, Teton or Teton Sioux, is a Siouan languages, Siouan language spoken by the Lakota people of the Sioux tribes. Lakota is mutually intelligible with the two dialects of the Dakota language, especially Dakota language#Comparison of the dialects, Western Dakota, and is one of the three major variety (linguistics), varieties of the Sioux language. Speakers of the Lakota language make up one of the largest Native American language speech communities in the United States, with approximately 2,000 speakers, who live mostly in the northern plains states of North Dakota and South Dakota. Many communities have immersion programs for both children and adults. Like many indigenous languages, the Lakota language did not have a written form traditionally. However, efforts to develop a written form of Lakota began, primarily through the work of Christian missionaries and linguists, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The orthography has since evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latvian Language
Latvian (, ), also known as Lettish, is an East Baltic languages, East Baltic language belonging to the Indo-European language family. It is spoken in the Baltic region, and is the language of the Latvians. It is the official language of Latvia as well as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 1.5 million native Latvian speakers in Latvia and 100,000 abroad. Altogether, 2 million, or 80% of the population of Latvia, spoke Latvian in the 2000s, before the total number of inhabitants of Latvia slipped to 1.8 million in 2022. Of those, around 1.16 million or 62% of Latvia's population used it as their primary language at home, though excluding the Latgale Planning Region, Latgale and Riga Planning Region, Riga regions it is spoken as a native language in villages and towns by over 90% of the population. As a Baltic languages, Baltic language, Latvian is most closely related to neighboring Lithuanian language, Lithuanian (as well as Old Prussian language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Sorbian Language
Lower Sorbian () is a West Slavic minority language spoken in eastern Germany in the historical province of Lower Lusatia, today part of Brandenburg. Standard Lower Sorbian is one of the two literary Sorbian languages, the other being the more widely spoken Upper Sorbian. The Lower Sorbian literary standard was developed in the 18th century, based on a southern form of the Cottbus dialect. The standard variety of Lower Sorbian has received structural influence from Upper Sorbian. Lower Sorbian is spoken in and around the city of Cottbus in Brandenburg. Signs in this region are typically bilingual, and Cottbus has a '' Lower Sorbian Gymnasium'' where one language of instruction is Lower Sorbian. It is a heavily endangered language. Most native speakers today belong to the older generations. Phonology The phonology of Lower Sorbian has been greatly influenced by contact with German, especially in Cottbus and larger towns. For example, German-influenced pronunciation tends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovene Language
Slovene ( or ) or Slovenian ( ; ) is a South Slavic languages, South Slavic language of the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. Most of its 2.5 million speakers are the inhabitants of Slovenia, the majority of them ethnic Slovenes. As Slovenia is part of the European Union, Slovene is also one of its 24 Languages of the European Union, official and working languages. Its grammar is highly fusional languages, fusional, and it has a Dual (grammatical number), dual grammatical number, an archaic feature shared with some other Indo-European languages. Two accentual norms (one characterized by Pitch-accent language, pitch accent) are used. Its flexible word order is often adjusted for emphasis or stylistic reasons, although basically it is an subject–verb–object word order, SVO language. It has a T–V distinction: the use of the V-form demonstrates a respectful attitude towards superiors and the elderly, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |