Zika virus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Zika virus'' (ZIKV; pronounced or ) is a member of the
 Zika is primarily spread by the female ''Aedes aegypti'' mosquito, which is active mostly in the daytime. The mosquitos must feed on blood to lay eggs. The virus has also been isolated from a number of
Zika is primarily spread by the female ''Aedes aegypti'' mosquito, which is active mostly in the daytime. The mosquitos must feed on blood to lay eggs. The virus has also been isolated from a number of
 Zika fever (also known as ''Zika virus'' disease) is an illness caused by ''Zika virus''. Around 80% of cases are estimated to be asymptomatic, though the accuracy of this figure is hindered by the wide variance in data quality, and figures from different outbreaks can vary significantly. Symptomatic cases are usually mild and can resemble
Zika fever (also known as ''Zika virus'' disease) is an illness caused by ''Zika virus''. Around 80% of cases are estimated to be asymptomatic, though the accuracy of this figure is hindered by the wide variance in data quality, and figures from different outbreaks can vary significantly. Symptomatic cases are usually mild and can resemble
 It is advised, for an affected person with the zika virus, to drink a lot of water to stay hydrated, to lie down, and to treat the fever and agony with liquid solutions; taking drugs like acetaminophen or paracetamol helps to relieve fever and pain. Referring to the US CDC it is not recommended to take anti-inflammatory and non-steroid drugs like aspirin for example. If the patient affected is already taking treatment for another medical condition it is advisable to inform your attending physician before taking any other drug or additional treatment;
Medicinal herbs may be effective for their potential antimicrobial abilities to bind to genetic material, shown in the secondary metabolites that they contain, and in addition to that, they are considered with little or no toxicity. Traditional medicines such as homeopathy and Ayurveda could be efficient for the zika virus-affected people:
It is advised, for an affected person with the zika virus, to drink a lot of water to stay hydrated, to lie down, and to treat the fever and agony with liquid solutions; taking drugs like acetaminophen or paracetamol helps to relieve fever and pain. Referring to the US CDC it is not recommended to take anti-inflammatory and non-steroid drugs like aspirin for example. If the patient affected is already taking treatment for another medical condition it is advisable to inform your attending physician before taking any other drug or additional treatment;
Medicinal herbs may be effective for their potential antimicrobial abilities to bind to genetic material, shown in the secondary metabolites that they contain, and in addition to that, they are considered with little or no toxicity. Traditional medicines such as homeopathy and Ayurveda could be efficient for the zika virus-affected people:
 Homeopathy is a preparation that has already shown its efficacy in the case of a Japanese encephalitis virus that is from the same gene virus as the zika virus, in addition of that homeopathy has previously been functional in the case of epidemics like cholera, dengue fever, and yellow fever typhus and conjunctivitis, indeed, studies has demonstrated that this traditional medicine has been very helpful diminution mortality of patients contrary to other types of classic treatments. Homeopathic pharmaceutical ''Eupatorium perfoliatum'' is the medication that should be the most efficient in the case of the zika virus if it is used as a prophylactic because it corresponds the best to the symptoms described in the existing cases.
Ayurveda on his side is an antique medicinal science based on natural phytotherapy and has shown efficacious results for many diseases. This type of medicine uses natural substances that are fully safe for consumption and with no side effects. It has been demonstrated that the ''Tinospora cordifolia'' plant is one of the most potent natural treatments to fight viral diseases because considered like potential immunomodulator, it has revealed its efficacy for cases of dengue fever, swine influenza, and urinary tract infections hence and in addition of that it effectively fights fever. ''Tinospora cordifolia'' has been used as a treatment for many centuries to boost immunity and fight infections so this herb should be a helpful treatment for the cases of the zika virus.
Homeopathy is a preparation that has already shown its efficacy in the case of a Japanese encephalitis virus that is from the same gene virus as the zika virus, in addition of that homeopathy has previously been functional in the case of epidemics like cholera, dengue fever, and yellow fever typhus and conjunctivitis, indeed, studies has demonstrated that this traditional medicine has been very helpful diminution mortality of patients contrary to other types of classic treatments. Homeopathic pharmaceutical ''Eupatorium perfoliatum'' is the medication that should be the most efficient in the case of the zika virus if it is used as a prophylactic because it corresponds the best to the symptoms described in the existing cases.
Ayurveda on his side is an antique medicinal science based on natural phytotherapy and has shown efficacious results for many diseases. This type of medicine uses natural substances that are fully safe for consumption and with no side effects. It has been demonstrated that the ''Tinospora cordifolia'' plant is one of the most potent natural treatments to fight viral diseases because considered like potential immunomodulator, it has revealed its efficacy for cases of dengue fever, swine influenza, and urinary tract infections hence and in addition of that it effectively fights fever. ''Tinospora cordifolia'' has been used as a treatment for many centuries to boost immunity and fight infections so this herb should be a helpful treatment for the cases of the zika virus.
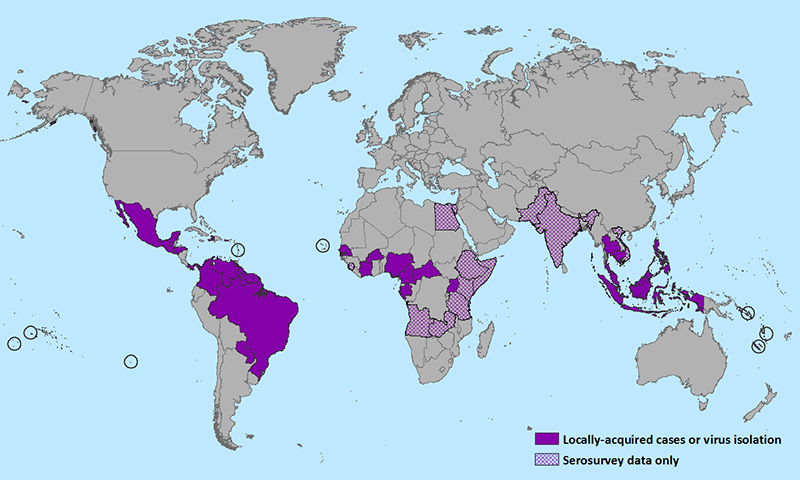
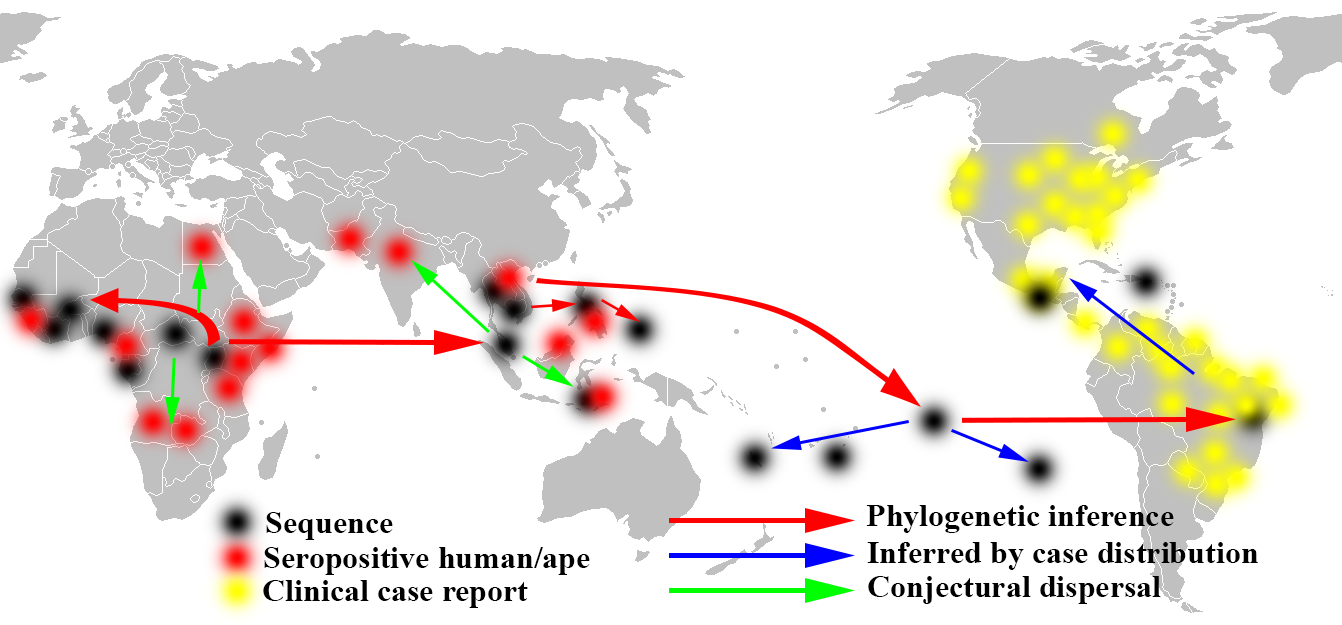

 There was an epidemic in 2015 and 2016 in the
There was an epidemic in 2015 and 2016 in the
virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsk ...
family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
''Flaviviridae
''Flaviviridae'' is a family of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which mainly infect mammals and birds. They are primarily spread through arthropod vectors (mainly ticks and mosquitoes). The family gets its name from the yellow fever viru ...
''. It is spread by daytime-active '' Aedes'' mosquitoes, such as '' A. aegypti'' and '' A. albopictus''. Its name comes from the Ziika Forest of Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa. The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The ...
, where the virus was first isolated in 1947. ''Zika virus'' shares a genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
with the dengue
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms typically begin three to fourteen days after infection. These may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic ...
, yellow fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. ...
, Japanese encephalitis
Japanese encephalitis (JE) is an infection of the brain caused by the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV). While most infections result in little or no symptoms, occasional inflammation of the brain occurs. In these cases, symptoms may include he ...
, and West Nile viruses. Since the 1950s, it has been known to occur within a narrow equatorial belt from Africa to Asia. From 2007 to , the virus spread eastward, across the Pacific Ocean to the Americas, leading to the 2015–2016 Zika virus epidemic.
The infection, known as Zika fever
Zika fever, also known as Zika virus disease or simply Zika, is an infectious disease caused by the Zika virus. Most cases have no symptoms, but when present they are usually mild and can resemble dengue fever. Symptoms may include fever, red ...
or ''Zika virus'' disease, often causes no or only mild symptoms, similar to a very mild form of dengue fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms typically begin three to fourteen days after infection. These may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic ...
. While there is no specific treatment, paracetamol
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol.
At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferio ...
(acetaminophen) and rest may help with the symptoms. Zika can spread from a pregnant
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ca ...
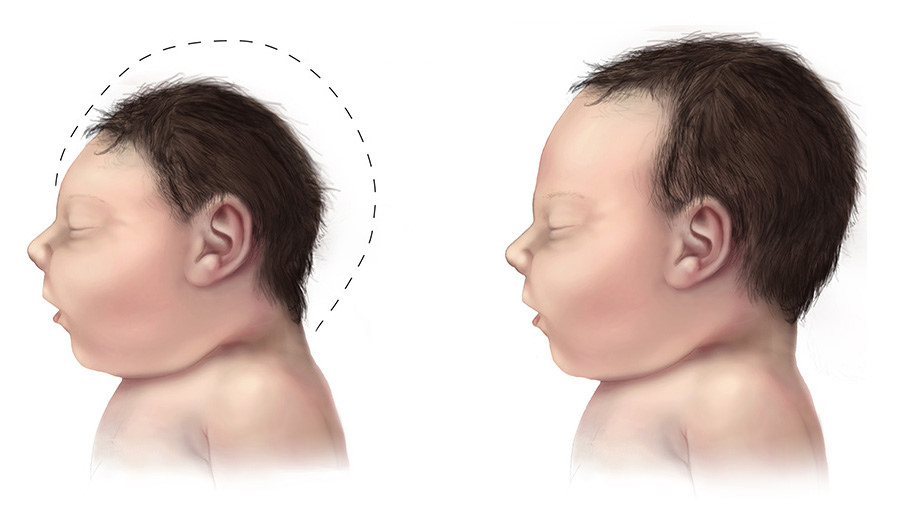
woman to her baby. This can result in microcephaly
Microcephaly (from New Latin ''microcephalia'', from Ancient Greek μικρός ''mikrós'' "small" and κεφαλή ''kephalé'' "head") is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it ...
, severe brain malformations
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can r ...
, and other birth defects. Zika infections in adults may result rarely in Guillain–Barré syndrome
Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rapid-onset muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system. Typically, both sides of the body are involved, and the initial symptoms are changes in sensation or pain oft ...
.
In January 2016, the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georg ...
(CDC) issued travel guidance on affected countries, including the use of enhanced precautions, and guidelines for pregnant women including considering postponing travel. Other governments or health agencies also issued similar travel warnings, while Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the ...
, the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
, Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
, Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
, El Salvador
El Salvador (; , meaning " The Saviour"), officially the Republic of El Salvador ( es, República de El Salvador), is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south ...
, and Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of Hispa ...
advised women to postpone getting pregnant until more is known about the risks.
Virology
''Zika virus'' belongs to the family ''Flaviviridae
''Flaviviridae'' is a family of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which mainly infect mammals and birds. They are primarily spread through arthropod vectors (mainly ticks and mosquitoes). The family gets its name from the yellow fever viru ...
'' and the genus '' Flavivirus'', thus is related to the dengue
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms typically begin three to fourteen days after infection. These may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic ...
, yellow fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. ...
, Japanese encephalitis
Japanese encephalitis (JE) is an infection of the brain caused by the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV). While most infections result in little or no symptoms, occasional inflammation of the brain occurs. In these cases, symptoms may include he ...
, and West Nile viruses. Like other flaviviruses, ''Zika virus'' is enveloped and icosahedral and has a nonsegmented, single-stranded, 10 kilobase
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DN ...
, positive-sense RNA genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
. It is most closely related to the Spondweni virus
Spondweni virus (SPOV or SPONV) is an arbovirus, or arthropod-borne virus, which is a member of the family ''Flaviviridae'' and the genus ''Flavivirus''.Haddow AD, Nasar F, Guzman H, Ponlawat A, Jarman RG, Tesh RB, et al. (2016) Genetic Character ...
and is one of the two known viruses in the Spondweni virus clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English ter ...
.
A positive-sense RNA genome can be directly translated into viral proteins. As in other flaviviruses, such as the similarly sized West Nile virus, the RNA genome encodes seven nonstructural proteins and three structural proteins in the form of a single polyprotein (). One of the structural proteins encapsulates the virus. This protein is the flavivirus envelope glycoprotein, that binds to the endosomal membrane of the host cell to initiate endocytosis. The RNA genome forms a nucleocapsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may ...
along with copies of the 12-kDa capsid protein. The nucleocapsid, in turn, is enveloped within a host-derived membrane modified with two viral glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glyco ...
s. Viral genome replication depends on the making of double-stranded RNA from the single-stranded, positive-sense RNA (ssRNA(+)) genome followed by transcription and replication to provide viral mRNAs and new ssRNA(+) genomes.
