|
Émile Dorand
Jean-Baptiste Émile Dorand (; 14 May 1866 – 1 July 1922), was a French military engineer and aircraft designer. Early career Émile Dorand was born in Semur-en-Auxois in eastern France. He attended the École Polytechnique from 1886 to 1888 in the Quartier Latin, Latin Quarter of Paris. He then went to the Fontainebleau Application School, a military college, which he left after two years as a Lieutenant in the French Army. In an engineering regiment, he met the airship pioneer Charles Renard, and was soon authorised to direct free Balloon (aeronautics), balloon flights. He studied aeronautics and the problems of flight including working to improve kites, long range photography, and flight test methodology. From 1895 to 1896, he was assigned to the Expeditionary Engineer Corps with whom he managed Gas balloon, hydrogen balloons and bridging equipment in Madagascar. He returned to France as a Captain, and was posted to Avignon, Dijon and Versailles. Aircraft development and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semur-en-Auxois
Semur-en-Auxois () is a Communes of France, commune of the Côte-d'Or Departments of France, department in eastern France. The politician François Patriat, the engineers Edmé Régnier L'Aîné (1751–1825) and Émile Dorand (1866-1922), and the Encyclopédistes, Encyclopédiste Philippe Guéneau de Montbeillard (1720–1785) were born in Semur-en-Auxois, while the military engineer Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban, Vauban (1633–1707) was educated at the Carmelite college. Semur-en-Auxois has a medieval core, built on a pink granite bluff more than half-encircled by the River Armançon. The river formerly provided motive power for tanneries and mills, but its flow is now somewhat reduced by the Lac de Pont. The dam was built upstream in the 19th century to provide water for the Canal de Bourgogne. Sport Semur-en-Auxois was the start of Stage 6 in the 2007 Tour de France. Population Sights *The church, La Collégiale Notre-Dame, was founded in 1225 and built in flamboyan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landing Gear
Landing gear is the undercarriage of an aircraft or spacecraft that is used for taxiing, takeoff or landing. For aircraft, it is generally needed for all three of these. It was also formerly called ''alighting gear'' by some manufacturers, such as the Glenn L. Martin Company. For aircraft, Stinton makes the terminology distinction ''undercarriage (British) = landing gear (US)''. For aircraft, the landing gear supports the craft when it is not flying, allowing it to take off, land, and taxi without damage. Wheeled landing gear is the most common, with skis or Seaplane, floats needed to operate from snow/ice/water and skids for vertical operation on land. Retractable undercarriages fold away during flight, which reduces drag (physics), drag, allowing for faster airspeeds. Landing gear must be strong enough to support the aircraft and its design affects the weight, balance and performance. It often comprises three wheels, or wheel-sets, giving a tripod effect. Some unusual land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Stagger
In aviation, stagger is the relative horizontal fore-aft positioning of stacked wings in a biplane, triplane, or multiplane. An aircraft is said to have ''positive stagger'', or simply ''stagger'', when the upper wing is positioned forward of the lower (bottom) wing,NACA technical report No.310 ''Wind Tunnel Pressure Distribution Tests on a Series of Biplane Wing Models'' (July 1929), p.17. Retrieved on 8 February 2009. Examples include the or . Conversely, an aeroplane is said to ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
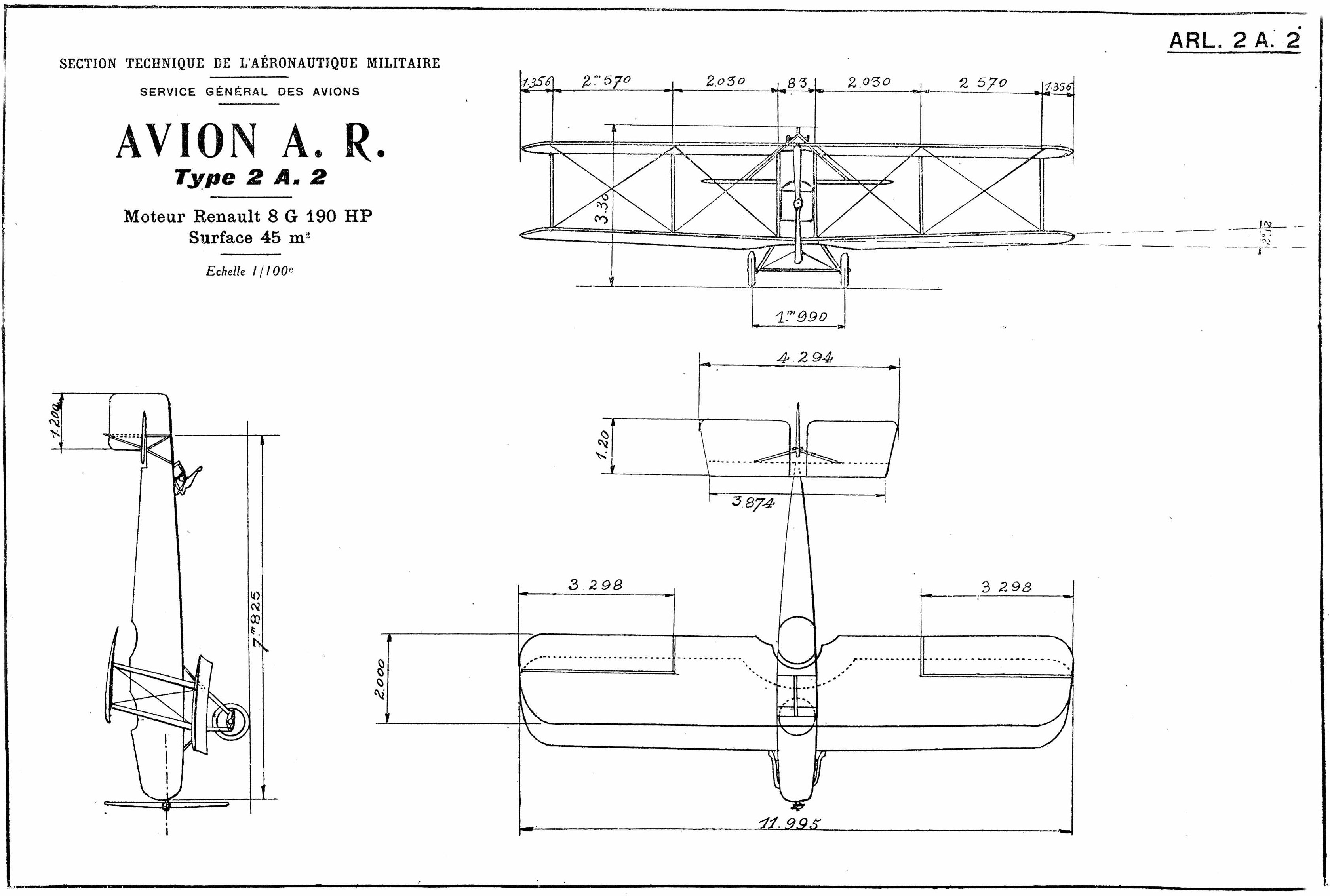
Dorand AR
The Dorand AR.1 was a World War I France, French two-seat observation biplane aircraft used by the French Air Force, the American Expeditionary Force and, in small numbers, by Serbian Air Force and Air Defense, Serbian Aviation. Design and development Designed by Captain Georges Lepère of the STAé to replace the obsolescent Farman F.40 pusher configuration, pusher aircraft, Dorand AR-series were two-seater reconnaissance biplanes that were named after the STAé director, Lt. Col. Dorand. They were characterized by backward-staggered two-bay wings and angular all-moving tail surfaces. The pilot sat beneath the leading edge of the upper wing, with the observer's cockpit being under the trailing edge, and there were cut-outs in both wings to improve the latter's field of view. Rather unusually for a single-engine tractor configuration, tractor biplane of the era, the lower wing was not directly attached to the fuselage, instead being somewhat below it, supported by struts. Pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Service Technique De L'AĂ©ronautique
