Ziram on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate is a
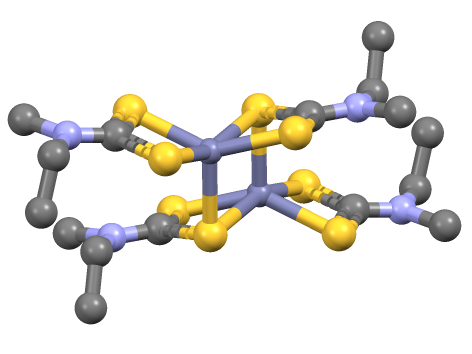
coordination complex
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as '' ligands'' or complexing agents. M ...
of zinc with dimethyldithiocarbamate
Dimethyldithiocarbamate is the organosulfur anion with the formula (CH3)2NCS2−. It is one of the simplest organic dithiocarbamate.
Uses
It is a component of various pesticides and rubber chemicals in the form of its salts sodium dimethyldithio ...
. It is a pale yellow solid that is used as a fungicide
Fungicides are biocidal chemical compounds or biological organisms used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. A fungistatic inhibits their growth. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in critical losses of yield, quality ...
, the sulfur vulcanization
Sulfur vulcanization is a chemical process for converting natural rubber or related polymers into materials of varying hardness, elasticity, and mechanical durability by heating them with sulfur or sulfur-containing compounds. Sulfur forms cr ...
of rubber, and other industrial applications.
Applications
Known as ziram in agriculture, it was introduced in the United States in 1960 as a broad-spectrum fungicide. It was used to address scab on apples and pears, leaf curl in peaches, andanthracnose
A plant canker is a small area of dead tissue, which grows slowly, often over years. Some cankers are of only minor consequence, but others are ultimately lethal and therefore can have major economic implications for agriculture and horticultur ...
and blight
Blight refers to a specific symptom affecting plants in response to infection by a pathogenic organism.
Description
Blight is a rapid and complete chlorosis, browning, then death of plant tissues such as leaves, branches, twigs, or floral orga ...
in tomatoes. In 1981, additional uses for ziram were approved, including the prevention of leaf blight and scab on almonds, shot-hole in apricots, brown rot and leaf spot in cherries, and scab and anthracnose in pecans. Ziram also began to be used on residential ornaments as a bird and mammal repellent. As a protectant fungicide, it active on the plant’s surface where it forms a chemical
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., w ...
barrier between the plant and a fungus. A protectant fungicide is not absorbed into the plant and must be applied prior to infection. Ziram can either be directly sprayed on to a plant’s leaf or it can be used as a soil and seed treatment. The top five crops ziram is used on are: almonds
The almond (''Prunus amygdalus'', syn. ''Prunus dulcis'') is a species of tree native to Iran and surrounding countries, including the Levant. The almond is also the name of the edible and widely cultivated seed of this tree. Within the genus ...
, peaches
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and cultivated in Zhejiang province of Eastern China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and others (the glossy-skinned, non-fu ...
, nectarines
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and cultivated in Zhejiang province of Eastern China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and others (the glossy-skinned, no ...
, pear
Pears are fruits produced and consumed around the world, growing on a tree and harvested in the Northern Hemisphere in late summer into October. The pear tree and shrub are a species of genus ''Pyrus'' , in the Family (biology), family Rosacea ...
s, and table and raisin
A raisin is a dried grape. Raisins are produced in many regions of the world and may be eaten raw or used in cooking, baking, and brewing. In the United Kingdom, Ireland, New Zealand, and Australia, the word ''raisin'' is reserved for the ...
grapes.
Alternatively, ziram is used as an additive ingredient in industrial adhesive
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
The use of adhesives offers certain advant ...
s, caulking
Caulk or, less frequently, caulking is a material used to seal joints or seams against leakage in various structures and piping.
The oldest form of caulk consisted of fibrous materials driven into the wedge-shaped seams between boards on ...
, and paint. It also serves as a bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
and mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur ...
repellent on outdoor ornamental items.
Chemistry
The compound is a prototypical zinc dithiocarbamate, a broad class ofcoordination complex
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as '' ligands'' or complexing agents. M ...
es with the formulae Zn(R2NCS2)2, where R can be varied. Such compounds are produced by treating zinc and dithiocarbamate
In organic chemistry, a dithiocarbamate is a functional group with the general formula and structure . It is the analog of a carbamate in which both oxygen atoms are replaced by sulfur atoms (when only 1 oxygen is replaced the result is thioca ...
(R2NCS2−), as illustrated with dimethyldithiocarbamate:
:2 (CH3)2NCS2− + Zn2+ → Zn((CH3)2NCS2)2
Annually, approximately 1.9 million pounds of the active ziram ingredient are used. Ziram is often sold in powder or granule form.
Zinc bis(diethyldithiocarbamate) complexes degrade thermally to give zinc sulfide
Zinc sulfide (or zinc sulphide) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula of ZnS. This is the main form of zinc found in nature, where it mainly occurs as the mineral sphalerite. Although this mineral is usually black because of various ...
.
Structure
Compounds of the type Zn(S2CNR2)2 are dimeric, i.e. their proper formula is n(S2CNR2)2sub>2. Each Zn center is in a distorted pentacoordinate site, with four Zn-S bonds of 2.3 Å length and one Zn---S interaction >2.8 Å in length. Mono-zinc derivatives are obtained by adding strong ligands (L) such as amines, which give adducts Zn(S2CNR2)2L.
Ecological effects
Ziram only moderately persists in soils, as it has a fieldhalf-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ...
of 30 days
In water, ziram is the most stable of all metallic dithiocarbamate fungicides, which means biodegradation
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegra ...
is rather slow. If ziram reaches the bottom of a body of water, it may stay there for months.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale ...
has concluded that ziram poses a low toxicity risk to mammals, a moderate risk to birds, and a high risk to aquatic species. After reviewing studies that investigated the effect of ziram on aquatic organisms, the Pesticide Action Network
Pesticide Action Network (PAN) is "an international coalition of around 600 NGO
A non-governmental organization (NGO) or non-governmental organisation (see spelling differences) is an organization that generally is formed independent from ...
Pesticide Database concluded that its LC50 dose (amount of pesticide that is lethal to 50% of the test organisms within the stated study time) for amphibians
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arbo ...
places it in the "highly toxic" category.
See also
*Iron tris(dimethyldithiocarbamate)
Iron tris(dimethyldithiocarbamate) is the coordination complex of iron with dimethyldithiocarbamate with the formula Fe(S2CNMe2)3 (Me = methyl). It is marketed as a fungicide.
Synthesis, structure, bonding
Iron tris(dithiocarbamate)s are typic ...
- a related complex, but with three dimethyldithiocarbamate ligands
* Nickel bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate)
Nickel bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) is the coordination complex on nickel and dimethyldithiocarbamate, with the formula Ni(S2CNMe2)2 (Me = methyl). It is the prototype for a large number of bis(dialkhyldithiocarbamate)s of nickel(II), which feat ...
- a related compound where zinc has been replaced with nickel
References
External links
* http://pmep.cce.cornell.edu/profiles/extoxnet/pyrethrins-ziram/ziram-ext.html *{{PPDB, 684 Fungicides biszinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...