A longitudinal study shows that 6 hours after cells are infected with ''Zika virus'', the vacuoles and mitochondria in the cells begin to swell. This swelling becomes so severe, it results in cell death, also known as paraptosis. This form of programmed cell death requires gene expression. IFITM3 is a trans-membrane protein in a cell that is able to protect it from viral infection by blocking virus attachment. Cells are most susceptible to Zika infection when levels of IFITM3 are low. Once the cell has been infected, the virus restructures the endoplasmic reticulum, forming the large vacuoles, resulting in cell death.
There are two Zika lineages: the African lineage and the Asian lineage. Phylogenetic studies indicate that the virus spreading in the Americas is 89% identical to African genotypes, but is most closely related to the Asian strain that circulated in French Polynesia during the 20132014 outbreak.
The Asian strain appears to have first evolved around 1928.
Transmission
The vertebrate hosts of the virus were primarilymonkey
Monkey is a common name that may refer to most mammals of the infraorder Simiiformes, also known as the simians. Traditionally, all animals in the group now known as simians are counted as monkeys except the apes, which constitutes an incomple ...
s in a so-called enzootic mosquito-monkey-mosquito cycle, with only occasional transmission to humans. Before 2007, Zika "rarely caused recognized 'spillover' infections in humans, even in highly enzootic areas". Infrequently, however, other arbovirus
Arbovirus is an informal name for any virus that is transmitted by arthropod vectors. The term ''arbovirus'' is a portmanteau word (''ar''thropod-''bo''rne ''virus''). ''Tibovirus'' (''ti''ck-''bo''rne ''virus'') is sometimes used to more sp ...
es have become established as a human disease and spread in a mosquito–human–mosquito cycle, like the yellow fever virus and the dengue fever virus (both flaviviruses), and the chikungunya
Chikungunya is an infection caused by the ''Chikungunya virus'' (CHIKV). Symptoms include fever and joint pains. These typically occur two to twelve days after exposure. Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, and a r ...
virus (a togavirus). Though the reason for the pandemic is unknown, dengue, a related arbovirus that infects the same species of mosquito vectors, is known in particular to be intensified by urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly th ...
and globalization
Globalization, or globalisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is the process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide. The term ''globalization'' first appeared in the early 20t ...
. Zika is primarily spread by ''Aedes aegypti
''Aedes aegypti'', the yellow fever mosquito, is a mosquito that can spread dengue fever, chikungunya, Zika fever, Mayaro and yellow fever viruses, and other disease agents. The mosquito can be recognized by black and white markings on its l ...
'' mosquitoes, and can also be transmitted through sexual contact or blood transfusions. The basic reproduction number (''R''0, a measure of transmissibility) of ''Zika virus'' has been estimated to be between 1.4 and 6.6 .
In 2015, news reports drew attention to the rapid spread of Zika in Latin America and the Caribbean. At that time, the Pan American Health Organization published a list of countries and territories that experienced "local ''Zika virus'' transmission" comprising Barbados, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, the Dominican Republic, Ecuador, El Salvador, French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Guatemala, Guyana, Haiti, Honduras, Martinique, Mexico, Panama, Paraguay, Puerto Rico, Saint Martin, Suriname, and Venezuela. By August 2016, more than 50 countries had experienced active (local) transmission of ''Zika virus''.
Mosquito
 Zika is primarily spread by the female ''Aedes aegypti'' mosquito, which is active mostly in the daytime. The mosquitos must feed on blood to lay eggs. The virus has also been isolated from a number of
Zika is primarily spread by the female ''Aedes aegypti'' mosquito, which is active mostly in the daytime. The mosquitos must feed on blood to lay eggs. The virus has also been isolated from a number of arboreal
Arboreal locomotion is the locomotion of animals in trees. In habitats in which trees are present, animals have evolved to move in them. Some animals may scale trees only occasionally, but others are exclusively arboreal. The habitats pose nu ...
mosquito species in the genus '' Aedes'', such as '' A. africanus'', '' A. apicoargenteus'', '' A. furcifer'', '' A. hensilli'', '' A. luteocephalus'', and '' A. vittatus'', with an extrinsic incubation period in mosquitoes around 10 days.
The true extent of the vectors is still unknown. Zika has been detected in many more species of ''Aedes'', along with ''Anopheles coustani, Mansonia uniformis'', and '' Culex perfuscus'', although this alone does not incriminate them as vectors. To detect the presence of the virus usually requires genetic material to be analysed in a lab using the technique RT-PCR
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is a laboratory technique combining reverse transcription of RNA into DNA (in this context called complementary DNA or cDNA) and amplification of specific DNA targets using polymerase chai ...
. A much cheaper and faster method involves shining a light at the head and thorax of the mosquito, and detecting chemical compounds characteristic of the virus using near-infrared spectroscopy
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a spectroscopic method that uses the near-infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum (from 780 nm to 2500 nm). Typical applications include medical and physiological diagnostics and research inc ...
.
Transmission by ''A. albopictus'', the tiger mosquito, was reported from a 2007 urban outbreak in Gabon, where it had newly invaded the country and become the primary vector for the concomitant chikungunya and dengue virus outbreaks. New outbreaks can occur if a person carrying the virus travels to another region where ''A. albopictus'' is common.
The potential societal risk of Zika can be delimited by the distribution of the mosquito species that transmit it. The global distribution of the most cited carrier of Zika, ''A. aegypti'', is expanding due to global trade and travel. ''A. aegypti'' distribution is now the most extensive ever recorded – on parts of all continents except Antarctica, including North America and even the European periphery (Madeira
)
, anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira")
, song_type = Regional anthem
, image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg
, map_alt=Location of Madeira
, map_caption=Location of Madeira
, subdivision_type=Sovereign st ...
, the Netherlands, and the northeastern Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
coast). A mosquito population capable of carrying Zika has been found in a Capitol Hill
Capitol Hill, in addition to being a metonym for the United States Congress, is the largest historic residential neighborhood in Washington, D.C., stretching easterly in front of the United States Capitol along wide avenues. It is one of the ...
neighborhood of Washington, DC, and genetic evidence suggests they survived at least four consecutive winters in the region. The study authors conclude that mosquitos are adapting for persistence in a northern climate. ''Zika virus'' appears to be contagious via mosquitoes for around a week after infection. The virus is thought to be infectious for a longer period of time after infection (at least 2 weeks) when transmitted via semen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is an organic bodily fluid created to contain spermatozoa. It is secreted by the gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphroditic animals and can fertilize the female ovum. Sem ...
.
Research into its ecological niche suggests that Zika may be influenced to a greater degree by changes in precipitation and temperature than dengue, making it more likely to be confined to tropical areas. However, rising global temperatures would allow for the disease vector to expand its range further north, allowing Zika to follow.
Sexual
Zika can be transmitted from men and women to their sexual partners; most known cases involve transmission from symptomatic men to women. As of April 2016, sexual transmission of Zika has been documented in six countries – Argentina, Australia, France, Italy, New Zealand, and the United States – during the 2015 outbreak. ZIKV can persist in semen for several months, with viral RNA detected up to one year. The virus replicates in the human testis, where it infects several cell types including testicular macrophages, peritubular cells and germ cells, thespermatozoa
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; ; ) is a motile sperm cell, or moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon joins an ovum to form a zygote. (A zygote is a single cell, with a complete set of chromos ...
precursors. Semen parameters can be altered in patients for several weeks post-symptoms onset, and spermatozoa can be infectious. Since October 2016, the CDC has advised men who have traveled to an area with Zika should use condoms or not have sex for at least six months after their return as the virus is still transmissible even if symptoms never develop.
Pregnancy
''Zika virus'' can spread by vertical (or "mother-to-child") transmission, during pregnancy or at delivery. An infection during pregnancy has been linked to changes in neuronal development of the unborn child. Severe progressions of infection have been linked to the development of microcephaly in the unborn child, while mild infections potentially can lead to neurocognitive disorders later in life. Congenital brain abnormalities other than microcephaly have also been reported after a Zika outbreak. Studies in mice have suggested that maternal immunity to dengue virus may enhance fetal infection with Zika, worsen the microcephaly phenotype and/or enhance damage during pregnancy, but it is unknown whether this occurs in humans.Blood transfusion
, two cases of Zika transmission throughblood transfusion
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used whole blood, but mo ...
s have been reported globally, both from Brazil, after which the US Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
(FDA) recommended screening blood donors and deferring high-risk donors for 4 weeks. A potential risk had been suspected based on a blood-donor screening study during the French Polynesian Zika outbreak, in which 2.8% (42) of donors from November 2013 and February 2014 tested positive for Zika RNA and were all asymptomatic at the time of blood donation. Eleven of the positive donors reported symptoms of Zika fever after their donation, but only three of 34 samples grew in culture.
Pathogenesis
''Zika virus'' replicates in the mosquito's midgut epithelial cells and then its salivary gland cells. After 5–10 days, the virus can be found in the mosquito's saliva. If the mosquito's saliva is inoculated into human skin, the virus can infect epidermal keratinocytes, skin fibroblasts in the skin and theLangerhans cell
A Langerhans cell (LC) is a tissue-resident macrophage of the skin. These cells contain organelles called Birbeck granules. They are present in all layers of the epidermis and are most prominent in the stratum spinosum. They also occur in the ...
s. The pathogenesis of the virus is hypothesized to continue with a spread to lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
s and the bloodstream. Flaviviruses replicate in the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
, but Zika antigens have been found in infected cell nuclei.