The (STAé) was a French state body responsible for coordinating technical aspects of aviation in France. Formed in 1916 as the the STAé continued until 1980 when its functions were distributed among other French governmental bodies, including the (STPA), (STPA) and the (SCPM). History In 1877 (Central Establishment of the air balloon of Chalais- Meudon) was formed as the first aeronautical laboratory in the world, with a mission to design and assemble all French military aero-static equipment, from components made in industry, and train personnel in their use. At the beginning of 1916 French military aircraft were being surpassed in performance and armament. The lack of technical coordination lead to disagreements between the views and desires of command and the capabilities of manufacturers, resulting in development delays and technological dead ends. At the instigation of the Deputy Secretary of State for Aeronautics René Besnard and Minister of War General Gallieni, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalais-Meudon
Chalais-Meudon is an aeronautical research and development centre in Meudon, to the south-west of Paris. It was originally founded in 1793 in the nearby Château de Meudon and has played an important role in the development of French aviation. Starting with the development and production of balloons, the site has been a centre of aviation development, mainly but not exclusively military, ever since. Many famous French aircraft designers and engineers worked here or used its resources, such as hangars, wind tunnels, and laboratories to further their activities, and the site continues as an aerospace research hub into the 21st century. The site was the original home of the world's first aviation museum, now known as the Musée de l'air et de l'espace at Paris–Le Bourget Airport. History Balloons The story of aviation at Chalais-Meudon starts in October 1793 when the French Committee of Public Safety ordered the construction of an observation balloon capable of carrying two obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AĂ©ronautique Militaire
The French Air and Space Force (, , ) is the air force, air and space force of the French Armed Forces. Formed in 1909 as the ("Aeronautical Service"), a service arm of the French Army, it became an independent military branch in 1934 as the French Air Force (). On 10 September 2020, it assumed its current name, the French Air and Space Force, to reflect an "evolution of its mission" into the area of outer space. The number of aircraft in service with the French Air and Space Force varies depending on the source; the Ministry of Armed Forces (France), Ministry of Armed Forces gives a figure of 658 aircraft in 2014. According to 2025 data, this figure includes 207 combat aircraft: 99 Dassault Mirage 2000 and 108 Dassault Rafale. the French Air and Space Force employs a total of 40,500 regular personnel, with a military reserve forces of France, reserve element of 5,187 in 2014. The Chief of Staff of the French Air and Space Force (CEMAAE) is a direct subordinate of the Chief of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuselage
The fuselage (; from the French language, French ''fuselé'' "spindle-shaped") is an aircraft's main body section. It holds Aircrew, crew, passengers, or cargo. In single-engine aircraft, it will usually contain an Aircraft engine, engine as well, although in some amphibious aircraft the single engine is mounted on a hardpoint, pylon attached to the fuselage, which in turn is used as a floating Hull (watercraft), hull. The fuselage also serves to position the Flight control surfaces, control and Stabilizer (aeronautics), stabilization surfaces in specific relationships to Wing, lifting surfaces, which is required for aircraft stability and maneuverability. Types of structures Truss structure This type of structure is still in use in many lightweight aircraft using welding, welded steel tube trusses. A box truss fuselage structure can also be built out of wood—often covered with plywood. Simple box structures may be rounded by the addition of supported lightweight strin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |