|
(Drawing) Rings Around The World
"(Drawing) Rings Around the World" is a song by Super Furry Animals and was the second single taken from the band's fifth album, '' Rings Around the World''. The track reached number 28 on the UK Singles Chart on release in October 2001. Singer Gruff Rhys has described the song as being about "rings of communication around the world. All the rings of pollution". Critical reaction to the track was generally positive with many reviewers comparing the song to the work of other groups such as Status Quo, ELO and The Beach Boys. A promotional music video was produced to accompany "(Drawing) Rings Around the World"'s release as a single. Directed by Pedro Romhanyi the video features images of fictional television stations including "SFA TV", which shows the band playing along with the track. An alternative video, directed by Sean Hillen, was included on the DVD version of ''Rings Around the World'' on its release in July 2001. This video features the lyrics to the track scrolling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Super Furry Animals
Super Furry Animals are a Welsh rock band formed in Cardiff in 1993. For the duration of their professional career, the band consisted of Gruff Rhys (lead vocals, guitar), Huw Bunford (lead guitar, vocals), Guto Pryce (bass guitar), Cian Ciaran (keyboards, synthesisers, various electronics, occasional guitar, vocals), Dafydd Ieuan (drums, vocals). An earlier incarnation of the band featured actor Rhys Ifans on lead vocals. Super Furry Animals has recorded nine UK Albums Chart Top 25 studio albums (one BPI certified Gold and four certified Silver), plus numerous singles, EPs, compilations and collaborations. The band were known as central to the Cool Cymru era during which they were dominant, and are the act with the most top 75 hits without reaching the UK Singles Chart Top 10. Over the course of nine albums, Super Furry Animals has been described as "one of the most imaginative bands of our time" by ''Billboard'', while according to a 2005 article in '' NME'', "There' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrolling
In computer displays, filmmaking, television production, and other kinetic displays, scrolling is sliding text, images or video across a monitor or display, vertically or horizontally. "Scrolling," as such, does not change the layout of the text or pictures but moves ( pans or tilts) the user's view across what is apparently a larger image that is not wholly seen. A common television and movie special effect is to scroll credits, while leaving the background stationary. Scrolling may take place completely without user intervention (as in film credits) or, on an interactive device, be triggered by touchscreen or a keypress and continue without further intervention until a further user action, or be entirely controlled by input devices. Scrolling may take place in discrete increments (perhaps one or a few lines of text at a time), or continuously (smooth scrolling). Frame rate is the speed at which an entire image is redisplayed. It is related to scrolling in that changes to text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conclusion (music)
In music, the conclusion is the ending of a composition and may take the form of a coda or outro. Pieces using sonata form typically use the recapitulation to conclude a piece, providing closure through the repetition of thematic material from the exposition in the tonic key. In all musical forms other techniques include "altogether unexpected digressions just as a work is drawing to its close, followed by a return...to a consequently more emphatic confirmation of the structural relations implied in the body of the work." Perle, George (1990). ''The Listening Composer''. California: University of California Press. . For example: * The slow movement of Bach's '' Brandenburg Concerto No. 2'', where a "diminished-7th chord progression interrupts the final cadence." * The slow movement of Symphony No. 5 by Beethoven, where, "echoing afterthoughts", follow the initial statements of the first theme and only return expanded in the coda. * Varèse's '' Density 21.5'', where part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge (music)
In music, especially Western popular music, a bridge is a contrasting section that prepares for the return of the original material section. In a piece in which the original material or melody is referred to as the "A" section, the bridge may be the third eight-bar phrase in a thirty-two-bar form (the B in AABA), or may be used more loosely in verse-chorus form, or, in a compound AABA form, used as a contrast to a full AABA section. The bridge is often used to contrast with and prepare for the return of the verse and the chorus. "The b section of the popular song chorus is often called the ''bridge'' or ''release''." Etymology The term comes from a German word for bridge, ''Steg'', used by the Meistersingers of the 15th to the 18th century to describe a transitional section in medieval bar form. The German term became widely known in 1920s Germany through musicologist Alfred Lorenz and his exhaustive studies of Richard Wagner's adaptations of bar form in his popular 19th-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fade (audio Engineering)
In audio engineering, a fade is a gradual increase or decrease in the level of an audio signal. The term can also be used for film cinematography or theatre lighting in much the same way (see fade (filmmaking) and fade (lighting)). A recorded song may be gradually reduced to silence at its end (fade-out), or may gradually increase from silence at the beginning (fade-in). Fading-out can serve as a recording solution for pieces of music that contain no obvious ending. Both fades and crossfades are very valuable since they allow the engineer to quickly and easily make sure that the beginning and the end of any audio is smooth, without any prominent glitches.Langford, S. 2014. Digital Audio Editing. Burlington: Focal Press. pp. 47-57. It is necessary that there is a clear section of silence prior to the audio. Fade-ins and -outs can also be used to change the characteristics of a sound, such as to soften the attack in vocals where very plosive (‘b’, ‘d’, and ‘p’) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord (music)
A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of pitches/frequencies consisting of multiple notes (also called "pitches") that are heard as if sounding simultaneously. For many practical and theoretical purposes, arpeggios and broken chords (in which the notes of the chord are sounded one after the other, rather than simultaneously), or sequences of chord tones, may also be considered as chords in the right musical context. In tonal Western classical music (music with a tonic key or "home key"), the most frequently encountered chords are triads, so called because they consist of three distinct notes: the root note, and intervals of a third and a fifth above the root note. Chords with more than three notes include added tone chords, extended chords and tone clusters, which are used in contemporary classical music, jazz and almost any other genre. A series of chords is called a chord progression. One example of a widely used chord progression in Western traditional music an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
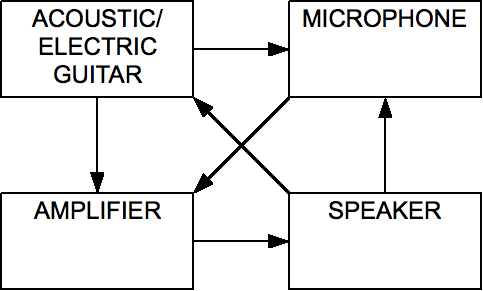
Audio Feedback
Audio feedback (also known as acoustic feedback, simply as feedback) is a positive feedback situation which may occur when an acoustic path exists between an audio input (for example, a microphone or guitar pickup) and an audio output (for example, a loudspeaker). In this example, a signal received by the microphone is amplified and passed out of the loudspeaker. The sound from the loudspeaker can then be received by the microphone again, amplified further, and then passed out through the loudspeaker again. The frequency of the resulting howl is determined by resonance frequencies in the microphone, amplifier, and loudspeaker, the acoustics of the room, the directional pick-up and emission patterns of the microphone and loudspeaker, and the distance between them. The principles of audio feedback were first discovered by Danish scientist Søren Absalon Larsen, hence it is also known as the Larsen effect. Feedback is almost always considered undesirable when it occurs with a sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AllMusic
AllMusic (previously known as All-Music Guide and AMG) is an American online music database. It catalogs more than three million album entries and 30 million tracks, as well as information on musicians and bands. Initiated in 1991, the database was first made available on the Internet in 1994. AllMusic is owned by RhythmOne. History AllMusic was launched as All-Music Guide by Michael Erlewine, a "compulsive archivist, noted astrologer, Buddhist scholar and musician". He became interested in using computers for his astrological work in the mid-1970s and founded a software company, Matrix, in 1977. In the early 1990s, as CDs replaced LPs as the dominant format for recorded music, Erlewine purchased what he thought was a CD of early recordings by Little Richard. After buying it, he discovered it was a "flaccid latter-day rehash". Frustrated with the labeling, he researched using metadata to create a music guide. In 1990, in Big Rapids, Michigan, he founded ''All Music Guid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B Major
B major (or the key of B) is a major scale based on B. The pitches B, C, D, E, F, G, and A are all part of the B major scale. Its key signature has five sharps. Its relative minor is G-sharp minor, its parallel minor is B minor, and its enharmonic equivalent is C-flat major. The B major scale is: Although B major is usually considered a remote key (due to its distance from C major in the circle of fifths and fairly large number of sharps), Frédéric Chopin regarded its scale as the easiest of all to play on the piano, as its black notes fit the natural positions of the fingers well; as a consequence he often assigned it first to beginning piano students, leaving the scale of C major until last because he considered it the hardest of all scales to play completely evenly (because of its complete lack of black notes). Few large-scale works in B major exist: these include Haydn's Symphony No. 46. The aria " La donna è mobile" from Verdi's opera ''Rigoletto'' is i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counter-melody
In music, a counter-melody (often countermelody) is a sequence of notes, perceived as a melody, written to be played simultaneously with a more prominent lead melody. In other words, it is a secondary melody played in counterpoint with the primary melody. A counter-melody performs a subordinate role, and it is typically heard in a texture consisting of a melody plus accompaniment. In marches, the counter-melody is often given to the trombones or horns. American composer David Wallis Reeves is credited with this innovation in 1876. The more formal term countersubject applies to a secondary or subordinate melodic idea in a fugue In music, a fugue () is a contrapuntal compositional technique in two or more voices, built on a subject (a musical theme) that is introduced at the beginning in imitation (repetition at different pitches) and which recurs frequently in the co .... A countermelody differs from a harmony part sung by a backup singer in that whereas the harmon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; however, with its larger volume, Saturn is over 95 times more massive. Saturn's interior is most likely composed of a core of iron–nickel and rock (silicon and oxygen compounds). Its core is surrounded by a deep layer of metallic hydrogen, an intermediate layer of liquid hydrogen and liquid helium, and finally, a gaseous outer layer. Saturn has a pale yellow hue due to ammonia crystals in its upper atmosphere. An electrical current within the metallic hydrogen layer is thought to give rise to Saturn's planetary magnetic field, which is weaker than Earth's, but which has a magnetic moment 580 times that of Earth due to Saturn's larger size. Saturn's magnetic field strength is around one-twentieth of Jupiter's. The outer atmosphere is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |