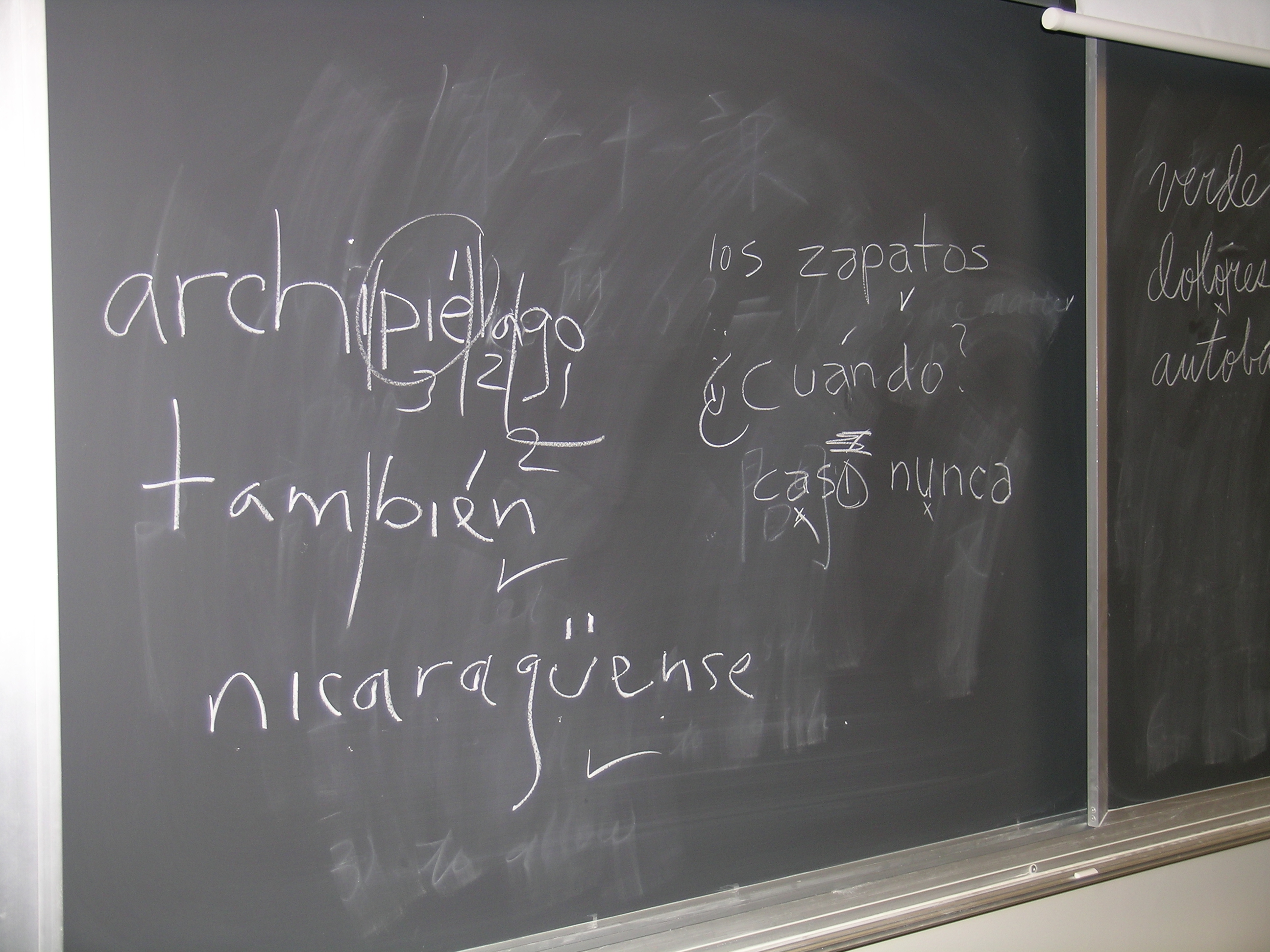|
Tilde
The tilde (, also ) is a grapheme or with a number of uses. The name of the character came into English from Spanish , which in turn came from the Latin , meaning 'title' or 'superscription'. Its primary use is as a diacritic (accent) in combination with a base letter. Its freestanding form is used in modern texts mainly to indicate approximation. History Use by medieval scribes The tilde was originally one of a variety of marks written over an omitted letter or several letters as a scribal abbreviation (a "mark of contraction"). Thus, the commonly used words ''Anno Domini'' were frequently abbreviated to ''Ao Dñi'', with an elevated terminal with a contraction mark placed over the "n". Such a mark could denote the omission of one letter or several letters. This saved on the expense of the scribe's labor and the cost of vellum and ink. Medieval European charters written in Latin are largely made up of such abbreviated words with contraction marks and other abbreviations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Guarani Language
Guarani (Avañe'ẽ), also called Paraguayan Guarani, is a language of South America that belongs to the Tupi–Guarani branch of the Tupian languages, Tupian language family. It is one of the two official languages of Paraguay (along with Spanish language, Spanish), where it is spoken by the majority of the population, and where half of the rural population are monolingual speakers of the language. Variants of the language are spoken by communities in neighboring countries including parts of northeastern Argentina, southeastern Bolivia and southwestern Brazil. It is a second official language of the Provinces of Argentina, Argentine province of Corrientes Province, Corrientes since 2004 and in the Municipalities of Brazil, Brazilian city of Tacuru since 2010. Guarani is also one of the three official languages of Mercosur, alongside Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Guarani is one of the most widely spoken indigenous languages of the Americas, Native American langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spanish Alphabet
Spanish orthography is the orthography used in the Spanish language. The alphabet uses the Latin script. The spelling is fairly phonemic orthography, phonemic, especially in comparison to more opaque orthographies like English orthography, English, having a relatively consistent mapping of graphemes to phonemes; in other words, the pronunciation of a given Spanish-language word can largely be predicted from its spelling and to a slightly lesser extent vice versa. Spanish punctuation uniquely includes the use of inverted question and exclamation marks: . Spanish uses capital letters much less often than English; they are not used on adjectives derived from proper nouns (e.g. ''francés'', ''español'', ''portugués'' from ''Francia'', ''España'', and ''Portugal'', respectively) and book titles capitalize only the first word (e.g. ''The Revolt of the Masses, La rebelión de las masas''). Spanish uses only the acute accent over any vowel: . This accent is used to mark the tonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chamorro Language
Chamorro (, ; [Northern Mariana Islands] or [Guam] ) is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language spoken by about 58,000 people, numbering about 25,800 on Guam and about 32,200 in the Northern Mariana Islands and elsewhere. It is the historic native language of the Chamorro people, who are indigenous people, indigenous to the Mariana Islands, although it is less commonly spoken today than in the past. Chamorro has three distinct dialects: Guamanian, Rotanese, and that in the other Northern Mariana Islands (NMI). Classification Unlike most of its neighbors, Chamorro is not classified as a Micronesian languages, Micronesian or Polynesian languages, Polynesian language. Rather, like Palauan language, Palauan, it possibly constitutes an independent branch of the Malayo-Polynesian languages, Malayo-Polynesian language family. At the time the Spanish rule over Guam ended, it was thought that Chamorro was a semi-creole language, with a substantial amount of the vocabulary of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ny (digraph)