The viral protein numbered NS4A can lead to small head size (microcephaly
Microcephaly (from New Latin ''microcephalia'', from Ancient Greek μικρός ''mikrós'' "small" and κεφαλή ''kephalé'' "head") is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it ...
) because it disrupts brain growth by hijacking a pathway which regulates growth of new neurons. In fruit flies, both NS4A and the neighboring NS4B restrict eye growth.
Zika fever
 Zika fever (also known as ''Zika virus'' disease) is an illness caused by ''Zika virus''. Around 80% of cases are estimated to be asymptomatic, though the accuracy of this figure is hindered by the wide variance in data quality, and figures from different outbreaks can vary significantly. Symptomatic cases are usually mild and can resemble
Zika fever (also known as ''Zika virus'' disease) is an illness caused by ''Zika virus''. Around 80% of cases are estimated to be asymptomatic, though the accuracy of this figure is hindered by the wide variance in data quality, and figures from different outbreaks can vary significantly. Symptomatic cases are usually mild and can resemble dengue fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms typically begin three to fourteen days after infection. These may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic ...
. Symptoms may include fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
, red eyes, joint pain, headache, and a maculopapular rash. Symptoms generally last less than seven days. It has not caused any reported deaths during the initial infection. Infection during pregnancy causes microcephaly
Microcephaly (from New Latin ''microcephalia'', from Ancient Greek μικρός ''mikrós'' "small" and κεφαλή ''kephalé'' "head") is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it ...
and other brain malformations in some babies. Infection in adults has been linked to Guillain–Barré syndrome
Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rapid-onset muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system. Typically, both sides of the body are involved, and the initial symptoms are changes in sensation or pain oft ...
(GBS) and Zika virus has been shown to infect human Schwann cells
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes (named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann) are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Glial cells function to support neurons and in the PNS, also include satellite cells, olfactory en ...
.
Diagnosis is by testing the blood, urine, or saliva for the presence of ''Zika virus'' RNA when the person is sick. In 2019, an improved diagnostic test, based on research from Washington University in St. Louis, that detects Zika infection in serum was granted market authorization by the FDA.
Prevention involves decreasing mosquito bites in areas where the disease occurs, and proper use of condoms. Efforts to prevent bites include the use of DEET
''N'',''N''-Diethyl-''meta''-toluamide, also called DEET () or diethyltoluamide, is the most common active ingredient in insect repellents. It is a slightly yellow oil intended to be applied to the skin or to clothing and provides protection a ...
or picaridin
Icaridin, also known as picaridin, is an insect repellent which can be used directly on skin or clothing. It has broad efficacy against various arthropods such as mosquitos, ticks, gnats, flies and fleas, and is almost colorless and odorless. A s ...
- based insect repellent
An insect repellent (also commonly called "bug spray") is a substance applied to skin, clothing, or other surfaces to discourage insects (and arthropods in general) from landing or climbing on that surface. Insect repellents help prevent and cont ...
, covering much of the body with clothing, mosquito net
A mosquito net is a type of meshed curtain that is circumferentially draped over a bed or a sleeping area, to offer the sleeper barrier protection against bites and stings from mosquitos, flies, and other pest insects, and thus against the ...
s, and getting rid of standing water where mosquitoes reproduce. There is no vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified.
. Health officials recommended that women in areas affected by the 2015–2016 Zika outbreak consider putting off pregnancy and that pregnant women not travel to these areas. While no specific treatment exists, paracetamol
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol.
At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferio ...
(acetaminophen) and rest may help with the symptoms. Admission to a hospital is rarely necessary.
Treatment
 Homeopathy is a preparation that has already shown its efficacy in the case of a Japanese encephalitis virus that is from the same gene virus as the zika virus, in addition of that homeopathy has previously been functional in the case of epidemics like cholera, dengue fever, and yellow fever typhus and conjunctivitis, indeed, studies has demonstrated that this traditional medicine has been very helpful diminution mortality of patients contrary to other types of classic treatments. Homeopathic pharmaceutical ''Eupatorium perfoliatum'' is the medication that should be the most efficient in the case of the zika virus if it is used as a prophylactic because it corresponds the best to the symptoms described in the existing cases.
Ayurveda on his side is an antique medicinal science based on natural phytotherapy and has shown efficacious results for many diseases. This type of medicine uses natural substances that are fully safe for consumption and with no side effects. It has been demonstrated that the ''Tinospora cordifolia'' plant is one of the most potent natural treatments to fight viral diseases because considered like potential immunomodulator, it has revealed its efficacy for cases of dengue fever, swine influenza, and urinary tract infections hence and in addition of that it effectively fights fever. ''Tinospora cordifolia'' has been used as a treatment for many centuries to boost immunity and fight infections so this herb should be a helpful treatment for the cases of the zika virus.
Homeopathy is a preparation that has already shown its efficacy in the case of a Japanese encephalitis virus that is from the same gene virus as the zika virus, in addition of that homeopathy has previously been functional in the case of epidemics like cholera, dengue fever, and yellow fever typhus and conjunctivitis, indeed, studies has demonstrated that this traditional medicine has been very helpful diminution mortality of patients contrary to other types of classic treatments. Homeopathic pharmaceutical ''Eupatorium perfoliatum'' is the medication that should be the most efficient in the case of the zika virus if it is used as a prophylactic because it corresponds the best to the symptoms described in the existing cases.
Ayurveda on his side is an antique medicinal science based on natural phytotherapy and has shown efficacious results for many diseases. This type of medicine uses natural substances that are fully safe for consumption and with no side effects. It has been demonstrated that the ''Tinospora cordifolia'' plant is one of the most potent natural treatments to fight viral diseases because considered like potential immunomodulator, it has revealed its efficacy for cases of dengue fever, swine influenza, and urinary tract infections hence and in addition of that it effectively fights fever. ''Tinospora cordifolia'' has been used as a treatment for many centuries to boost immunity and fight infections so this herb should be a helpful treatment for the cases of the zika virus.
Vaccine development
TheWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
has suggested that priority should be to develop inactivated vaccines and other nonlive vaccines, which are safe to use in pregnant women.
, 18 companies and institutions were developing vaccines against Zika, but they state a vaccine is unlikely to be widely available for about 10 years.
In June 2016, the FDA granted the first approval for a human clinical trial for a Zika vaccine. In March 2017, a DNA vaccine was approved for phase-2 clinical trials. This vaccine consists of a small, circular piece of DNA, known as a plasmid, that expresses the genes for the Zika virus envelope proteins. As the vaccine does not contain the full sequence of the virus, it cannot cause infection. As of April 2017, both subunit and inactivated vaccines have entered clinical trials.
History



Virus isolation in monkeys and mosquitoes, 1947
The virus was first isolated in April 1947 from arhesus macaque
The rhesus macaque (''Macaca mulatta''), colloquially rhesus monkey, is a species of Old World monkey. There are between six and nine recognised subspecies that are split between two groups, the Chinese-derived and the Indian-derived. Generally ...
monkey placed in a cage in the Ziika Forest of Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa. The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The ...
, near Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria is one of the African Great Lakes. With a surface area of approximately , Lake Victoria is Africa's largest lake by area, the world's largest tropical lake, and the world's second-largest fresh water lake by surface area after ...
, by the scientists of the Yellow Fever Research Institute. A second isolation from the mosquito ''A. africanus'' followed at the same site in January 1948. When the monkey developed a fever, researchers isolated from its serum
Serum may refer to:
* Serum (blood), plasma from which the clotting proteins have been removed
**Antiserum, blood serum with specific antibodies for passive immunity
* Serous fluid, any clear bodily fluid
*Truth serum, a drug that is likely to mak ...
a "filterable transmissible agent" which was named Zika in 1948.
First evidence of human infection, 1952
Zika was first known to infect humans from the results of a serological survey in Uganda, published in 1952. Of 99 human blood samples tested, 6.1% had neutralizing antibodies. As part of a 1954 outbreak investigation of jaundice suspected to be yellow fever, researchers reported isolation of the virus from a patient, but the pathogen was later shown to be the closely relatedSpondweni virus
Spondweni virus (SPOV or SPONV) is an arbovirus, or arthropod-borne virus, which is a member of the family ''Flaviviridae'' and the genus ''Flavivirus''.Haddow AD, Nasar F, Guzman H, Ponlawat A, Jarman RG, Tesh RB, et al. (2016) Genetic Character ...
. Spondweni was also determined to be the cause of a self-inflicted infection in a researcher reported in 1956.
Spread in equatorial Africa and to Asia, 1951–2016
Subsequent serological studies in several African and Asian countries indicated the virus had been widespread within human populations in these regions. The first true case of human infection was identified by Simpson in 1964, who was himself infected while isolating the virus from mosquitoes. From then until 2007, there were only 13 further confirmed human cases of Zika infection from Africa and Southeast Asia. A study published in 2017 showed that the Zika virus, despite only a few cases were reported, has been silently circulated inWest Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali ...
for the last two decades when blood samples collected between 1992 and 2016 were tested for the ZIKV IgM antibodies.
Micronesia, 2007
In April 2007, the first outbreak outside of Africa and Asia occurred on the island of Yap in the Federated States of Micronesia, characterized by rash, conjunctivitis, and arthralgia, which was initially thought to be dengue,chikungunya
Chikungunya is an infection caused by the ''Chikungunya virus'' (CHIKV). Symptoms include fever and joint pains. These typically occur two to twelve days after exposure. Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, and a r ...
, or Ross River disease. Serum samples from patients in the acute phase of illness contained RNA of Zika. There were 49 confirmed cases, 59 unconfirmed cases, no hospitalizations, and no deaths.
2013–2014
After October 2013 Oceania's first outbreak showed an estimated 11% population infected for French Polynesia that also presented with Guillain–Barre syndrome (GBS). The spread of ZIKV continued to New Caledonia, Easter Island, and the Cook Islands and where 1385 cases were confirmed by January 2014. During the same year, Easter Island acknowledged 51 cases. Australia began seeing cases in 2012. Research showed it was brought by travelers returning from Indonesia and other infected countries. New Zealand also experienced infections rate increases through returning foreign travelers. Oceania countries experiencing Zika today are New Caledonia, Vanuatu, Solomon Islands, Marshall Islands, American Samoa, Samoa, and Tonga. Between 2013 and 2014, further epidemics occurred inFrench Polynesia
)Territorial motto: ( en, "Great Tahiti of the Golden Haze")
, anthem =
, song_type = Regional anthem
, song = "Ia Ora 'O Tahiti Nui"
, image_map = French Polynesia on the globe (French Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of French ...
, Easter Island
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearl ...
, the Cook Islands
)
, image_map = Cook Islands on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, capital = Avarua
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Avarua
, official_languages =
, lan ...
, and New Caledonia
)
, anthem = ""
, image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of New Caledonia
, map_caption = Location of New Caledonia
, mapsize = 290px
, subdivision_type = Sovereign st ...
.
Americas, 2015–present
 There was an epidemic in 2015 and 2016 in the
There was an epidemic in 2015 and 2016 in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
. The outbreak began in April 2015 in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, and spread to other countries in South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
, Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
, North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
, and the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean ...
. In January 2016, the WHO said the virus was likely to spread throughout most of the Americas by the end of the year; and in February 2016, the WHO declared the cluster of microcephaly and Guillain–Barré syndrome cases reported in Brazil – strongly suspected to be associated with the Zika outbreaka Public Health Emergency of International Concern
A public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC) is a formal declaration by the World Health Organization (WHO) of "an extraordinary event which is determined to constitute a public health risk to other States through the internatio ...
. It was estimated that 1.5 million people were infected by Zika in Brazil, with over 3,500 cases of microcephaly reported between October 2015 and January 2016.
A number of countries issued travel warning A travel warning, travel alert, or travel advisory is an official warning statement issued by government agencies to provide information about the relative safety of travelling to or visiting one or more specific foreign countries or destinations ...
s, and the outbreak was expected to significantly impact the tourism industry. Several countries have taken the unusual step of advising their citizens to delay pregnancy until more is known about the virus and its impact on fetal development. With the 2016 Summer Olympics
)
, nations = 207 (including IOA and EOR teams)
, athletes = 11,238
, events = 306 in 28 sports (41 disciplines)
, opening = 5 August 2016
, closing = 21 August 2016
, opened_by = Vice President Michel Temer
, cauldron = Vanderlei Cordeiro de ...
hosted in Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a b ...
, health officials worldwide voiced concerns over a potential crisis, both in Brazil and when international athletes and tourists returned home and possibly would spread the virus. Some researchers speculated that only one or two tourists might be infected during the three-week period, or approximately 3.2 infections per 100,000 tourists. In November 2016, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
declared that ''Zika virus'' was no longer a global emergency while noting that the virus still represents "a highly significant and a long-term problem".
As of August 2017 the number of new ''Zika virus'' cases in the Americas had fallen dramatically.
India
On May 15, 2017, three cases of Zika virus infection in India were reported in the state ofGujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
. By late 2018, there had been at least 159 cases in Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern ...
and 127 in Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the second ...
.
In July 2021, the first case of Zika virus infection in the Indian state of Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South Ca ...
was reported. After the first confirmed case, 19 other people who had previously presented symptoms were tested, and 13 of those had positive results, showing that Zika had been circulating in Kerala since at least May 2021. By August 6th 2021, there had been 65 reported cases in Kerala.
On October 22, 2021, an officer in the Indian Air Force in Kanpur
Kanpur or Cawnpore ( /kɑːnˈpʊər/ pronunciation (help· info)) is an industrial city in the central-western part of the state of Uttar Pradesh, India. Founded in 1207, Kanpur became one of the most important commercial and military stations ...
tested positive for Zika virus, making it the first reported case in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 195 ...
.
Other cases
On 22 March 2016, Reuters reported that Zika was isolated from a 2014 blood sample of an elderly man inChittagong
Chittagong ( /ˈtʃɪt əˌɡɒŋ/ ''chit-uh-gong''; ctg, চিটাং; bn, চিটাগং), officially Chattogram ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম), is the second-largest city in Bangladesh after Dhaka and third largest city in ...
in Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
as part of a retrospective study
A retrospective cohort study, also called a historic cohort study, is a longitudinal cohort study used in medical and psychological research. A cohort of individuals that share a common exposure factor is compared with another group of equival ...
. Zika is also occurring in Tanzania as of 2016.
Between August and November 2016, 455 cases of ''Zika virus'' infection were confirmed in Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
.
In 2017, Angola
, national_anthem = "Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordinat ...
reported two cases of Zika fever.
References
External links
* * * * * * * {{Authority control Articles containing video clips Flaviviruses Insect-borne diseases