Ny is a digraph in a number of languages such as Catalan, Ganda, Filipino/Tagalog, Hungarian, Swahili and Malay. In most of these languages, including all of the ones named above, it denotes the palatal nasal (). To represent the palatal nasal in other languages, the letter nj is used, such as in Albanian and the countries using Gaj's Latin alphabet and the countries that make up the former Yugoslavia. It has had widespread use for languages of West Africa, though in some countries, the IPA letter '' ɲ'' is now used. It is sometimes used in modern Spanish where '' ñ'' cannot be used, such as in earlier computer programming or Internet domain names. FAQ about .es domain names: . ''N'' and ''ny'' are mentioned as substitutes for ''ñ''. Aragonese The writing of the palatal nasal in Aragonese has been a matter of debate since the first orthographic codification of the language (''grafía de Uesca'') in 1987 by the '' Consello d'a Fabla Aragonesa'' at a convention in Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Quechua Alphabet
The Quechua alphabet () is based on the Latin alphabet. It is used to write the Quechuan languages. The Quechua alphabet has been use in Peru since 1975, following the Officialization of Quechua by Decree Law in May 1975 that made Quechua co-equal with Spanish. History As far as is known, there was no writing system in the Andes before the Spaniards' Conquest, so that it seems that Quechua languages were first written in some version of the Latin alphabet. Quechua language colonial orthography was an adaptation and of Golden Age Spanish typographic conventions. For example, the 5 Latin vowel characters, well-suited for Spanish 5-vowel phoneme system, were used for writing Quechua vowel sounds in a phonologically hyperdifferentiating manner. On addition, labial–velar approximant phoneme was variably transcribed as . Main points in that evolution were Third Lima Ecclesiastical Council orthography and Diego Gonzalez Holguin orthography. The latter used doubled letters to signal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chavacano
Chavacano or Chabacano () is a group of Spanish-based creole language varieties spoken in the Philippines. The variety spoken in Zamboanga City, located in the southern Philippine island group of Mindanao, has the highest concentration of speakers. Other currently existing varieties are found in Cavite City and Ternate, located in the Cavite province on the island of Luzon. Chavacano is the only Spanish-based creole in Asia. The 2020 Census of Population and Housing counted 106,000 households generally speaking Chavacano. The one responsible for this Spanish creole was Don Sebastian Hurtado de Corcuera, then governor of Panama, who was also responsible for settling Zamboanga City by employing Peruvian soldiers and colonists. There was an Asian-American route, which led to traders and adventurers carrying silver from Peru through Panama to reach Acapulco, Mexico before sailing to Manila, Philippines using the famed Manila galleons. The different varieties of Chavacano dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Basque Language
Basque ( ; ) is a language spoken by Basques and other residents of the Basque Country (greater region), Basque Country, a region that straddles the westernmost Pyrenees in adjacent parts of northern Spain and southwestern France. Basque is classified as a language isolate (unrelated to any other known languages), the only one in Europe. The Basques are indigenous to and primarily inhabit the Basque Country. The Basque language is spoken by 806,000 Basques in all territories. Of them, 93.7% (756,000) are in the Spanish area of the Basque Country and the remaining 6.3% (50,000) are in the French portion. Native speakers live in a contiguous area that includes parts of four Spanish provinces and the French Basque Country, three "ancient provinces" in France. Gipuzkoa, most of Biscay, a few municipalities on the northern border of Álava and the northern area of Navarre formed the core of the remaining Basque-speaking area before measures were introduced in the 1980s to stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Asturian Alphabet
Asturian (; )Art. 1 de lLey 1/1998, de 23 de marzo, de uso y promoción del bable/asturiano [Law 1/93, of March 23, on the Use and Promotion of the Asturian Language/nowiki>] is a West Iberian languages, West Iberian Romance languages, Romance language spoken in the Principality of Asturias, Spain. Asturian is part of a wider linguistic group, the Asturleonese languages. The number of speakers is estimated at 100,000 (native) and 450,000 (second language). The dialects of the Astur-Leonese language family are traditionally classified in three groups: Western, Central, and Eastern. For historical and demographic reasons, the standard is based on Central Asturian. Asturian has a distinct grammar, dictionary, and orthography. It is regulated by the Academy of the Asturian Language. Although it is not an official language of Spain, it is protected under the Statute of Autonomy of Asturias and is an elective language in schools. For much of its history, the language has been ig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Galician Alphabet
The Galician alphabet is used for writing the Galician language. According to the modern and official standard, it has 23 letters and 6 digraphs. The extraneous letters , , and are sporadically found in foreign words, abbreviations and international symbols. As in Portuguese and unlike in Spanish, Galician letter names are of masculine grammatical gender In linguistics, a grammatical gender system is a specific form of a noun class system, where nouns are assigned to gender categories that are often not related to the real-world qualities of the entities denoted by those nouns. In languages wit .... The Medieval Galician alphabet, still used today by advocates of reintegrationism, featured the additional letters /ʃ/ and /θ/ (or /s/ in areas with sigmatism) as well as the digraphs /ʎ/, /ɲ/ and /s/. References {{Reflist Latin alphabets Galician language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Papiamento Orthography
Papiamento has two standardised orthographies, one used on the island of Aruba and the other on the islands of Curaçao and Bonaire. The Aruban orthography is more etymological in nature, while the other is more phonemic. Among the differences between the two standards, one obvious difference is the way the name of the language is written. In Aruba it is written ''Papiamento'', while in Curaçao and Bonaire it is written ''Papiamentu''. The governments of Curaçao and Aruba formally standardised orthographic rules in 1976 and 1977, respectively. History Development The first efforts to formalise the language began in the early 1970s, with the first step made in 1969 in Curaçao. R.G. Römer presented to the Central Government of the Netherlands Antilles his (''Draft of a spelling for Papyamento''). In 1970 the Maduro Commission consisting of eight members, R.G. Römer included, was formed. With a modified proposition, they presented their recommendations to the Minister of Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nh (digraph)
Nh is a digraph of the Latin alphabet, a combination of N and H. Together with '' lh'' and the interpunct, it is a typical feature of Occitan, a language illustrated by medieval troubadours. It commonly represents the voiced palatal nasal , which is the same sound as the Spanish letter Ñ. African languages In some African languages, such as Gogo, nh is a voiceless . In the pre-1985 orthography of Guinea for its languages, nh represented a velar , which is currently written ŋ. Asian languages In the Gwoyeu Romatzyh romanization of Mandarin Chinese, initial ''nh-'' indicates an even tone on a syllable beginning in , which is otherwise spelled ''n-.'' Japanese Early romanizations of Japanese, influenced by Portuguese orthography, sometimes used nh to represent a prepalatal. Today, this is usually written ny. Vietnamese In Vietnamese, nh represents a palatal word-initially. It was formerly considered a distinct letter, but is no longer. When this digraph occurs word-fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |